Class 7 Science Chapter 7 HOTS Questions - Transportation in Animals and Plants
Q1: How do the transportation systems in plants differ from those in animals?
Ans: Plants use xylem to transport water and minerals upward from the roots and phloem to move sugars throughout the plant. In contrast, animals have a circulatory system with arteries that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, veins that return oxygen-poor blood, and capillaries for substance exchange. Thus, plants rely on passive transport, while animals use a pumping heart.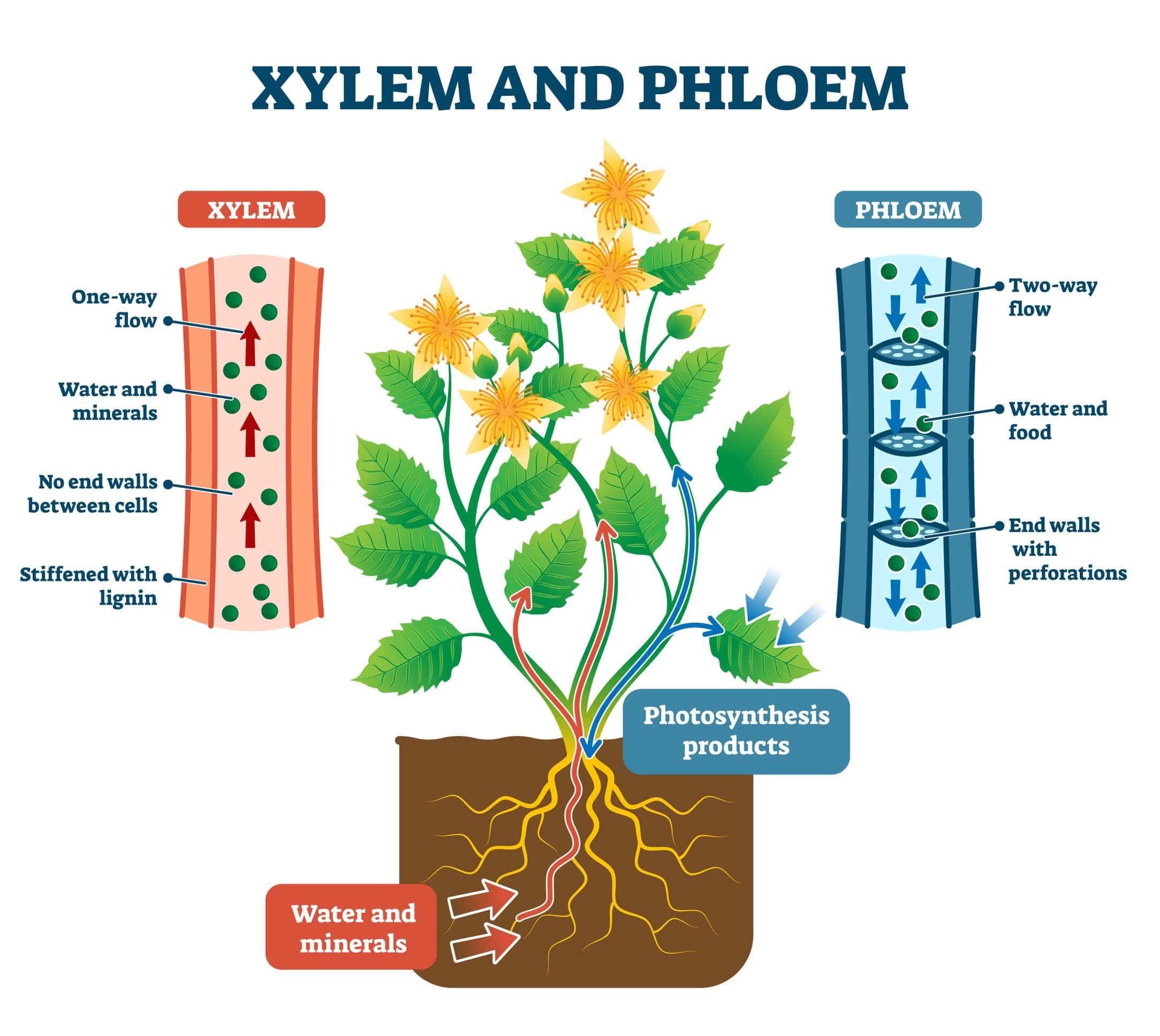 Vascular tissues
Vascular tissues
Q2: Veins have valves which allow blood to flow only in one direction. Arteries do not have valves. Yet the blood flows in one direction only. Can you explain why?
Ans: Veins have valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards and pooling, whereas arteries pump blood at very high pressures, which naturally prevents back flow.
Q3: Kidneys are the major excretory organs in humans. How will the waste products released will be excreted out if the kidneys are damaged or unfunctional?
Ans: Artificial ways of waste removal are used like dialysis which are referred to as artificial kidneys.
Q4: Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Ans: An athlete breathes faster and deeper after a race because their body needs more oxygen to produce energy. During the race, the muscles use up oxygen quickly and can even start working without enough oxygen for a short time. After the race, faster and deeper breathing helps bring in more oxygen to break down food and release more energy, helping the body recover.
Q5: What is the relation between the rate of heartbeat and pulse rate? If a pulse rate of an athlete Is 96/min, what will be the number of his heartbeat at the same time?
Ans:
- The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the heart is called heartbeat. Whereas, the rhythmical throbbing of the arteries as the blood is pushed forward through them is called pulse. It can be felt in the wrist, temples, etc.
- Pulse rate is the number of heartbeats per minutes. The number of heartbeat is equal to the number of pulse per minute.
Therefore, if a pulse rate of an athlete is 96/min then the number of his heartbeat at the same time will also be 96/min
Q6: Paheli noticed water being pulled up by a motor pump to an overhead tank of a five storeyed building. She wondered how water moves up to great heights in the tall trees standing next to the building. Can you tell why?
Ans: When the water is pulled up by a motor-pump to an overhead tank of a five storeyed building, it moves to a great height due to the suction pull. This pull forms the continuous column of water and water rises up to a great height. Similarly, when transpiration occurs in the plants, water is evaporated and this creates a suction pull in the plants.
Q7: Paheli says her mother puts ladyfinger and other vegetables in water if they are somewhat dry. She wants to know how water enters into them.
Ans: Water enters dry vegetables through osmosis. When soaked, water moves from an area of higher concentration (outside) to lower concentration (inside the cells), rehydrating them until they become fresh again.
Q8: List some animals surrounding your locality group them into following groups.
(a) Animals that excrete ammonia in gaseous forms.
(b) Animals that excrete uric acid in the form of pellets.
(c) Animals that excrete urea in the form urine.
Ans:
Some animals that surround us are fish, frog, birds, tadpole larva, snake, cow, man, rat, monkey, lizard, toad and snail.
These can be grouped as follows
(a) Animals that excrete ammonia in gaseous form (i.e. ammonotelics)-Fish, tadpole larva.
(b) Animals that excrete uric acid in the form of pellets (i.e. uricotelics)—Bird, snake, lizard, snail.
(c) Animals that excrete urea in the form of urine (i.e. ureotelics)-Frog, cow, rat, man, monkey, toad.
Q9: Human have two major organs that perform transport of materials. Organ ‘A’ is bean-shaped and dark red in colour lie just above the waist. It helps in’ removal of ‘Q’, a waste material from blood. The organ ‘S’ is the opening at the end of the urinary bladder through which the waste material is eliminated.
Organ ‘B’ lies in the chest cavity slightly tilted towards the left side. It pumps continuously and pours liquid ‘C’ into arteries and through very fine tube-like structure ‘D’ distributes the liquid to various parts of the body. What are the name of these organs.
Ans: Organ ‘A’ is the kidney, which is bean-shaped and dark red, lying just above the waist. It removes urea (Q), a waste material, from blood. ‘S’ is the urethra, the opening at the end of the urinary bladder through which waste is eliminated. Organ ‘B’ is the heart, in the chest cavity, slightly tilted left. It pumps blood (liquid ‘C’) into arteries and through capillaries (D), fine tube-like structures, distributing blood to various body parts.
Q10: The major function of the arteries is to carry to oxygenated blood throughout the body and that of veins is to carry deoxygenated blood from body parts to heart for purification. There is one artery that carries deoxygenated blood and one vein that carries oxygenated blood. Name the artery and vein.
Ans: The artery which carries deoxygenated blood or blood rich in CO2 is pulmonary artery while the pulmonary vein is one which carries oxygenated blood. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs while pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
Q11: Paheli uprooted a rose plant from the soil. Most of the root tips with root hairs got left behind in the soil. She planted it in a pot with new soil and watered it regularly. Will the plant grow or die? Give reason for your answer.
Ans:
Reason:
- Without the root hairs, the roots will not be able to absorb water and nutrients and the plant will die.
- The stem of the rose plant may grow new roots and the plant will live.
- The rose plant may not be able to survive in a different type of soils.
Q12: (a) Name the only artery that carries carbon dioxide rich blood.
(b) Why is it called an artery if it does not carry oxygen-rich blood?
Ans:
(a) The only artery that carries carbon dioxide rich blood is pulmonary artery.
(b) The main function of artery is to carry blood away from heart. Also arteries have thick wall and do not contain valves in them. Blood flow in arteries, takes place at high pressure. All these characteristics are found in pulmonary artery. It carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs for oxygenation, therefore it is called artery.
Q13: Name the process and the organ which help in removing the following wastes from the body.
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Undigested food
(c) Urine
(d) Sweat
Ans: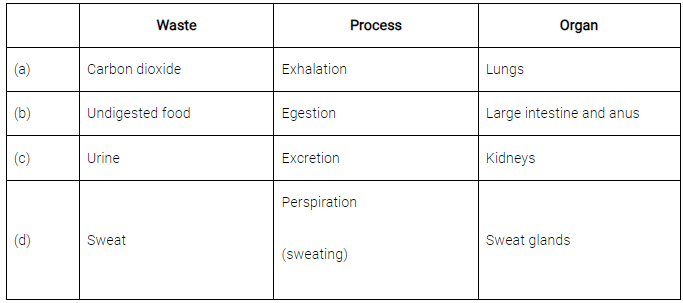
Q14: What is the special feature present in a human heart which does not allow mixing of blood when oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood reach the heart?
Ans: In human, the heart has four chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria and the two lower chambers are called the ventricles. The partition between the chambers helps to avoid mixing up of blood rich in oxygen with the blood rich in carbon dioxide.
Q15: While learning to ride a bicycle, Boojho lost his balance and fell. He got bruises on his knees and it started bleeding. However, the bleeding stopped after sometime.
(a) Why did the bleeding stop?
(b) What would be the colour of the wounded area and why?
(c) Which type of blood cells are responsible for clotting of blood?
Ans:
(a) When a cut or wound starts bleeding after sometime, a clot is formed which plugs the cut and bleeding stops.
(b) Wounded area becomes dark red in colour due to clotting of blood.
(c) The blood clot is formed due to the presence of the cells called platelets in the blood.
Q16: The absorption of nutrients and exchange of respiratory gases between blood and tissues takes place in
(a) veins
(b) arteries
(c) heart
(d) capillaries
Ans: (d) capillaries
Q17: In which of the following parts of human body are sweat glands absent?
(a) Scalp
(b) Armpits
(c) Lips
(d) Palms
Ans: (c) Lips
Q18: In a tall tree which force is responsible for pulling water and minerals from the soil?
(a) Gravitational force
(b) Transportation force
(c) Suction force
(d) Conduction force
Ans: (c) Suction force
Q19: Why do doctor often holds our wrist when we go for a check up?
Ans: Doctor holds our wrist to count our pulse rate and to check whether it is normal or not.
Q20: What will happen if oxygenated and deoxygenated blood gets mixed?
Ans: Mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood will lead to less oxygen supply to the cells. Under oxygen deficient condition, cells will not perform normally which may adversely affect the organism as a whole.
Q21: Sponges and Hydra do not possess any circulatory system. How nutrients and oxygen is transported inside their body?
Ans: The water in which sponges and Hydra live brings food and oxygen as it enters their bodies. The water also carries away waste material and carbon dioxide as it moves out. Thus, these animals do not need a circulatory system.
Q22: Which feature of heart does not allow mixing of oxygen-rich blood with carbon dioxide-rich blood?
Ans: Heart is divided into four chambers and are protected with valves which prevent their backflow. Thus, these features prevent mixing of oxygen-rich blood with carbon-dioxide rich blood.
Q23: Why wall of right ventricle is thinner than that of the left ventricle?
Ans: This is because the left ventricle has to pump blood all the way around the body, but the right ventricle only has to pump it to the lungs.
Q24: Does artery always carries oxygen-rich blood?
Ans: No. Pulmonary artery carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from heart to the lungs.
Q25: Water from soil moves inside the root cell but never comes out from root cell to soil. Why?
Ans: Water always moves from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration. This process is called osmosis. Concentration of water is more in the soil compared to its concentration inside the root cell, so it move from soil to the root cell and not from root cell to the soil.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 7 HOTS Questions - Transportation in Animals and Plants
| 1. What are the main transportation systems in animals and how do they function? |  |
| 2. How do plants transport water and nutrients? |  |
| 3. What role does the heart play in the transportation system of animals? |  |
| 4. How does the process of transpiration assist in the transport of water in plants? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between xylem and phloem in plants? |  |

















