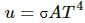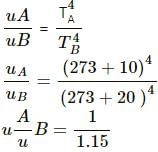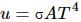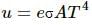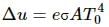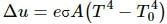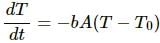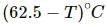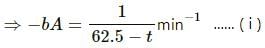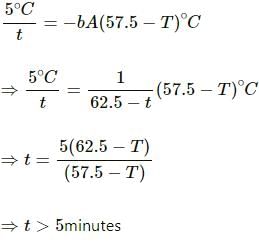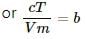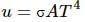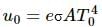Short Answers
Q.1. The heat current is written as 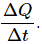 Why don't we write
Why don't we write 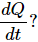
The amount of heat crossing through any cross-section of a slab in time ?t is called heat current.
It is written as ?Q/?t and not ?Q/?t as complete derivative . This is because the amount of heat crossing through any cross section is a function of many variables like temperature difference, area of cross-section, etc. So, we cannot write it as a complete derivative with respect to time.
Q.2. Does a body at 20°C radiate in a room, where the room temperature is 30°C? If yes, why does its temperature not fall further?
Yes, the body will radiate. However, its temperature will not fall down with time because as the temperature of the surroundings is greater than the temperature of the body so, its rate of absorption will be greater than its rate of emission.
Q.3. Why does blowing over a spoonful of hot tea cools it? Does evaporation play a role? Does radiation play a role?
Here, major role is played by convection. When we blow air over a spoonful of hot tea, the air coming from our mouth has less temperature than the air above the tea. Since hot air has less density, it rises up and cool air goes down. In this way, the tea cools down.
We know that any hot body radiates. So, the spoonful of tea will also radiate and as the temperature of the surrounding is less then the tea, the tea will cool down with time. Evaporation is also involved in this. On blowing over the hot tea, rate of evaporation increases and the cools down.
Q.4. On a hot summer day we want to cool our room by opening the refrigerator door and closing all the windows and doors. Will the process work?
No. When the door of the refrigerator is left open in a closed room, the heat given out by the refrigerator to the room will be more than that taken from the room. Therefore, instead of decreasing, the temperature of the room will increase at a slower rate.
Q.5. On a cold winter night you are asked to sit on a chair. Would you like to choose a metal chair or a wooden chair? Both are kept in the same lawn and are at the same temperature.
We will prefer to seat on a wooden chair because as the conductivity of wood is poorer than that of metal, heat flow from our body to the chair will be less in case of a wooden chair.
Q.6. Two identical metal balls one at T1 = 300 K and the other at T2 = 600 K are kept at a distance of 1 m in a vacuum. Will the temperatures equalise by radiation? Will the rate of heat gained by the colder sphere be proportional to 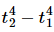 as may be expected from the Stefan's law?
as may be expected from the Stefan's law?
Yes, the temperature of the balls can be equalised by radiation. This is because both the spheres will emit radiations in all the directions at different rates.
The ball kept at the temperature of 300 K will gain some thermal energy by the radiation emitted by the ball kept at the temperature of 600 K. Also, it losses energy by radiation.
Similarly, the ball kept at the temperature of 600 K will gain some thermal energy by the radiation emitted by the ball kept at the temperature of 600 K. Also, it losses energy by radiation.
A time comes when the temperature of both the bodies becomes equal.
Yes, the rate of heat gained by the colder sphere is proportional to 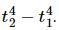
Q.7. An ordinary electric fan does not cool the air, still it gives comfort in summer. Explain.
An ordinary electric fan does not cool the air, still it gives comfort in summer because it circulates the air present in the room. Due to this, evaporation takes place and we feel cooler.
Q.8. The temperature of the atmosphere at a high altitude is around 500°C. Yet an animal there would freeze to death and not boil. Explain.
The temperature of the atmosphere at a high altitude is around 500°C, but density of air molecule is extremely low at this height. So, very less molecules of air collide with the body of the animal and transfer very less amount of heat. That is why the animal present there would freeze to death instead boiling.
Q.9. Standing in the sun is more pleasant on a cold winter day than standing in shade. Is the temperature of air in the sun considerably higher than that of the air in shade?
The heat coming from the sun to us is through the radiation. On colder winter days, when we stand in shade, we do not get the heat of the sun from the radiation. Though we feel cool in the shade, the temperature of the air in shady as well as non-shady regions is the same.
Q.10. Cloudy nights are warmer than the nights with clean sky. Explain.
During night, the earth's surface radiates infrared radiation of larger wavelength. Gas molecules in the air absorb some of this energy and radiate energy of their own in all directions. Also, water molecules, like the vapour that makes the clouds, absorb more frequencies of infrared energy than clear air does.
Both these factors contribute to the fact that clouds radiate more heat in all directions (including the earth) than clear air does. In turn, this makes the overall temperature on the earth warmer when there is a cloud cover. The heat energy radiated by the earth is reflected back to earth. Due to this, cloudy nights are warmer than the nights with clean sky.
Q.11. Why is a white dress more comfortable than a dark dress in summer?
A white colour dress reflects almost all the radiations falling on it. So, it does not absorb any heat from the sunlight and we feel more comfortable in it. On the other hand, a dark colour dress absorbs maximum radiation falling on it. So, we feel hot in a dark coloured dress during summers.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:The thermal conductivity of a rod depends on
Explanation
The thermal conductivity of a rod depends only on the material of the rod. For example, metals are much better conductors than non-metals because metals have large number of free electron that can move freely anywhere in the body of the metal and carry thermal energy from one place to other. Also, 2 copper rods having different lengths and areas of cross-section have same thermal conductivity that depends only on the number of free electrons in copper.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:In a room containing air, heat can go from one place to another
Explanation
In conduction, heat is transferred from one place to other by vibration of the molecules. In this process, the average position of a molecule does not change. Hence, there is no mass movement of matter.
In convection, heat is transferred from one place to other by actual motion of particles of the medium. When water is heated, hot water moves upwards and cool water moves downwards.
In radiation process, transfer of heat does not require any material medium. For a room containing air, heat can be transferred via radiation (no medium required) and convection (by the movement of air molecules) and by conduction (due to collision of hot air molecules with other molecules).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A solid at temperature T1 is kept in an evacuated chamber at temperature T2 > T1. The rate of increase of temperature of the body is proportional to
Explanation
From Stefan-Boltzmann law, the energy of thermal radiation emitted per unit time by a blackbody of surface area A is given by 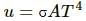
Here, σσ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
Since the temperature of the solid is less than the surroundings, the temperature of the solid will increase with time until it reaches equilibrium with the surroundings. The rate of emission from the solid will be proportional to T41 and rate of emission from the surroundings will be proportional to T42.
So, the net rate of increase in temperature will be proportional to 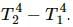
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:The thermal radiation emitted by a body is proportional to Tn where T is its absolute temperature. The value of n is exactly 4 for
Explanation
From Stefan-Boltzmann law, the energy of the thermal radiation emitted per unit time by a blackbody of surface area A is given by 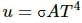 here , σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
here , σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
This law holds true for all the bodies.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:Two bodies A and B having equal surface areas are maintained at temperature 10°C and 20°C. The thermal radiation emitted in a given time by A and B are in the ratio
Explanation
From Stefan-Boltzmann law, energy of the thermal radiation emitted per unit time by a blackbody of surface area A is given by 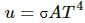
Here, σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
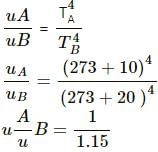
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:One end of a metal rod is kept in a furnace. In steady state, the temperature of the rod
Explanation
In steady state, the temperature of the rod is nonuniform maximum at the end near the furnace and minimum at the end that is away from the furnace.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:Newton's law of cooling is a special case of
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
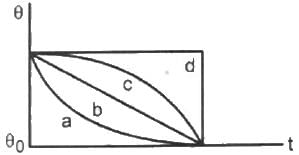
Try yourself:A hot liquid is kept in a big room. Its temperature is plotted as a function of time. Which of the following curves may represent the plot?
Explanation
When a hot liquid is kept in a big room, the liquid will loose its temperature with time. The thermal energy emitted by the liquid will be gained by the walls of the room. As the room is big, we can assume that the temperature difference between the room and the liquid is large. From Stephen's law, the liquid emits thermal energy in proportion to T4, where T is the initial temperature of the liquid.
As the temperature decreases, the rate of loss of thermal energy will also decrease. So, the slope of the curve will also decrease. Therefore, the plot of temperature with time is best represented by the curve (a).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A hot liquid is kept in a big room. The logarithm of the numerical value of the temperature difference between the liquid and the room is plotted against time. The plot will be very nearly
Explanation
When a hot liquid is kept in a big room, then the liquid will loose temperature with time. The thermal energy emitted by the liquid will be gained by the walls of the room. As the room is big, we can assume that the temperature difference between the room and the liquid is large. From Stephen's law, the liquid emits thermal energy in proportion to T4, where T is the initial temperature of the liquid. As the temperature decreases, the rate of loss will also decrease. So, the slope of the curve will also decrease. Finally, at equilibrium, the temperature of the room will become equal to the new temperature of the liquid. So, in steady state, the difference between the temperatures of the two will become zero.
A graph is plotted between the logarithm of the numerical value of the temperature difference between the liquid and the room is plotted against time.The logarithm converts the fourth power dependence into a linear dependence with some coefficient (property of log). So, the plot satisfying all the above properties will be a straight line.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A body cools down from 65°C to 60°C in minutes. It will cool down from 60°C to 55°C in
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:One end of a metal rod is dipped in boiling water and the other is dipped in melting ice.
Explanation
The heat transfer will take place from the hot end to the cold end of the rod via conduction. So, with time, the temperature of the rod will increase from the end dipped in boiling water to the end dipped in melting, until it comes in equilibrium with its surroundings. In steady state, the temperature of the rod is nonuniform and constant, maximum at the end dipped in boiling water and minimum at the end dipped in melting ice.
Equilibrium means that the system is stable. So, all the macroscopic variables describing the system will not change with time. Hence, the temperature of the rod will become constant once equilibrium is reached, but its value is different at different positions of the rod.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A blackbody does not
Explanation
A black body is an ideal concept. A black body is the one that absorbs all the radiation incident on it. So, a black body does not reflect and refract radiation.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:In summer, a mild wind is often found on the shore of a clam river. This is caused due to
Explanation
Convection current is the movement of air (or any fluid) due to the difference in the temperatures. During summer days, there is temperature difference of air above the land and river. Due to this, a convection current is set from the river to the land during daytime. On the other hand, during night, a convection current is set from the land to the river. Therefore, a mild air always flows on the shore of a calm river due to the convection current.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A piece of charcoal and a piece of shining steel of the same surface area are kept for a long time in an open lawn in bright sun.
Explanation
In steel, conductivity is higher than charcoal. So, if both are picked up by bare hands, then heat transfer from the body (steel or charcoal) to our hand will be larger in case of steel. Hence, steel will be hotter than the charcoal.
On the other hand, emissivity of charcoal is higher as compared to steel. So, if the two are picked up from the lawn and kept in a cold chamber, charcoal will lose heat at a faster rate than steel.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A heated body emits radiation which has maximum intensity near the frequency v0. The emissivity of the material is 0.5. If the absolute temperature of the body is doubled.
Explanation
From Wein's displacement law,
λmT = b ( a constant )
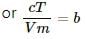
Here, T is the absolute temperature of the body.
So, as the temperature is doubled to keep the product on the left hand side constant, frequency is also doubled.
From Stefan's law, we know that the rate of energy emission is proportional to T4
This implies that total energy emitted will increase by a factor of (2)4, which is equal to 16.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 28: Heat Transfer- 1
Try yourself:A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of the same material and of equal radii are heated to the same temperature.
Explanation
Let the temperature of the surroundings be T0
From the Stefan-Boltzmann law, the energy of thermal radiation emitted per unit time by a blackbody of surface area A is given by 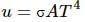
Here, σ is Stephen's constant.
Also, the energy absorbed per unit time by the body is given by 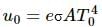
As the two spheres have equal radii and temperatures, their rate of absorption and emission will be equal in the beginning.
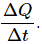 Why don't we write
Why don't we write 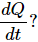
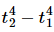 as may be expected from the Stefan's law?
as may be expected from the Stefan's law?






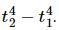
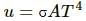
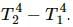
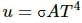 here , σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
here , σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant.