Half-Yearly Class 7 Science Set 1 (Solutions) | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections: A, B, C, and D.
(ii) All questions are compulsory.
(iii) Section A: Questions 1 to 15 are multiple-choice questions, carrying 1 mark each. Select the most appropriate response.
(iv) Section B: Questions 16 to 22 are short-answer questions, carrying 2 marks each.
(v) Section C: Questions 23 to 31 are short-answer questions, carrying 4 marks each.
(vi) Section D: Questions 32 to 34 are short-answer questions, carrying 5 marks each.
(vii) Answer the questions in the space provided or on a separate answer sheet as instructed.
(viii) Use of calculators is not permitted.
Section A
Q1. What is the first step in a scientific investigation? (1 mark)
(a) Making guesses
(b) Observing and asking questions
(c) Ignoring observations
(d) Drawing conclusions
Ans: (b)
Sol: A scientific investigation begins with observing phenomena and asking questions to understand them.
Q2. A substance that turns blue litmus paper red is: (1 mark)
(a) Basic
(b) Salty
(c) Neutral
(d) Acidic
Ans: (d)
Sol: An acidic substance turns blue litmus paper red.
Q3. In an electric circuit, the component that provides energy is: (1 mark)
(a) Switch
(b) Bulb
(c) Battery
(d) Wire
Ans: (c)
Sol: The battery provides electrical energy to the circuit.
Q4. Which of the following is a non-metal? (1 mark)
(a) Iron
(b) Sulphur
(c) Aluminium
(d) Copper
Ans: (b)
Sol: Sulphur is a non-metal, while iron, aluminium, and copper are metals.
Q5. Burning of a candle is an example of: (1 mark)
(a) Physical change
(b) Chemical change
(c) Reversible change
(d) Temporary change
Ans: (b)
Sol: Burning of a candle involves a chemical reaction, producing new substances like carbon dioxide and water.
Q6. Which hormone is responsible for growth spurts during adolescence? (1 mark)
(a) Insulin
(b) Growth hormone
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Thyroxine
Ans: (b)
Sol: Growth hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland, is responsible for growth spurts during adolescence.
Q7. The reaction between an acid and a base produces: (1 mark)
(a) Salt and water
(b) Sugar and water
(c) Acid and salt
(d) Base and water
Ans: (a)
Sol: Neutralization between an acid and a base produces a salt and water.
Q8. In an electric circuit, the lamp glows only when:
(a) The filament is broken
(b) The circuit is complete
(c) Only one wire is connected
(d) The cell is kept open
Ans: (b)
Sol: The lamp glows only when the circuit is complete, allowing electric current to flow through the filament.
Q9. Which non-metal is essential for breathing? (1 mark)
(a) Carbon
(b) Sulphur
(c) Oxygen
(d) Phosphorus
Ans: (c)
Sol: Oxygen, a non-metal, is essential for breathing.
Q10. Which of the following is a physical change that occurs while burning a candle? (1 mark)
(a) Formation of carbon dioxide
(b) Melting of wax
(c) Burning of the wick
(d) Production of heat and light
Ans: (b)
Sol: Melting of wax is a physical change because no new substance is formed.
Q11. Which of the following is a reversible change? (1 mark)
(a) Baking a cake
(b) Melting of wax
(c) Rusting of iron
(d) Burning of wood
Ans: (b)
Sol: Melting of wax is a reversible physical change, as it can solidify again.
Q12. The change in voice during adolescence in boys is due to: (1 mark)
(a) Growth of muscles
(b) Lengthening of vocal cords
(c) Increase in height
(d) Change in diet
Ans: (b)
Sol: The voice change in boys is due to the lengthening of vocal cords during adolescence.
Q13. Which material is a good conductor of electricity? (1 mark)
(a) Rubber
(b) Plastic
(c) Copper
(d) Wood
Ans: (c)
Sol: Copper is a good conductor of electricity, unlike rubber, plastic, or wood.
Q14. An indicator used to identify acids and bases is: (1 mark)
(a) Sugar solution
(b) Salt solution
(c) Turmeric
(d) Distilled water
Ans: (c)
Sol: Turmeric changes color in the presence of a base (yellow to reddish-brown) but does not change in acids.
Q15. Which of the following is a chemical change? (1 mark)
(a) Tearing of paper
(b) Cooking of food
(c) Boiling of water
(d) Folding of paper
Ans: (b)
Sol: Cooking of food involves chemical changes, forming new substances.
Section B
Q16. What is meant by a scientific investigation? Give one example. (2 marks)
Ans: A scientific investigation is a process of exploring natural phenomena through observation, questioning, and experimentation to find answers.
Example: Observing why iron nails rust in water and conducting an experiment to test the effect of moisture on rusting.
Q17. Name two substances that are acidic and two that are basic, found at home. (2 marks)
Ans:
- Acidic: Lemon juice, vinegar
- Basic: Baking soda, soap solution
Q18. Draw a simple electric circuit diagram showing a battery, bulb, and switch. (2 marks)
Ans:
Draw a battery (long and short line), a bulb (circle with a loop inside), a switch (open/close symbol), and connecting wires in a closed loop.
Q19. List one physical property each of a metal and a non-metal. (2 marks)
Ans:
- Metal: Shiny (lustrous), e.g., copper.
- Non-metal: Dull (non-lustrous), e.g., sulphur.
Q20. Differentiate between a physical change and a chemical change with one example each. (2 marks)
Ans:
- Physical change: A change that affects only the physical properties (shape, size, state) without forming new substances.
Example: Melting of ice.- Chemical change: A change that forms new substances with different properties.
Example: Burning of paper.
Q21. Name two secondary sexual characteristics that appear in girls during adolescence. (2 marks)
Ans:
- Development of breasts
- Widening of hips
Q22. Why is Aluminium used to make cooking utensils? (2 marks)
Ans: Aluminium is used because it is a good conductor of heat, allowing even cooking, and it is lightweight, making utensils easy to handle.
Section C
Q23. Explain how you can use litmus paper to test whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral. (4 marks)
Ans:
- Take a small amount of the substance (liquid or solution).
- Dip blue litmus paper into it: If it turns red, the substance is acidic.
- Dip red litmus paper into it: If it turns blue, the substance is basic.
- If neither litmus paper changes color, the substance is neutral.
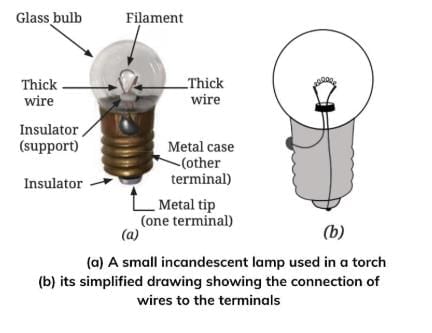
Q24.Explain the structure and working of an incandescent lamp with the help of a neat diagram. Why does the lamp stop glowing when the filament breaks? (4 marks)
Ans: An incandescent lamp has a glass bulb with a thin wire called a filament inside. The filament is supported by two thicker wires. These wires are connected to two terminals—one at the metal case of the base and the other at the metal tip in the center.
When electric current passes through the filament, it becomes very hot and starts glowing, which produces light. The lamp works even if the positive and negative terminals of the cell are connected in any way.
If the filament breaks, the circuit becomes incomplete, so the current cannot flow. This makes the lamp fuse and it stops glowing.
Q25. List two physical and two chemical properties of metals with examples. (4 marks)
Ans:
Physical properties:
- Malleability: Metals can be beaten into sheets, e.g., aluminium foil.
- Conductivity: Metals conduct electricity, e.g., copper wires.
Chemical properties:
- Reaction with oxygen: Metals form oxides, e.g., iron forms rust (iron oxide).
- Reaction with acids: Metals produce hydrogen gas, e.g., zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Q26. What is rusting? Describe two methods to prevent the rusting of iron. (4 marks)
Ans: Rusting: Rusting is a chemical process where iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form iron oxide (rust).
Prevention methods:
- Painting: Coating iron with paint prevents contact with air and moisture.
- Galvanization: Coating iron with zinc protects it from rusting.
Q27. Explain four physical changes that occur in boys during adolescence. (4 marks)
Ans:
- Growth spurt: Rapid increase in height and weight.
- Voice change: Deepening of voice due to lengthening of vocal cords.
- Facial hair growth: Appearance of beard and mustache.
- Muscle development: Increased muscle mass and strength.
Q28. What is neutralisation? Write the chemical equation for the reaction between sulphuric acid and sodium hydroxide. (4 marks)
Ans:
- Neutralization: It is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt and water.
- Chemical equation: H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Q29. Explain with the help of a diagram how an electric circuit makes a lamp glow. What will happen if the circuit is not connected properly? (4 marks)
Ans:
The two terminals of the electric cell are connected to the two terminals of the lamp using wires.
When the circuit is complete, electric current flows from the negative terminal of the cell, passes through the wires and the filament of the lamp, and returns to the positive terminal of the cell.
The filament becomes hot and starts glowing, which produces light.
If the circuit is not connected properly (e.g., loose wire or open connection), the current does not flow and the lamp will not glow.
Q30. Why are non-metals important? Give two examples of non-metals and their uses in daily life. (4 marks)
Ans: Importance: Non-metals are essential for life, used in industries, and form compounds vital for biological processes.
Examples and uses:
- Oxygen: Used for breathing and in medical oxygen supplies.
- Carbon: Found in fuels (coal) and used in pencils (graphite).
Q31. What is weathering of rocks? Differentiate between physical and chemical weathering with examples.(4 marks)
Ans:
Weathering of Rocks: It is the process in which rocks break down into smaller pieces due to physical or chemical changes, resulting in the formation of soil.
Physical Weathering: Rocks break into smaller pieces because of temperature changes, the action of tree roots, or water freezing in cracks.
Example: Sand, soil, and stones collect at the base of mountains.Chemical Weathering: The chemical composition of rocks changes when water or other chemicals react with them.
Example: Basalt rock reacts with water or air to form a red layer of iron oxide, similar to rust.
Section D
Q32. (a) Explain the importance of observation in a scientific investigation. (3 marks)
(b) Describe an activity to observe the effect of heat on a candle, identifying physical and chemical changes. (2 marks)
Ans: (a) Importance of observation: Observation is crucial as it helps identify patterns, ask questions, and collect data to understand natural phenomena. It forms the basis for further investigation and experimentation.
(b) Activity:
- Light a candle and observe its behavior.
- Physical change: Wax melts due to heat, changing from solid to liquid (reversible upon cooling).
- Chemical change: Wax burns, reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat (irreversible).
- Record observations of melting wax and burning flame.
Q33. (a) What is adolescence? Explain the role of hormones in physical changes during this stage. (3 marks)
(b) Discuss two emotional changes during adolescence and suggest ways to cope with them. (2 marks)
Ans: (a) Adolescence: The period of transition from childhood to adulthood, typically between 11–18 years, marked by physical and emotional changes.
Role of hormones: Growth hormone causes height increase, sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen) lead to secondary sexual characteristics like voice change in boys and breast development in girls.
(b) Emotional changes and coping:
- Mood swings: Due to hormonal changes.
Coping: Talk to trusted adults, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing.- Peer pressure: Desire to fit in.
Coping: Build self-confidence, choose supportive friends.
34. (a) Compare metals and non-metals based on their physical properties (at least four points). (3 marks)
(b) Explain the process of galvanisation and its role in preventing corrosion. (2 marks)
Ans: (a) Comparison:
- Lustre: Metals are shiny (e.g., copper); non-metals are dull (e.g., sulphur).
- Malleability: Metals can be beaten into sheets (e.g., aluminium); non-metals are brittle (e.g., carbon).
- Conductivity: Metals conduct electricity (e.g., copper); non-metals do not (e.g., plastic).
- Ductility: Metals can be drawn into wires (e.g., iron); non-metals cannot (e.g., sulphur).
(b) Galvanization: Coating iron with a layer of zinc to prevent rusting. Zinc acts as a protective barrier, preventing iron from reacting with oxygen and moisture. Even if scratched, zinc corrodes first, protecting the iron.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Half-Yearly Class 7 Science Set 1 (Solutions) - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What topics are likely covered in the Half-Yearly Science Question Paper for Class 7? |  |
| 2. How can students prepare effectively for the Half-Yearly Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can be expected in the Class 7 Science exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific strategies to tackle difficult science questions during the exam? |  |
| 5. How important is it to understand scientific concepts rather than rote memorization for the exam? |  |