Short Answers
Q.1. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, it gets polarised. The electric field in a polarised material is less than the applied field. When a paramagnetic substance is kept in a magnetic field, the field in the substance is more than the applied field. Explain the reason of this opposite behaviour.
This opposite behaviour is due to the opposite behaviour of magnetic dipole as compared to electric dipole. When the paramagnetic substance is kept in magnetic field, the direction of magnetic field at the centre of magnetic dipole of substance is along the direction of magnetic moment which is opposite to the case of dipole in electric field. Also, when paramagnetic substance is kept in the magnetic field then its magnetic dipole aligns in the direction of field. Thus, magnetic field due to the magnetic dipole adds up to the applied magnetic field.
Hence, an extra magnetic field produced in the direction of applied field.
Q.2. The property of diamagnetism is said to be present in all materials. Then, why are some materials paramagnetic or ferromagnetic?
When a diamagnetic material is placed in magnetic field, dipole moment are induced in its atoms by the applied magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field due to induced dipole moment is opposite to the applied magnetic field therefore the resultant magnetic field is smaller than the applied magnetic field. This process is called diamagnetism. As this process takes place for all the material, therefore all the material exhibit diamagnetism. However, some material consists of atoms having some magnetic moment on their own (without applying magnetic field). As a result of it, when they are placed in magnetic field, they aligns their atomic dipole in the direction of applied magnetic field and hence their resultant magnetic field is more then the applied magnetic field and exhibit paramagnetism or ferromagnetism.
Q.3. Do permeability and relative permeability have the same dimensions?
Magnetic permeability (μ) is the ratio of magnetic flux density (B) to the magnetising field strength (H).
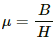
In CGS ( centimeter-gram-second) dimension of B and H is same. Hence, magnetic permeability is dimensionless. But in SI unit, dimension of B and H is not same. Thus, permeability is not dimensionless.
Relative permeability is defined as the ratio of magnetic permeabity of any medium to the permeability of the vaccum. Hence, it is dimensionless. Thus, permeability and relative permeability have the same dimensions in CGS system.
Q.4. A rod, when suspended in a magnetic field, stays in the east-west direction. Can we be sure that the field is in the east-west direction? Can it be in the north-south direction?
No, it depends on the nature of rod. As we know that when the diamagnetic substance is suspended in a uniform field they set their longer axis right angles to the direction of magnetic field. So, if the material of the rod will be diamagnetic then it will stay in the east-west direction in perpendicular magnetic field ( i.e. along north-south direction). But if the material of the rod is paramagnetic or ferromagnetic it will stay in east-west direction having magnetic field in east-west direction.
Q.5. Why is it not possible to make permanent magnets from paramagnetic materials?
Permanent magnets are made from the material that are easily magnetized and retain the magnetization even reverse magnetizing field is applied (high coercivity). Paramagnetic materials get small magnetization, if they are placed in magnetic field, they lose their magnetization easily if the reverse field is applied. Hence, they are not used to make permanent magnet.
Q.6. Can we have magnetic hysteresis in paramagnetic or diamagnetic substances?
No, magnetic hysteresis is the lagging of intensity of magnetization (I) behind magnetising force (H). When diamagnetic and paramagnetic materials are placed in a magnetic field they get weekly magnetised. Also, they lose their magnetization as the magnetic field is removed (low retentively). Therefore, they do not form magnetic hysteresis curve.
Q.7. When a ferromagnetic material goes through a hysteresis loop, its thermal energy is increased. Where does this energy come from?
When a ferromagnetic material is taken through the cycle of magnetisation, magnet dipoles of the material orient and reorient with time. This molecular motion within the material results in the production of heat, which increses thermal energy of material.
Q.8. What are the advantages of using soft iron as a core, instead of steel, in the coils of galvanometers?
The material used as a core in the moving coil galvanometer undergoes cycle of magnetization for long period. Therefore, low hysterisis loss is the first requirement for such material. In soft ron core, area under the hysteresis curve is small thus loss of energy is less as compared to steel. Further, it is easily magnetized by the magnetizing field, which increase the magnetic field and hence sensitivity of galvanometer.
Q.9. To keep valuable instruments away from the earth's magnetic field, they are enclosed in iron boxes. Explain.
As we know that iron have high permeability, therefore it will provide easy path for the magnetic field lines to pass. As a result of this, all the magnetic field lines of earth's magnetic field will prefer to pass through the wall of the box making magnetic field inside the box zero. Hence, it will keep the valuable instruments away from the earth's magnetic field.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A paramagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field. Consider the following statements:-
(A) If the magnetic field is increased, the magnetisation is increased.
(B) If the temperature is increased, the magnetisation is increased.
Explanation
If the magnetic field is increased, magnetisation of paramagnetic material placed in magnetic field is also increases. Hence, option (a) is correct.
Magnetization (I) is given by,
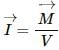
As the temperature is increased, magnetic moments of paramagnetic material becomes more randomly aligned due to incresed thermal motion. This leads decrease in the magnetization I.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A paramagnetic material is kept in a magnetic field. The field is increased till the magnetisation becomes constant. If the temperature is now decreased, the magnetisation ___________ .
Explanation
Magnetisation becomes constant i.e all the magnetic moments have got aligned in the direction of the applied field. So now, if the temperature is decreased, thermal vibration of the paramagnetic material will reduce, But as all the magnetic moments are already aligned in the direction of the field so no further alignment can take place due to reduced thermal motion. Thus, there will be no negative effect of decreasing the temperature on the magnetisation.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A ferromagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field. The magnetic domains ______________ .
Explanation
Atoms of ferromagnetic material in unmagnetised state form domains inside the ferromagnetic material. These domains have large magnetic moments due to the magnetic moment of atoms. In the absence of magnetic field, these domains have magnetic moment in different directions. But when the magnetic field is applied, domains aligned in the direction of the field grow in size and those aligned in the direction opposite to the field reduce in size.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A long, straight wire carries a current i. The magnetising field intensity H is measured at a point P close to the wire. A long, cylindrical iron rod is brought close to the wire, so that the point P is at the centre of the rod. The value of H at P will ______________ .
Explanation
From the Biot-Savart law, magnetic field (B) at a point P close to the wire carrying current i is given by,
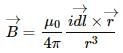
Magnetising field intensity (H) will be,
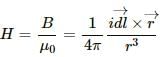
Now, as the cylindrical rod is brought close the wire such that centre of the rod is at P, then distance of point P from the wire(r) will remain same. Hence, magnetic field intensity will remain almost constant. Also even when the rod is carrying any current then B will be zero at the centre of the rod so the value of Magnetising field intensity will remain the same at point P.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The magnetic susceptibility is negative for _____________ .
Explanation
Magnetic susceptibility is defined as the ratio of the intensity of magnetisation induced in the material to magnetising foorce applied on it.
Magnetic susceptibility is negative for diamagnetic materials. Magnetic susceptibility is positive for paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The desirable properties for making permanent magnets are _________________ .
Explanation
Permanent magnets should have high retentivity so that the magnet is strong and high coercive force, so that magnetisation is not erased by stary magnetic fields, temperature change or due to rough handling etc.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Electromagnets are made of soft iron because soft iron has _______________ .
Explanation
Electromagnets are made of soft iron because soft iron has
low retentivity - When soft iron is placed inside a solenoid to make an electromagnet and current is passed through the solenoid,magnetism of the solenoid is incresed thousand folds. When the current is switched off, the magnetism is removed instantly because of the low retentivity of soft iron.
Low coercivity - it has low coercivity so that area under the hysteresis cureve for soft iron is very small hysterisis loss in case of soft iron is small.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Pick the correct options.
Explanation
Electrons of an atom moves in circular path around the nucleus and constitute electric current. Since a current loop has magnetic moment, therefore electron also has magnetic moment due to this orbit motion. It also has magnetic moment due to the spinning about its own axis.
Orbital motion of electron around the nucleus give rise to magnetic field around the proton (nucleus). This create a torque and thus magnetic dipole moment on proton.
All nuclei also have magnetic moment but it is several thousand times smaller than the magnetic moment of the electron so it can be ignored in comparison to the magnetic moment of an eletron.
Generally, an atom has no magnetic moment. Because the magnetic moments of electrons of an atom have a tendency to cancel in pairs.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The permanent magnetic moment of the atoms of a material is not zero. The material _______ .
Explanation
Diamagnetic material have zero magnetic moment on their own.
Paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials have non zero permanent magnetic moment. But we are not sure about the material, whether it is Paramagnetic or ferromagnetic. If the material has large value of permanent magnetic moment, then it will be ferromagnetic and if it has small value of permanent magnetic moment, then it will be Paramagnetic.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The permanent magnetic moment of the atoms of a material is zero. The material ______ .
Explanation
Paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials have non zero permanent magnetic moment on their own. Only atoms of diamagnetic materials have zero permanent magnetic moment.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Which of the following pairs has quantities of the same dimensions?
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:When a ferromagnetic material goes through a hysteresis loop, the magnetic susceptibility
Explanation
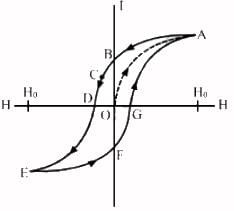
We know,
Magnetic susceptibility = I/H
At point B, the value of H is zero but I is non zero. Magnetic susceptibility is infinity here. At point C, value of magnetic susceptibility will be negative. Here Magnetic field is applied in opposite direction to reduce the intensity of magnetization to zero. The applied field to reduce the residual magnetization to zero is called coercivity. At point D, I is zero but H is not zero so susceptibility of the material will be zero.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Mark out the correct options.
Explanation
When a material is placed in magnetic field, dipole moment are induced in the atoms by the applied magnetic field. Since the direction of magnetic field due to induced dipole moment is opposite to the applied magnetic field. Therefore, resultant magnetic field is smaller than the applied magnetic field. This process is called diamagnetism. As this process takes place for all the material, therefore all the material exhibit diamagnetism. Hence, option (a) and (d) are correct.
Diamagnetic material do not have permanent magnetic moment on their own. When they are placed in magnetic field, dipole moments are induced by the applied magnetic field. Thus, there is no net alignment of permanent magnetic moment so these mterials do not have any permanenet magnetic momentof their own. Hence, option (b) is incorrect.
Magnetic field intensity is not zero in free space. Hence, option (c) is incorrect.

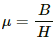
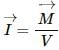
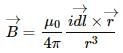
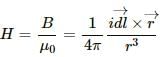
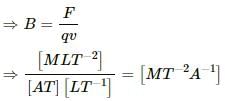
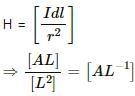
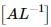 as both Magnetising field intensity H and intensity of magnetisation I are measured in Am-1.
as both Magnetising field intensity H and intensity of magnetisation I are measured in Am-1.




















