Q1: Why is copper used more commonly than silver in electrical wiring, even though silver is a better conductor?
Ans: Silver allows electricity to pass through it even better than copper, but it is very expensive and not easily available. Copper is also a good conductor and much cheaper than silver. That’s why copper is used in most wires—it does the job well and costs less.
Q2: If a torchlight using an incandescent lamp stops glowing, how will you determine whether the issue is with the filament or the battery?
Ans: First, try changing the battery. If the torch still doesn't glow, then the problem is likely with the filament inside the lamp. If the thin wire (filament) is broken, electricity can’t pass through it, so the lamp won’t glow. That means the lamp is “fused.”
Q3: In an emergency where no torchlight is available, how could you use everyday objects to construct a simple lighting device?
Ans: You can take a battery from a remote, a small bulb from a toy, and some wires. Connect one wire from the positive end of the battery to the bulb, and another wire from the bulb to the negative end. If connected correctly, the bulb will glow and act like a torch.
Q4. Why does an LED require a current-limiting resistor in most circuits, while an incandescent bulb does not? Discuss in terms of material properties and power consumption.
Ans: An LED has a very low forward resistance and can allow excess current to flow, causing it to overheat and fail. Its semiconductor material operates efficiently only within a narrow voltage and current range. In contrast, an incandescent bulb has a high-resistance filament that naturally limits current and converts electrical energy into heat and light. Additionally, LEDs are more sensitive to voltage surges, hence requiring a resistor to regulate current and ensure longevity.
Q5: Explain how electricity from a hydroelectric dam like Bhakra Nangal travels to your home and powers a device like a lamp.
Ans: Water stored at a height in a dam falls down and spins big machines called turbines. These turbines produce electricity. The electricity travels through long wires to reach our homes. When we switch on a lamp, electricity flows through the wires and makes the lamp glow.
Q6: Can a circuit still function if the switch is placed before the battery instead of after it? Justify your answer.
Ans: Yes, the circuit will still work. The switch can be placed anywhere in the loop—as long as it is part of the circuit. When the switch is turned ON, electricity flows, and the lamp will glow no matter where the switch is placed.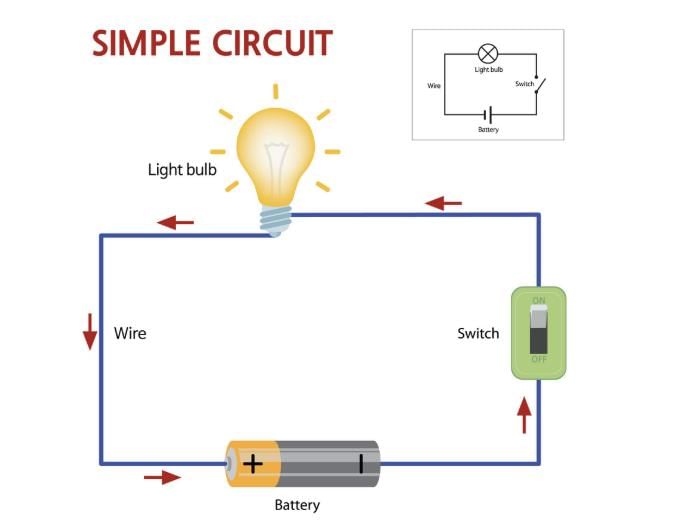
Q7. Consider a closed circuit with multiple components: a battery, a switch, an LED, and a resistor. The LED is not glowing even though the battery and switch seem functional. Suggest multiple potential reasons and how to verify each.
Ans: Several possibilities could be responsible:
- Incorrect LED polarity: LEDs are directional; if terminals are reversed, no current flows through them.
- Burnt-out LED: Excess voltage or current could damage the LED; replacement or testing with a multimeter is necessary.
- Resistor value too high: A high-resistance value might limit the current below the LED's threshold; test with a lower resistance.
- Loose or broken connections: Disconnected wires or dry solder joints could disrupt the path.
- Faulty switch: Even if physically moving, the switch might not be making proper contact inside.
- Testing each component individually in a simplified circuit helps identify the faulty part.
Q8: Compare the working of an LED lamp and an incandescent lamp. Why is the LED considered more efficient?
Ans: An incandescent lamp has a wire (filament) inside it. When electricity flows, the wire gets hot and glows. But it also wastes energy as heat. An LED lamp doesn't have a filament—it glows directly when electricity flows in one direction. It saves energy and lasts longer, so it is more efficient.
Q9. In what ways does the internal resistance of a cell affect the performance of a circuit, especially in high-load conditions?
Ans: Every cell has internal resistance, which consumes some of the supplied voltage. In high-load conditions (when more current is drawn), the voltage drop across the internal resistance increases, reducing the effective voltage across external components. This leads to dimmer bulbs, slower motors, or malfunctioning electronics. In extreme cases, it can generate heat and reduce battery life. High internal resistance is also why old batteries perform poorly under load.
Q10. Why do household power systems use alternating current (AC) instead of direct current (DC), even though DC is simpler for small circuits?
Ans: AC systems are preferred in household power supply because:
- Voltage transformation using transformers is easy in AC, enabling long-distance transmission with minimal loss.
- AC generators are more durable and efficient for power plants.
- Safety systems and appliances are designed around predictable AC waveforms.
- DC, though simple, suffers from significant energy loss over distance and is difficult to step up or down in voltage. While DC is excellent for portable electronics, AC is more practical for centralized power distribution.
Q11. If a conductor is heated, its resistance increases. How can this affect the brightness of a bulb and the efficiency of a circuit?
Ans:
As a conductor (like a filament) heats up, the atoms vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to flow, thus increasing resistance. In a bulb, this causes more energy to be lost as heat, and the brightness may reduce slightly if the power source is not regulated. In sensitive electronic circuits, this effect can cause voltage drops, component stress, or instability, reducing overall efficiency and performance.
Q12. A circuit contains a parallel connection of three bulbs. If one bulb is removed or blows out, the other two continue to glow. Explain the reason using circuit theory.
Ans: In a parallel circuit, each bulb is connected independently to the power source. This means each branch provides an individual current path. If one bulb fails, the remaining paths remain uninterrupted, allowing current to continue flowing through the other branches. Unlike series circuits where one break halts the entire circuit, parallel configurations offer reliability and consistent performance, which is why they are used in homes and buildings.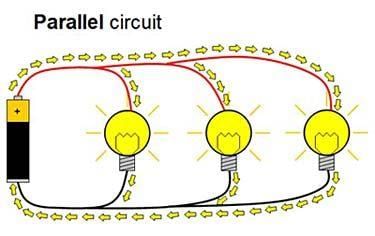
Q13. A student claims that adding more cells to a circuit always makes a bulb glow brighter. Critically evaluate this statement.
Ans: While adding cells increases voltage, which can initially make the bulb brighter, it's not always beneficial. Exceeding the voltage rating of a bulb can shorten its lifespan or burn it out. Furthermore, higher voltage increases current, which can overheat wires or damage other components. So, the statement is partially correct, but only when voltage is within the device's safe operating range. Beyond that, it causes damage and energy waste.
Q14. If a 3V LED is connected directly to a 9V battery without a resistor, what will happen? Explain the science behind it.
Ans: The excess voltage will force a much higher current through the LED than it is rated for. This leads to thermal runaway—as the LED heats up, its resistance drops, allowing more current, which causes more heat, and eventually burns the LED out. The circuit lacks a current-limiting resistor, which is crucial for protecting the LED from voltage higher than its forward rating. This example shows why circuit components must match voltage ratings.
Q15. How can the concept of a complete circuit be used to design a burglar alarm that triggers when a door is opened?
Ans: A burglar alarm can be designed using a normally closed circuit with a switch at the door hinge:
- When the door is closed, the switch is pressed, keeping the circuit open (alarm OFF).
- When the door opens, the switch releases, completing the circuit and activating the alarm.
This uses the concept that current only flows in a closed circuit. The system must also include a power source, buzzer, and wires, forming a logic-based safety circuit for security applications.