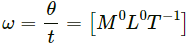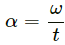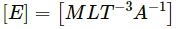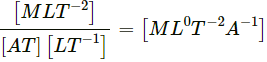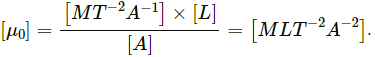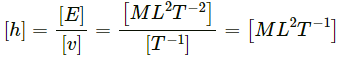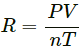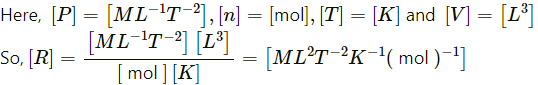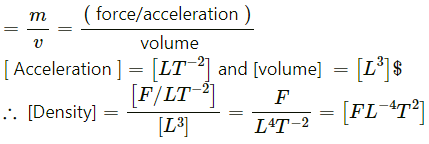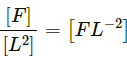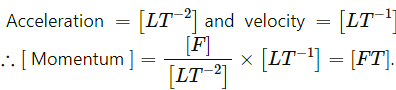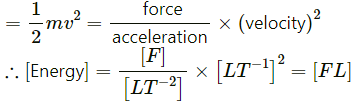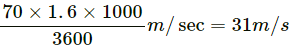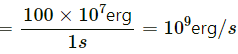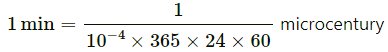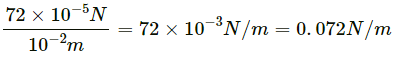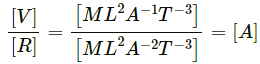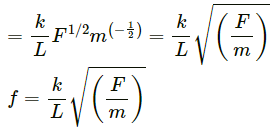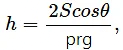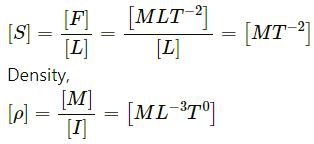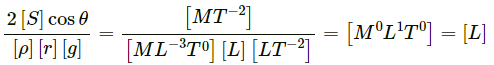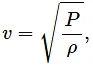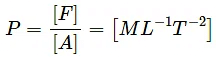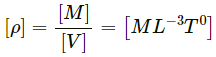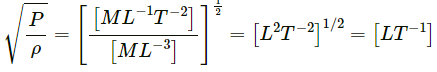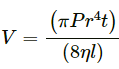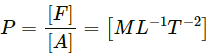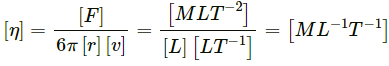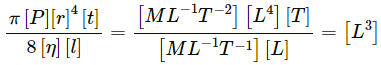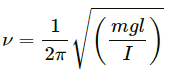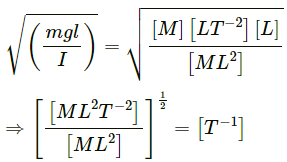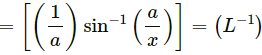HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 1- Introduction to Physics- 1 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Exercise
Q1. Find the dimensions of
(a) linear momentum
(b) frequency
(c) pressure
(a) Linear momentum = mv
Here, [m] = [M] and [v] = [LT−1]
∴ Dimension of linear momentum, [mv] = [MLT−1](b) Frequency = 1/Time
∴ Dimension of frequency = [1/T] = [M0L0T-1](c) pressure = Force/Area
Dimension of force = [MLT-2]
Dimension of area = [L2]
∴ Dimension of pressure = (MLT-2)/L = [ML-1T-2].
Q2. Find the dimensions of
(a) angular speed ω,
(b) angular acceleration α,
(c) torque τ and
(d) moment of inertia I.
Some of the equations involving these quantities are 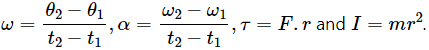 The symbols have standard meanings.
The symbols have standard meanings.
(a) Dimensions of angular speed,
(b) Angular acceleration,
Here, ω = [M0L0T−1] and t = [T]
So, dimensions of angular acceleration = [M0L0T−2]
(c) Torque, τ =Frsinθ
Here, F = [MLT−2] and r = [L]
So, dimensions of torque = [ML2T−2]
(d) Moment of inertia = mr2
Here, m = [M] and r2 = [L2]
So, dimensions of moment of inertia = [ML2T0]
Q3. Find the dimensions of
(a) electric field E
(b) magnetic field B
(c) magnetic permeability μ0
The relevant equations are 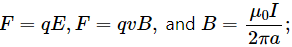 where F is force, q is charge, v is speed, I is current, and a is distance.
where F is force, q is charge, v is speed, I is current, and a is distance.
(a) Electric field is defined as electric force per unit charge.
i.e., E = F/q
Also,So, dimension of electric field,
(b) Magnetic field,
B = F/qv
Here,So, dimension of magnetic field, [B] =
(c) Magnetic permeability,
Here,
So, dimension of magnetic permeability,
Q4. Find the dimensions of
(a) electric dipole moment p
(b) magnetic dipole moment M
The defining equations are p = q.d and M = IA;
where d is distance, A is area, q is charge and I is current.
(a) Electric dipole moment, P = q.(2d)
Here, [q] = [AT] and d = [L]
∴ Dimension of electric dipole moment = [LTA](b) Magnetic dipole moment, M = IA
Here, A = [L2]
∴ Dimension of magnetic dipole moment = [L2A]
Q5. Find the dimensions of Planck's constant h from the equation E = hv where E is the energy and v is the frequency.
E = hv, where E is the energy and v is the frequency
Here,So,
Q6. Find the dimensions of:
(a) the specific heat capacity c
(b) the coefficient of linear expansion α
(c) the gas constant R.
Some of the equations involving these quantities are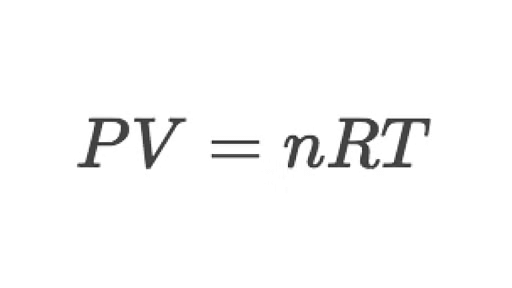
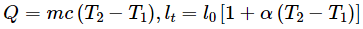
(a) Specific heat capacity,
(b) Coefficient of linear expansion,
(c) Gas constant,
Q7. Taking force, length, and time to be the fundamental quantities, find the dimensions of:
(a) density
(b) pressure
(c) momentum
(d) energy
(a) Density
(b) Pressure = Force/area
[Area] = [L2]
∴ [Pressure] =(c) Momentum = mv = (force/acceleration) × velocity
(d) Energy
Q8. Suppose the acceleration due to gravity at a place is 10 m/s2. Find its value if cm/(minute)2.
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
∴ g = 10 m/s2 = 10 × 100 cm x [1/(1/60)2] = 10 x 100 x [1/(1/3600)]
∴ g = 1000 × 3600 cm/min2 = 36 × 105 cm/min2 = 3.6 x 106 cm/min2
Q9. The average speed of a snail is 0 . 020 miles/ hour and that of a leopard is 70 miles/ hour. Convert these speeds in SI units.
1 mile = 1.6 km = 1600 m
(1 km = 1000 m)
For the snail, average speed = 0.02 miles/hr =For the leopard, average speed = 70 miles/hr =
Q10. The height of the mercury column in a barometer in a Calcutta laboratory was recorded to be 75 cm. Calculate this pressure in SI and CGS units using the following data: Specific gravity of mercury = 13.6, Density of water = 103 kg/m3, g = 9.8 m/s2 at Calcutta. Pressure = hρg, where symbols have usual meanings.
Height, h = 75 cm = 0.75 m
Density of mercury = 13600 kg/m3
g = 9.8 m/s2
In SI units, pressure = hρg = 0.75 × 13600 × 9.8 = 10 × 104 N/m2 (approximately) = 105N/m2
In CGS units, pressure = 10 × 104 N/m2= 106 dyne/cm2
Q11. Express the power of a 100-watt bulb in its C.G.S. unit.
In SI unit, watt = joule/s
In CGS unit, 1 joule = 107 erg
So, 100 watt = 100 joule/s
Q12. The normal duration of I. Sc. Physics practical period in Indian colleges is 100 minutes. Express this period in microcenturies. 1 microcentury = 10−6 × 100 years. How many microcenturies did you sleep yesterday?
1 microcentury = 10−6 × 100 years = 10−4 × 365 × 24 × 60 minutes
=1.9 microcenturies
Suppose, I slept x minutes yesterday.
∴ x min = 0.019x microcenturies
Q13. The surface tension of water is 72 dyne/cm. Convert it to SI unit.
1 dyne = 10−5 N
1 cm = 10−2 m
∴ 72 dyne /cm =
Q14. The kinetic energy K of a rotating body depends on its moment of inertia I and its angular speedω. Assuming the relation to be K = kI0ωB where k is a dimensionless constant, find a and b. The moment of inertia of a sphere about its diameter is (2/5) Mr2
Kinetic energy of a rotating body is K = k I aωb.
Dimensions of the quantities are [K] = [ML2T−2], [I] = [ML2] and [ω] = [T−1].
Now, dimension of the right side are [I]a = [ML2]a and [ω]b = [T−1]b.
According to the principal of homogeneity of dimension, we have:
[ML2T−2] = [ML2]a [T−1]b
Equating the dimensions of both sides, we get:
2 = 2a
⇒ a = 1
And,
−2 = −b
⇒ b = 2
Q15. The theory of relativity reveals that mass can be converted into energy. The energy E so obtained is proportional to certain powers of mass m and the speed c of light. Guess a relation among the quantities using the method of dimensions.
According to the theory of relativity, E α ma cb
⇒ E = k ma cb, where k = proportionality constant
Dimension of the left side, [E] = [ML2T−2]
Dimension of the right side, [ma cb]= [M]a [LT−1]b
Equating the dimensions of both sides, we get:
[ML2T−2] = [M]a [LT−1]b
⇒ a = 1, b = 2
∴ E = kmc2
Q16. Let I = current through a conductor, R = its resistance, and V = potential difference across its ends. According to Ohm's law, the product of two of these quantities equals the third. Obtain Ohm's law from dimensional analysis. Dimensional formulae for R and V are ML2I-2T-3 and ML2T-3I-1 respectively.
Dimensional formula of resistance, [R] = [ML2A−2T−3]
Dimensional formula of potential difference, [V] = [ML2A−1T−3]V = IR
⇒ I = V/R
Dividing (2) by (1), we get:
Q17. The frequency of vibration of a string depends on the length L between the nodes, the tension F in the string, and its mass per unit length m. Guess the expression for its frequency from dimensional analysis.
Frequency, f ∝ La Fb mc
f = k La Fb mc ...(1)
Dimension of [f] = [T−1]
Dimension of the right side components:
[L] = [L]
[F] = [MLT−2]
[m] = [ML−1]
Writing equation (1) in dimensional form, we get:
[T−1] = [L]a [MLT−2]b [ML−1]c
[M0L0T−1] = [Mb + c La + b − c T−2b]
Equating the dimensions of both sides, we get:b + c = 0 ....(i)
a + b −c = 0 ....(ii)
−2b = −1 ....(iii)
Solving equations (i), (ii) and (iii), we get:∴ Frequency, f = kL−1 F1/2m−1/2
Q18. Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
(a)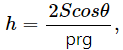
where h = height, S = surface tension, ρ = density, I = moment of inertia.
(b)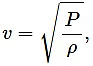 where v = frequency, ρ = density, P = pressure.
where v = frequency, ρ = density, P = pressure.
(c) 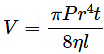 where v = frequency, P = pressure, η = coefficient of viscosity.
where v = frequency, P = pressure, η = coefficient of viscosity.
(d) 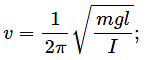 where h = height, S = surface tension, ρ = density, P = pressure, V = volume, η = coefficient of viscosity, v = frequency and I = moment of inertia.
where h = height, S = surface tension, ρ = density, P = pressure, V = volume, η = coefficient of viscosity, v = frequency and I = moment of inertia.
(a)
Height, [h] = [L]
Surface Tension,
Radius, [r] = [L], [g]= [LT−2]
Now,
Since the dimensions of both sides are the same, the equation is dimensionally correct.(b)
Velocity, [ν] = [LT−1]
Pressure,Density,
Now,
Since the dimensions of both sides of the equation are the same, the equation is dimensionally correct.(c)
Volume, [V] = [L3]
Pressure,
[r]= [L] and [t] = [T]
Coefficient of viscosity,
Now,
Since the dimensions of both sides of the equation are the same, the equation is dimensionally correct.(d)
Frequency, ν = [T−1]
Since the dimensions of both sides of the equation are the same, the equation is dimensionally correct.
Q19. Let x and a stand for distance. Is: 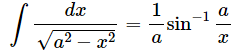 dimensionally correct?
dimensionally correct?
Dimension of the left side of the equation=
Dimension of the right side of the equation
So,Since the dimensions on both sides are not the same, the equation is dimensionally incorrect.
|
134 docs
|
FAQs on HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 1- Introduction to Physics- 1 - HC Verma Solutions - JEE
| 1. What is the importance of studying physics? |  |
| 2. How can I improve my understanding of physics concepts? |  |
| 3. What are the different branches of physics? |  |
| 4. How can I excel in my physics exams? |  |
| 5. How can physics be applied in real life? |  |