Group-1 Elements: Alkali Metal | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
What are S-Block Elements?
The elements in which the last electron enters the outermost s-orbital are called s-block elements. The group 1 and 2 of periodic table belong to the s-block.
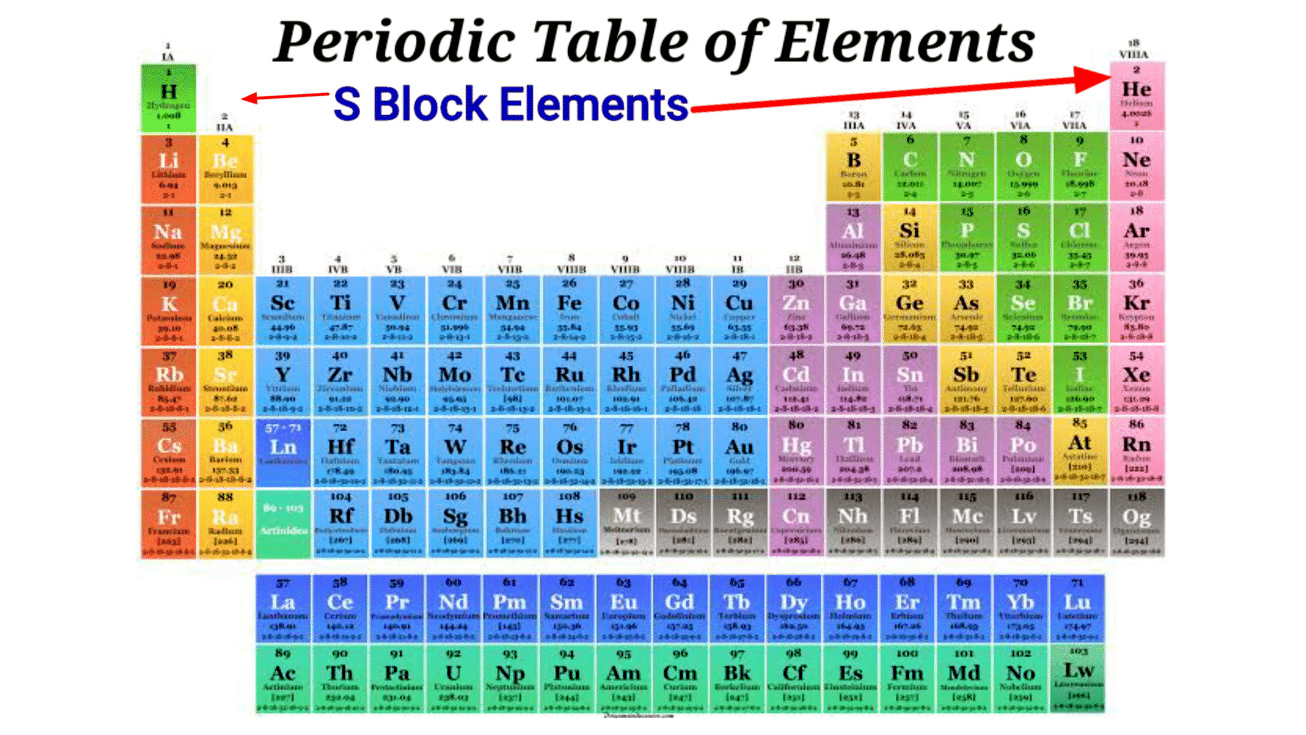
- The elements of Group-1 and Group-2 of the modern periodic table are called S-block elements. Two types of s block elements are possible i.e. the elements with one electron (s1)or the elements with two electrons (s2) in their s-subshell.
- S-block comprises 14 elements namely hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), helium (He), sodium (Na), beryllium (Be), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), rubidium (Rb), calcium (Ca), cesium (Cs), strontium (Sr), francium (Fr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
Electronic Configuration of Group-1 Elements:
The elements of Group-1 of Periodic Table are Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs Fr (Radioactive: t1/2 of Fr233 = 21 minutes). Group-1 elements are called alkali metals because they form hydroxides on reaction with water, which are alkaline in nature.
Electronic configuration
The alkali elements in the s-block consist of a single valence electron in their outermost shell. This outermost electron is loosely held which makes these metals highly electropositive. Due to which they are not available in the free state in nature. The general electronic configurations of s block elements – group 1 are as shown in the table below: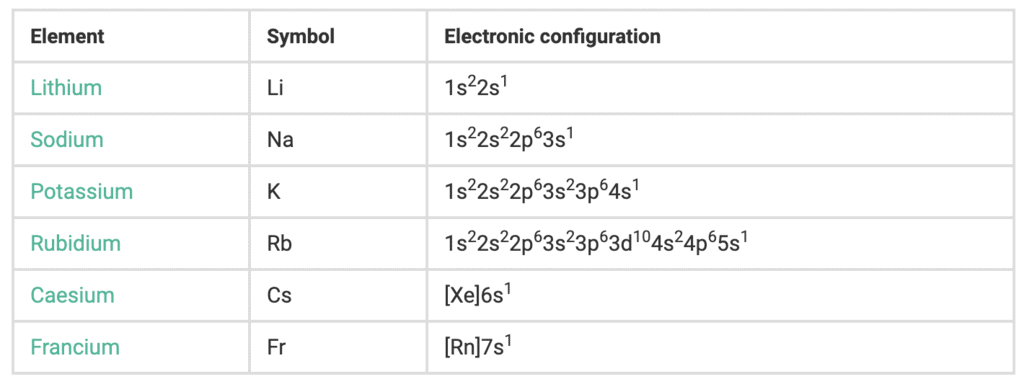
Physical Properties of Group-1 Elements
Atomic and Ionic radii
When the s block elements of the modern periodic table are observed it is seen that the size of the alkali metals is larger compared to other elements in a particular period. As the atomic number increases the total number of electrons increases along with the addition of shells.
On moving down the group the atomic number increases. As a result, the atomic and ionic radius of the alkali metals increases.
Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs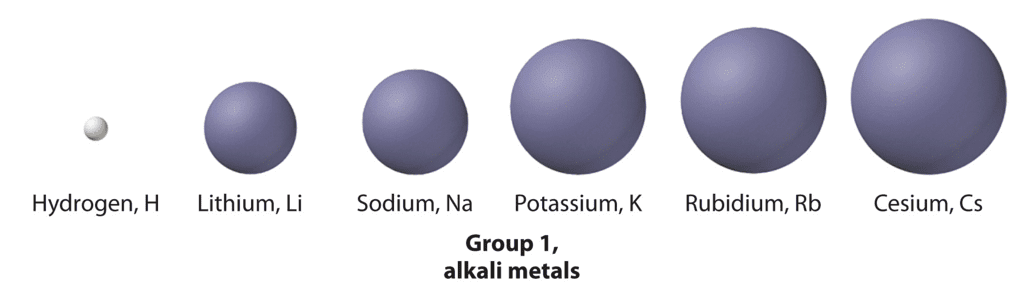
Density
The metals in this series are relatively light—lithium, sodium, and potassium are less dense than water (less than 1 g cm-3). It is difficult to develop a simple explanation for this trend because density depends on two factors, both of which change down the group. The atoms are packed in the same way, so the two factors considered are how many atoms can be packed in a given volume, and the mass of the individual atoms. The amount packed depends on the individual atoms' volumes; these volumes, in turn, depends on their atomic radius.
Li < K < Na < Rb < Cs.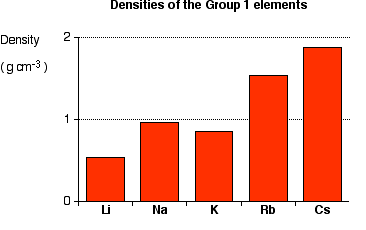
Ionization Energy
As we go down the group the size of the atoms increases due to which the attraction between the nucleus and the electrons in the outermost shell decreases. As a result, the ionization enthalpy decreases. The ionization enthalpy of the alkali metals is comparatively lesser than other elements.
Li > Na > K > Rb > Cs.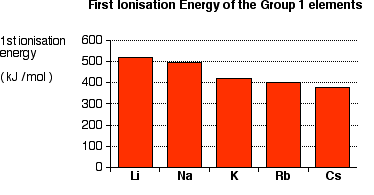
Hardness and Melting Points/Boiling Points
These metals are very soft and can be cut with a knife. Lithium is harder than any other alkali metal. The hardness depends upon cohesive energy.
M.P.: Li > Na > K > Rb > Cs
B.P.: Li > Na > K > Cs > Rb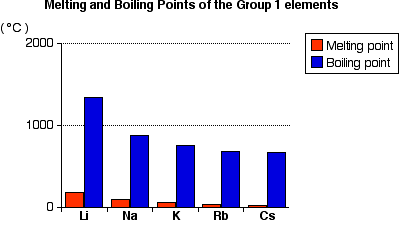
Electropositive Character or Metallic Character
Alkali metals are strongly electropositive and metallic. Down the group electropositive nature increase so metallic nature also increases.
i.e., M → M+ + e–
Metallic Nature: Electropositive character
Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs.Oxidation state:
Show +1 oxidation state because by losing one electron they get the stable noble gas configuration.Photoelectric effect:
The phenomenon of emission of electrons when electromagnetic rays strike against them is called the photoelectric effect; Alkali metals have low I.P. so show a photoelectric effect.
*Cs and K are used in photoelectric cells.
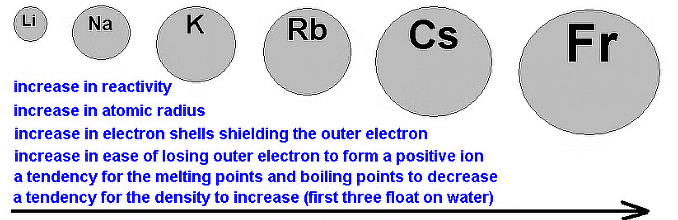 Trend Down Group 1 of Alkali Metals
Trend Down Group 1 of Alkali Metals
Chemical Properties of Group-1 Elements:
Reactions with air:
The alkali metals tarnish in dry air due to the formation of their oxides on their surface, which in turn react with water to form hydroxides.
4M + O2 → 2M2O
M2O + H2O →2MO
They react vigorously in oxygen forming following oxides.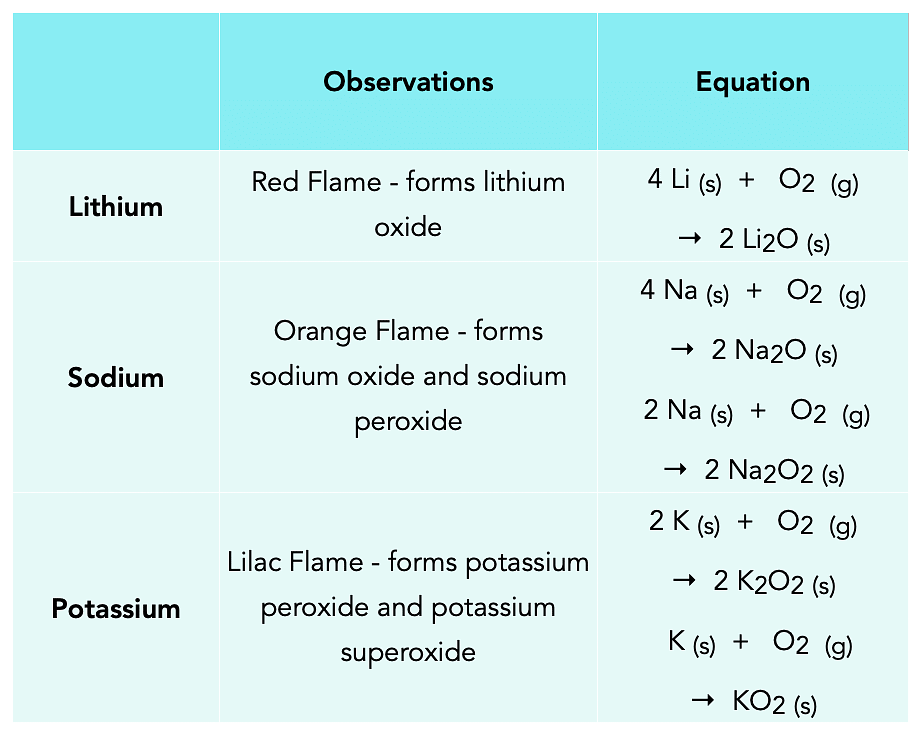 Alkali Metals Reaction with AirThey react vigorously in oxygen forming following oxides.
Alkali Metals Reaction with AirThey react vigorously in oxygen forming following oxides.
4 Li + O2 → 2 Li2O (Monoxide)
2 Na + O2 → Na2O2(Peroxide)
M + O2 → MO2(Superoxide) where M = K, Rb, CsSolution in liquid NH3
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia (high conc. 5 M) and give the blue solution which is conducting, reducing and paramagnetic in nature.Reason:
On dissolving Metal in NH3:
M+ + x(NH3) → [M(NH3)x]+ Ammoniated cation
e– + y(NH3) → [e(NH3)y]– Ammoniated electron
The blue colour is due to Ammoniated electron
The paramagnetic nature is due to → Ammoniated electron
The conducting nature is due to → Ammoniated M+ + Ammoniated electron
* On standing the colour fades due to the formation of amide,
In the absence of impurities like Fe, Pt, Zn etc, the solutions are stable.
* In concentrated solution, the blue colour changes to bronze colour and diamagnetic due to the formation of metal clusters and ammoniated electrons also associate to form electron pairs.
2 e–(NH3)y → [e–(NH3)4]2Reducing Nature
The reducing agent is an electron donor.
Alkali metals are strong reducing agents with lithium being the strongest and sodium the least powerful reducing agent. Na < K < Rb < Cs < Li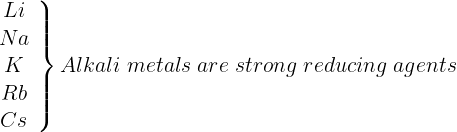 Note: Lithium is expected to be the least reducing agent due to its very high IE. However, it is strongest. (due to high hydration energy).
Note: Lithium is expected to be the least reducing agent due to its very high IE. However, it is strongest. (due to high hydration energy).Reaction with H2O
The reaction with water to form the hydroxides having the formula MOH:
2M + 2H2O → 2MOH + H2
(Highly Reactive)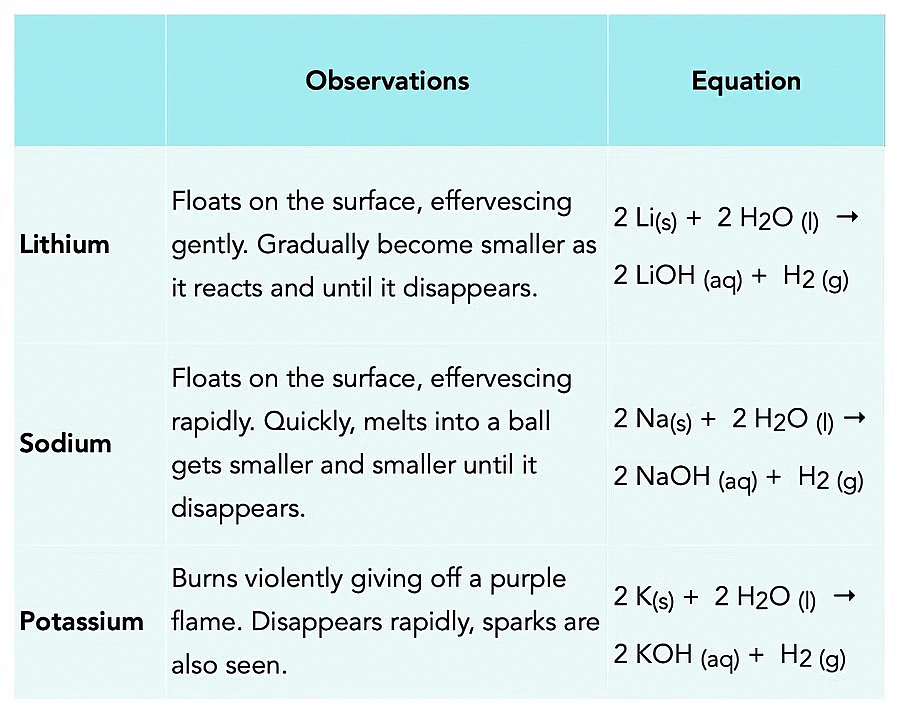 Alkali Metals Reaction with Air
Alkali Metals Reaction with AirReaction with H2
They react with H2 forming metal hydrides with formula MH which are of ionic nature. Stability of hydride decreases down the group.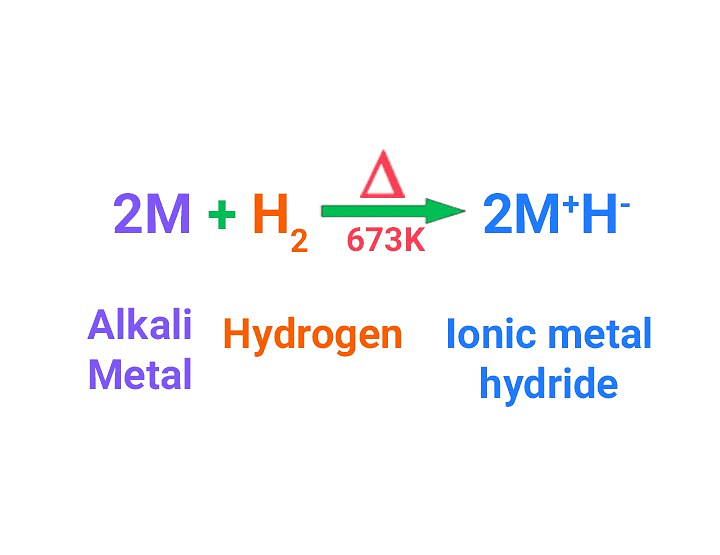
Reaction with N2
Only Lithium reacts with N2 to form ionic lithium nitride Li3N.
3Li + 3/2N2 → Li3NReaction with halogens X2
The alkali metals react vigorously with halogens to form ionic halides, M+X-
2M + X2 → 2MX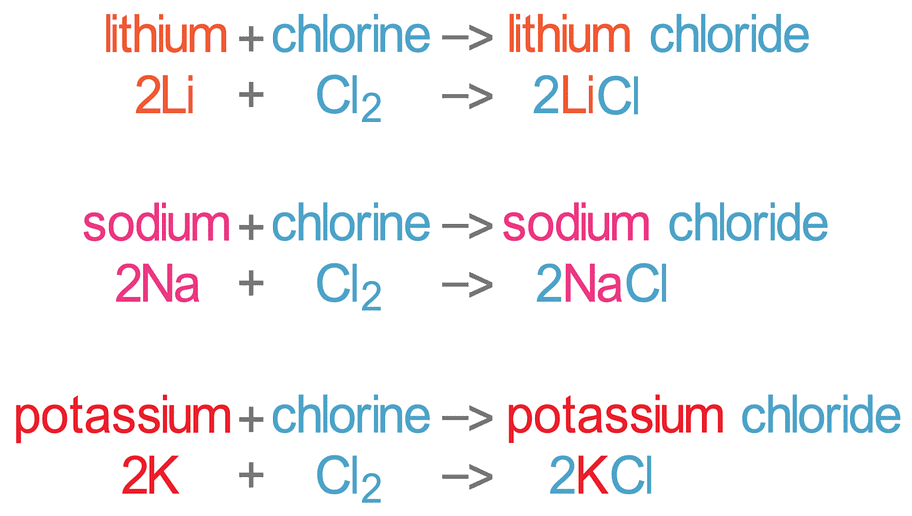
Sulphides
All metals react with S forming sulphides such as Na2S and Na2Sn(n = 2,3,4,5 or 6). The polysulphide ions are made from zig-zag chains of sulphur atoms.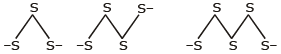
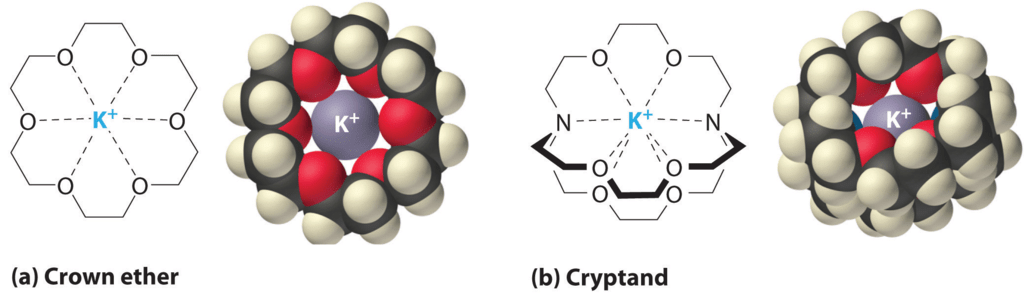
Crown Ethers and Cryptands:
What are the Uses of Group-1 Elements or Alkali Metals?
- Hydrogen is used in: hydrogen fuel, weather balloons and it creates water.
- Lithium is used in: Batteries, in the form of lithium carbonate it is used to control certain mental disorders and glass.
- Sodium is used in: Sodium chloride as table salt, sodium nitrate is an ingredient in gunpowder and sodium is important for all living organisms.
- Potassium is used in: fertilizers, potassium hydroxide is used in detergents and potassium bromide is a chemical used in photography.
Rubidium is used in: a compound of rubidium is used to treat depression.
Cesium is used in: glass and radiation detection equipment.
Francium is not used in anything except for research because it is one of the rarest elements and it is a radioactive element.
Different Compounds of Group-1 Elements
The Group 1 elements, also known as the alkali metals, include lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). These elements are highly reactive and form compounds with a wide range of other elements. Discussed below are some important compounds of Alkali Metals or Group-1 Elements.
Peroxides of Sodium and Potassium:
Controlled oxidation of alkali metals like sodium and potassium with moisture-free oxygen gas at around 300°C gives peroxides.
2M + O2 → M2O2
Peroxides form hydrogen peroxide with cold water and oxygen at higher temperatures.
M2O2 + 2H2O → H2O2 + 2MOH
2M2O2 + 2H2O → O2 + 4MOH
Alkali metal peroxides are used to produce other peroxides, bleach, preparing perborate and purification of air in small spaces.
Potassium Superoxide
It is prepared by heating potassium with excess oxygen or passing ozone through potassium Hydroxide. It is an orange solid and paramagnetic. Superoxides of alkali metals are a powerful oxidizing agent due to the release of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen in an aqueous solution.
2KO2 + 2H2O → H2O2 + O2 + 2KOH
Sodium Carbonate – Na2CO3
It is prepared by the Solvay process. Raw materials needed are brine, carbon dioxide and ammonia. Carbon dioxide is obtained by calcining limestone. Ammonia and carbon dioxide react to form ammonium bicarbonate, which is used to precipitate less soluble sodium bicarbonate from the aqueous solution using brine.
On heating, bicarbonate produces sodium carbonate. Calcium oxide on treatment with water gives calcium hydroxide which on treating with the byproduct releases ammonia for reuse.
CaCO3 + 2NaCl → Na2CO3 + CaCl2
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate is precipitated out of a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium carbonate by carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NaHCO3
The aqueous solution is alkaline. The bicarbonate ion is amphiprotic i.e. both proton donor and acceptor.
Baking soda
Baking soda is a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and weak solid organic acids like tartaric acid and a diluent like cornstarch. The mixture produces carbon dioxide by the reaction between the acid and the carbonate giving a porous structure in baking products.
Hydroxides
Hydroxides are produced by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of brine. Hydrogen and chlorine are obtained as the by-products. Hydroxides of alkali metals are strong bases. They are deliquescent and form carbonate by reacting with carbon dioxide. Some metal salts of Zn, Al, precipitate metallic hydroxides, which dissolve in excess alkali.
ZnCl2 + 2NaOH → Zn(OH)2 + 2NaCl
Zn(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + 2H2O
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are S-Block Elements?
Ans. S-Block elements are the elements in the periodic table that belong to the first two groups, i.e., Group 1 and Group 2. These elements have valence electrons in the S orbital, and their properties are mainly characterized by the presence of one or two valence electrons.
2. What are the physical properties of Group-1 Elements?
Ans. Group-1 elements, also known as alkali metals, have some common physical properties, such as low densities, low melting and boiling points, and high reactivity. They have a silvery-white appearance and are soft and malleable.
3. What are the chemical properties of Group-1 Elements?
Ans. The alkali metals are highly reactive due to their low ionization energies and the presence of only one valence electron. They readily react with non-metals such as halogens, oxygen, and water, forming ionic compounds. They also have a strong tendency to lose their valence electron and form cations.
4. What are the uses of Group-1 Elements or Alkali Metals?
Ans. The alkali metals have several important uses in different industries. For example, sodium and potassium are used in the production of soaps and detergents, while lithium is used in batteries. Sodium is also used in the production of chemicals and in the purification of metals, and potassium is used in fertilizers.
5. What are the different compounds of Group-1 Elements?
Ans. Group-1 elements form different compounds, such as oxides, hydroxides, and halides. For example, sodium forms sodium oxide, Na2O, and sodium hydroxide, NaOH. Similarly, potassium forms potassium oxide, K2O, and potassium hydroxide, KOH. The halides of these elements, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium iodide (KI), are also widely used.
|
334 videos|656 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Group-1 Elements: Alkali Metal - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are S-Block Elements? |  |
| 2. What is the electronic configuration of Group-1 elements? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of Group-1 elements? |  |
| 4. What are the chemical properties of Group-1 elements? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of Group-1 elements or alkali metals? |  |






















