Class 7 Science Chapter 13 HOTS Questions - Wastewater Story
Q1: State beneficial activity of microbes in sewage disposal.
Answer: Microbes present in sewage water help to digest organic matter present in it and thus purifying water aerobically. Anaerobic microbes help in digestion of sludge into useful manures.
Q2: How the terms sewage, sewers and sewerage are interlinked to each other?
Answer: Sewage is the wastewater coming from houses and other places. Sewers are the pipes which carry sewage whereas network of sewers, manholes, pumping stations, drains, etc. form sewerage.
Q3: What is effluent?
Answer: Effluent is a liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea.
Q4: What are the common symptoms of water-borne diseases?
Answer: Common symptoms of water-borne diseases are vomiting, stomachache, diarrhoea, fever, loss of appetite, etc.
Q5: Why should we not throw
(a) Cooking oils and fats down the drains?
(b) Cotton buds, napkins and nappies down the toilets?
Answer:
(a) Cooking oils and fats can harden and block the pipes.
(b) Cotton buds, napkins and nappies are flushed with difficulties and are not easily degradable. They can block the drains.
Q6: The Eucalyptus trees are planted along sewage ponds. Give reason.
Answer: The Eucalyptus trees are planted along sewage ponds because these trees absorb all surplus wastewater rapidly and release pure water vapour into the atmosphere.
Q7: Bleaching powder is mixed in water, why? Think and give appropriate reason for it.
Answer: Bleaching powder is mixed in water to make it safe for drinking because it kills the harmful germs present in water.
Q8: In the chemical process of water treatment, water is treated with some chemicals. Describe chlorination in light of it.
Answer: Chlorination is the process of adding chlorine (chemical) in water to make it safe for drinking.
Q9: Water in a river is cleaned naturally. Do you agree? Think and explain.
Answer: Yes, river water is cleaned naturally by a process that is similar to wastewater treatment plant. As muddy water when flows through grass or weeds on its way to a stream, mud and solid particles get filtered out. At the bottom of a lake or stream, microorganism brings chemical changes in the water. The natural filtration process removes pollution from the roundwater throughout the process making it clean and fit for drinking.
Q10: A sewage treatment plant involves few steps in its working.
Aeration tank, grit and sand removal tank, second sedimentation tank, bar screen, first sedimentation tank.
(a) Arrange all the above steps in the correct order in which they occur in the sewage treatment plant.
(b) Which step gives most of the sludge?
Answer:
(a) Bar screen, grit and sand removal tank, first sedimentation tank, aeration tank, second sedimentation tank.
(b) First sedimentation tank.
Q11: A man travelling in a train threw an empty packet of food on the platform. Do you think this is a proper waste disposal method? Elaborate.
Answer:
- No, one must always put the waste in a nearby dustbin or carry it home and dispose it in dustbins there.
- Waste, not properly disposed may enter into the drains and choke them. It also makes public places dirty and unhygienic.
Q12: Observe the given figure and answer the following:
(a) What does this figure show?
(b) State the functions of each part of the figure?
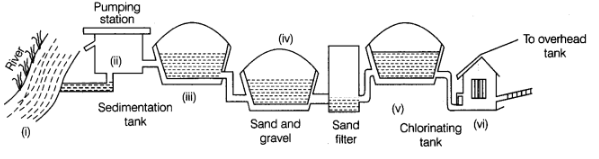
Answer:
(a) This figure shows the supply of drinking water, its processing and its source as well. Functions of each part of the figure.
(b)
- River It is the source of water.
- Pumping station Pump the water to collect it in reservoir.
- Sedimentation tank Impurities are settle in the bottom of tank.
- Sand and gravel and sand filter Remove the dirt from the water.
- Chlorinating tank Chlorine is mixed in water to disinfect the eater and to kill the germs.
- To overhead tank Purified water is stored in this tank for supply to the households for drinking.
Q13: There are many alternative sewage disposal systems which have been developed as per needs of the community, persons, occasions, etc.. Few situations/specifications of the sewage need are given below. Write the name of sewage which can be used in the following conditions.
(a) A toilet which can provide high quality manure.
(b) The toilet which is used in aeroplane during flight.
(c) A toilet which can be used in some out door gathering.
(d) A toilet used in limited water supply.
(e) A toilet which contaminates water of hand pump installed nearby.
Answer:
(a) Vermi-composting toilets
(b) Vacuum toilets
(c) Chemical toilets
(d) Composting toilets
(e) Septic tank toilets
Q14: Name two inorganic impurities present in sewage.
Answer: Inorganic impurities present in sewage are nitrates and phosphates.
Q15: Animal waste, oil and urea are some of the organic impurities present in sewage. Name two more organic impurities present in sewage.
Answer: Fruits and vegetable wastes, pesticides and herbicides are organic impurities present in sewage other than animal wastes, oil and urea.
Q16: The terms sewage, sewers and sewerage are interlinked with each other. Can you explain, how?
Answer: The terms like sewage, sewers and sewerage are interlinked with each other because sewage is a mixture of wastewater coming out of homes and other places. Sewers are pipes which carry sewage and sewerage is a network of sewage carrying pipes.
Q17: Give reasons for each of the following.
(a) We should not throw used tea leaves into sink.
(b) We should not throw cooking oil and fats down the drain.
Answer:
(a) We should not throw used tea leaves into sink because it may choke the drain-pipe of the sink.
(b) We should not throw cooking oil and fats down the drain as it can harden and block the drain-pipes.
Q18: Three statements are provided here which define the terms, i.e. sludge, sewage and wastewater.
Pick out the correct definition for each of these terms.
(a) The settled solids that are removed in wastewater treatment with a scraper.
(b) Water from kitchen used for washing dishes.
(c) Wastewater released from homes, industries, hospitals and other public buildings.
Answer:
(a) The settled solids that are removed in wastewater treatment with a scraper is sludge.
(b) Water from kitchen which is used for washing dishes is wastewater.
(c) Wastewater released from homes, industries, hospitals and other public buildings is sewage.
Q19: Open drain system is a breeding place for which of the following?
(a) Flies
(b) Mosquitoes
(c) Organisms which cause diseases
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Q20: Sewage is mainly a
(a) liquid waste
(b) solid waste
(c) gaseous waste
(d) mixture of solid and gas
Answer: (a) liquid waste
Q21: Which of the following is/are products of wastewater treatment?
(a) Biogas
(b) Sludge
(c) Both biogas and sludge
(d) Aerator
Answer: (c) Both biogas and sludge
Q22: The system of a network of pipes used for taking away wastewater from homes or public buildings to the treatment plant is known as
(a) sewers
(b) sewerage
(c) transport system
(d) treatment plant
Answer: (b) sewerage
Q23: Which of the following is a part of inorganic impurities of the sewage?
(a) Pesticides
(b) Urea
(c) Phosphates
(d) Vegetable waste
Answer: (c) Phosphates
Q24: True / False
(ii) Sewage is a solid waste which causes water pollution and soil pollution.
(ii) Where underground sewerage systems and refuse disposal systems are not available, the high cost onsite sanitation system can be adopted.
Ans:
(i) False, sewage is a liquid waste which causes water pollution and soil pollution.
(ii) False, where underground sewerage systems and refuse disposal systems are not available, the low cost onsite sanitation system can be adopted.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 13 HOTS Questions - Wastewater Story
| 1. What is wastewater? |  |
| 2. How is wastewater treated? |  |
| 3. Why is wastewater treatment important? |  |
| 4. Can wastewater be reused? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges in wastewater management? |  |
















