High Courts - Composition, Jurisdiction and Powers | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| High Court Jurisdiction |

|
| Eligibility Criteria for High Court Judge |

|
| Salary and Perks of High Court Judges |

|
| Powers and Functions of the High Court |

|
| High Court Powers |

|
Introduction
The highest judicial court in a state is the High Court. It is termed as the second-highest in the country after Supreme Court of India. Currently, India has 25 High Courts established in different states of the country.
How many High Courts are there in India?
There are 25 High Courts in India:
- It was in 1858 when on the recommendation of the Law Commission, the Parliament passed the Indian High Courts Act 1861 which suggested the establishment of High Courts in place of Supreme Court in three Presidencies: Calcutta, Madras and Bombay. The Charter of High Court of Calcutta was ordered in May 1862 and that of Madras and Bombay were order in June 1862. Thereby, making the Calcutta High Court the first High Court of the country.
- The reason for the implementation of this act was the need for a separate judiciary body for different states. The British Government, therefore, decided to abolish the then-existing Supreme Court and Sadar Adalat and replaced it with High Court.
- Certain rules and eligibility criteria were set for the appointment of a Judge in any High Court and later after independence as per Article 214 of the Indian Constitution, it was declared that every Indian state must have their own High Court.
- The British created laws were different from the ones that were stated in the Indian Penal code and the entire legal system of the country changed after the independence of the country.
Which is the Newest High Court of India?
Andhra Pradesh is the recent state to have the High Court. High Court was established in Andhra Pradesh on 1st January 2019.
Constitution of High Court – Under the British rule, each High Court has a Chief Justice and maximum 15 other puisne judges. But later certain changes were brought about in the composition of the High Court in India:
- Every High Court shall have a Chief Justice appointed by the President
- Unlike before, there was no fixed number of Judges who could be appointed for each High Court
- Additional Judges can also be appointed for the clearance of cases pending in the court. But their tenure cannot exceed more than two years
One thing that must be noted is that no one above the age of 62 years can be appointed as a High Court Judge. There is no uniformity among the High Courts regarding the number of Judges they will have. A smaller state shall have less number of judges in comparison to a larger state.
High Court Jurisdiction
The jurisdictions of a High Court are as mentioned below:
- Original Jurisdiction – In such kind of cases the applicant can directly go to the High Court and does not require to raise an appeal. It is mostly applicable for cases related to the State Legislative Assembly, marriages, enforcement of fundamental rights and transfer cases from other courts.
- Power of Superintendence – It a special power enjoyed only by High Court and no other subordinate court has this power of superintendence. Under this, the High Court holds the right to order its subordinate offices and courts the way of maintaining records, prescribe rules for holding proceedings in the court and also settle the fees paid to sheriff clerks, officers and legal practitioners.
- Court of Record – It involves recording the judgments, proceedings and acts of high courts for perpetual memory. These records cannot be further questioned in any court. It has the power to punish for contempt of itself.
- Appellate Jurisdiction – This is for cases where people have risen a complaint about a review of the judgement given by the district level or subordinate court of that territory. This power is further divided into two categories:
- Civil Jurisdiction – this includes orders and judgements of the district court, civil district court and subordinate court
- Criminal Jurisdiction – this includes judgements and orders of the sessions court and additional sessions court.
How is a High Court Judge Appointed?
A High Court Judge is appointed by the President of India. He is solely responsible for the appointment of any judge in a High Court. However, he may consult the Governor of the State, the acting Chief Justice of India and Chief Justice of that particular state’s High Court.
A High Court judge is also liable to get transferred to other High Courts. This decision is entirely dependent on the Chief Justice of India. Transfer of judges is done with an aim to ensure proper and just trial for every case fought in the court of law.
Eligibility Criteria for High Court Judge
There are certain eligibility criteria that need to be fulfilled to be appointed as a judge in any High court in India. Given below are the set of eligibility criteria mandatory for the appointment of High Court judges:
- Any of the given qualifications must be fulfilled:
- The person should have been a Barrister for more than five years
- Has been a civil servant for over 10 years along with serving the Zila court for at least 3 years
- A person who has been a pleader for over 10 years in any High Court.
- No judge should be of more than 62 years of age
The law states that every state must have a separate High Court, however, there still are certain states that do not have an individual High Court. For example – both Punjab and Haryana come under the jurisdiction of Punjab High Court sitting at Chandigarh. Besides, there is a common High Court for seven states – Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Salary and Perks of High Court Judges
There has been a massive increase in the salary paid to a High Court judge. The table below gives the salary description of a judge in the High Court:
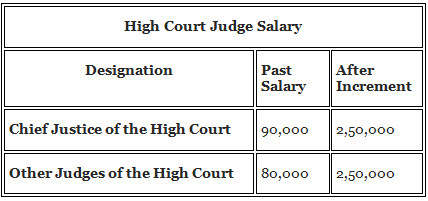
Apart from the salary, there are various other perks and allowances provided to a Judge in High Court.
Powers and Functions of the High Court
The High Court is the highest court in a state in India. Articles 214 to 231 in the Indian Constitution talk about the High Courts, their organisation and powers. The Parliament can also provide for the establishment of one High Court for two or more states.
For instance, Haryana, Punjab and the Union Territory of Chandigarh have a common High Court. The northeastern states also have one common High Court. In addition, Tamil Nadu shares a High Court with Puducherry.
Currently, there are 25 High Courts in India.
The High Courts of Calcutta, Madras and Bombay were established by the Indian High Courts Act 1861.
What are the functions of the High Court?
The functions of the High Court are described in the below section under subsections such as its jurisdiction, powers, role, etc.
High Court Jurisdiction
The various kinds of the jurisdiction of the High Court are briefly given below:
Original Jurisdiction
- The High Courts of Calcutta, Bombay and Madras have original jurisdiction in criminal and civil cases arising within these cities.
- An exclusive right enjoyed by these High Courts is that they are entitled to hear civil cases which involve property worth over Rs. 20000.
- Regarding Fundamental Rights: They are empowered to issue writs in order to enforce fundamental rights.
- With respect to other cases: All High Courts have original jurisdiction in cases that are related to will, divorce, contempt of court and admiralty.
- Election petitions can be heard by the High Courts.
Appellate Jurisdiction
- In civil cases: an appeal can be made to the High Court against a district court’s decision.
- An appeal can also be made from the subordinate court directly if the dispute involves a value higher than Rs. 5000/- or on a question of fact or law.
- In criminal cases: it extends to cases decided by Sessions and Additional Sessions Judges.
- If the sessions judge has awarded imprisonment for 7 years or more.
- If the sessions judge has awarded capital punishment.
- The jurisdiction of the High Court extends to all cases under the State or federal laws.
- In constitutional cases: if the High Court certifies that a case involves a substantial question of law.
High Court Powers
Apart from the above, the High Courts have several functions and powers which are described below.
As a Court of Record
- High Courts are also Courts of Record (like the Supreme Court).
- The records of the judgements of the High Courts can be used by subordinate courts for deciding cases.
- All High Courts have the power to punish all cases of contempt by any person or institution.
Administrative Powers
- It superintends and controls all the subordinate courts.
- It can ask for details of proceedings from subordinate courts.
- It issues rules regarding the working of the subordinate courts.
- It can transfer any case from one court to another and can also transfer the case to itself and decide the same.
- It can enquire into the records or other connected documents of any subordinate court.
- It can appoint its administration staff and determine their salaries and allowances, and conditions of service.
Power of Judicial Review
High Courts have the power of judicial review. They have the power to declare any law or ordinance unconstitutional if it is found to be against the Indian Constitution.
Power of Certification
A High Court alone can certify the cases fit for appeal before the Supreme Court.
High Court Autonomy
The independence of the High Courts can be corroborated by the points given below:
- Appointment of Judges: The appointment of judges of the High Courts lies within the judiciary itself and is not connected to the legislature or the executive.
- Tenure of the Judges: High Court judges enjoy the security of tenure till the age of retirement, which is 62 years. A High Court cannot be removed except by an address of the President.
- Salaries and allowances: The High Court judges enjoy good salaries, perks and allowances and these cannot be changed to their disadvantage except in case of a financial emergency. The expenses of the High Court are charged on the Consolidated Fund of the State, which is not subject to vote in the state legislature.
- Powers: The Parliament and the state legislature cannot cut the powers and jurisdiction of the High Court as guaranteed by the Constitution.
- Conduct of judges: Unless a motion of impeachment has been moved, the conduct of the High Court judges cannot be discussed in the Parliament.
- Retirement: After retirement, High Court judges cannot hold an office of emolument under the Government of India or that of a state. There is an exception to this clause, however, when, with the consent of the Chief Justice of India, retired judges can be nominated to a temporary office, and in the situation of emergencies.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on High Courts - Composition, Jurisdiction and Powers - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the composition of High Courts in India? |  |
| 2. What is the jurisdiction of High Courts in India? |  |
| 3. What are the powers of High Courts in India? |  |
| 4. How are the judges of High Courts appointed? |  |
| 5. Can High Courts hear cases against decisions of lower courts? |  |




















