Class 7 Science Chapter 8 HOTS Questions - Measurement of Time and Motion
Q1: Paheli and Boojho have to cover different distances to reach their school but they take the same time to reach the school. What can you say about their speed?
Ans: They do not have equal speed because they cover unequal distance in equal intervals of time. One of them has higher speed whom has to cover larger distance with respect to other.
Q2: If Boojho covers a certain distance in one hour and Paheli covers the same distance in two hours, who travels with a higher speed?
Ans: Boojho travels with a higher speed as he has covered same distance in lesser time with respect to Paheli.
Q3: If you did not have a clock, how would you decide what time of the day is?
Ans: We can decide time of the day without a clock by seeing the shadow formed by the sun, e.g. at noon, the shadow formed by the sun is shorter than at evening.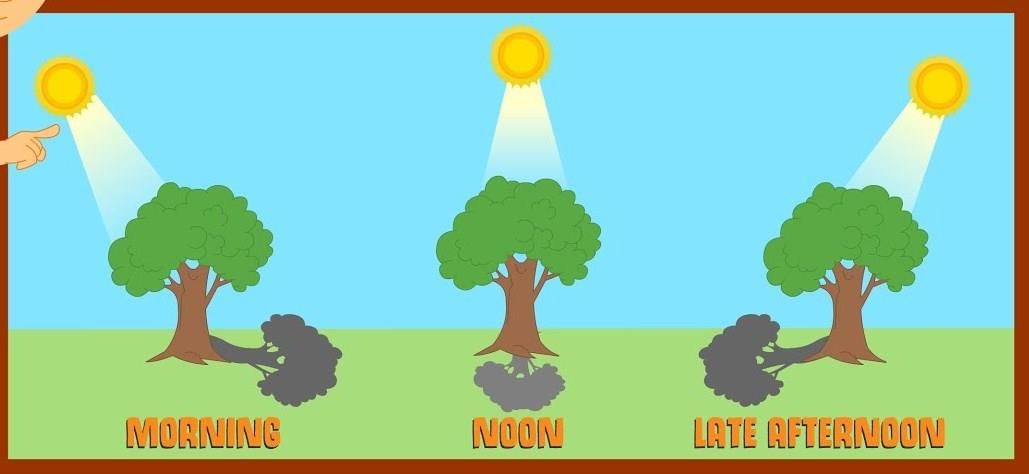
Q4: Distance between Bholu’s and Golu’s house is 9 km. Bholu has to attend Golu’s birthday party at 7 O’ clock. He started his journey from his home at 6 O’ clock on his bicycle and covered a distance of 6 km in 40 min. At that point, he met Chintu and he spoke to him for 5 min and reached Golu’s birthday party at 7 O’ clock. With what speed, did he cover the second part of the journey? Calculate-his average speed for the entire journey.
Ans: From the question, Bholu covers 3 km distance in 15 min.
Q5: Why did ancient water clocks like the Ghatika-yantra use sinking bowls, and what problem did this design solve?
Ans: Earlier water clocks slowed down because the water level dropped, changing the flow rate. The Ghatika-yantra used a bowl that sank slowly in water over a fixed time (24 minutes), providing a consistent way to measure time regardless of water level. This design solved the problem of changing flow rates and was used for announcements in monasteries and towns.
Q6: Boojho walks to his school which is at a distance of 3 km from his home in 30 min. On reaching, he finds that the school is closed and comes back by a bicycle with his friend and reaches home in 20 min. His average speed in km/h is
(a) 8.3
(b) 7.2
(c) 5
(d) 3.6
Ans: (b)
Given, total distance = 3+ 3 = 6km, total time = 30 + 20 = 50 min
Q7: What would happen if you changed the length of the pendulum? How would it affect the time period?
Ans: Increasing the length of the pendulum makes it swing more slowly, so the time period increases (each oscillation takes longer). Decreasing the length makes the pendulum swing faster, reducing the time period. This means the time period depends on the length of the pendulum.
Q8: How is speed defined, and what are its units? Why do we use different units like m/s and km/h?
Ans: Speed is how fast something moves, calculated by dividing distance covered by the time taken. The SI unit is metres per second (m/s) for scientific precision. For everyday travel, we use kilometres per hour (km/h) because distances and times are larger and more practical in those units.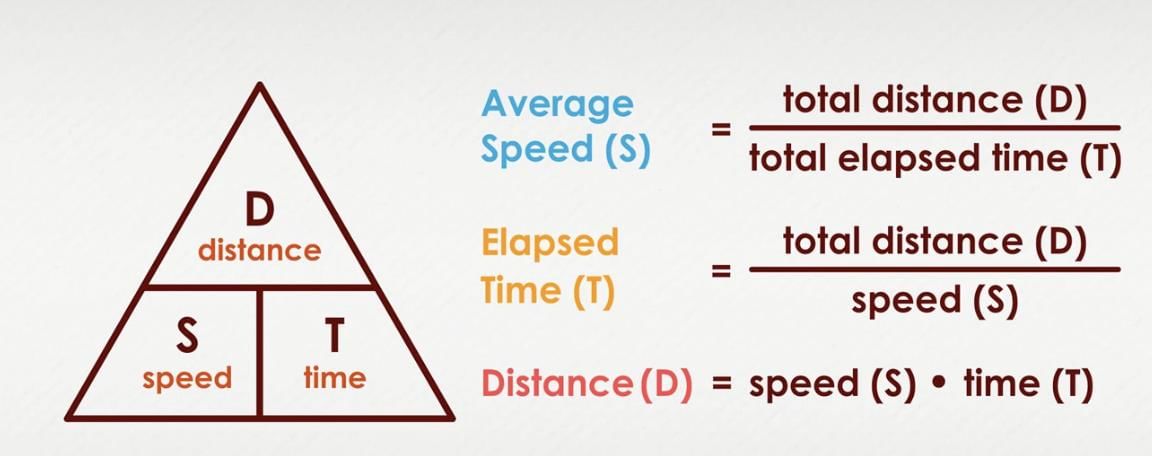
Q9: Imagine you are tasked with designing a modern clock based on the principles of the pendulum but suitable for use in a spacecraft where gravity is low. What challenges might you face, and how would you solve them?
Ans: Since pendulums rely on gravity to swing, in low gravity, they won’t work properly. One could use other periodic systems that don’t depend on gravity, like quartz crystal vibrations or atomic clocks, which measure time using precise vibrations of atoms or crystals instead.
Q10: Why is precise time measurement important in sports, medicine, and technology? Give examples.
Ans: In sports, precise timing decides winners in races where milliseconds matter. For example, Olympic races measure times to hundredths or thousandths of a second.
In medicine, devices like ECG machines record heartbeats in milliseconds to detect problems early.
In technology, smartphones and computers process data in microseconds to work efficiently and quickly. Accurate time measurement ensures these fields operate reliably.
|
50 videos|125 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 8 HOTS Questions - Measurement of Time and Motion
| 1. What are the different units of measurement for time and motion? |  |
| 2. How do we calculate speed using time and distance? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to measure time accurately in scientific experiments? |  |
| 5. How can we represent motion graphically? |  |





















