Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN) Scheduling Algorithm | Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
HRRN(Highest Response Ratio Next )Scheduling is a non-preemptive scheduling algorithm in the operating system. It is one of the optimal algorithms used for scheduling.
As HRRN is a non-preemptive scheduling algorithm so in case if there is any process that is currently in execution with the CPU and during its execution, if any new process arrives in the memory with burst time smaller than the currently running process then at that time the currently running process will not be put in the ready queue & complete its execution without any interruption.
HRRN is basically the modification of Shortest Job Next(SJN) in order to reduce the problem of starvation.
In the HRRN scheduling algorithm, the CPU is assigned to the next process that has the highest response ratio and not to the process having less burst time.
Now, let us first take a look at how to calculate the Response ratio.
Response Ratio = (W+S)/S
Where,
W=It indicates the Waiting Time.
S=It indicates the Service time that is Burst Time.
Algorithm of HRNN
- In the HRNN scheduling algorithm, once a process is selected for execution will run until its completion.
- The first step is to calculate the waiting time for all the processes. Waiting time simply means the sum of the time spent waiting in the ready queue by processes.
- Processes get scheduled each time for execution in order to find the response ratio for each available process.
- Then after the process having the highest response ratio is executed first by the processor.
- In a case, if two processes have the same response ratio then the tie is broken using the FCFS scheduling algorithm.
Now it's time to take a look at an example for the same:
HRRN Scheduling Example
Here, we have several processes with different burst and arrival times, and a Gantt chart to represent CPU allocation time.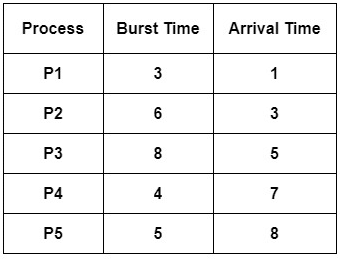
The Gantt Chart according to HRRN will be: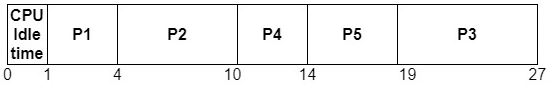
Explanation
Given below is the explanation of the above example
- At time = 0 there is no process available in the ready queue, so from 0 to 1 CPU is idle. Thus 0 to 1 is considered as CPU idle time.
- At time = 1, only the process P1 is available in the ready queue. So, process P1 executes till its completion.
- After process P1, at time = 4 only process P2 arrived, so the process P2 gets executed because the operating system did not have any other option.
- At time = 10, the processes P3, P4, and P5 were in the ready queue. So in order to schedule the next process after P2, we need to calculate the response ratio.
- In this step, we are going to calculate the response ratio for P3, P4, and P5.
Response Ratio = W+S/S
RR(P3) = [(10-5) +8]/8
= 1.625
RR(P4) = [(10-7) +4]/4
= 1.75
RR(P5) = [(10-8) +5]/5
= 1.4
From the above results, it is clear that Process P4 has the Highest Response ratio, so the Process P4 is schedule after P2.
- At time t=10, execute process P4 due to its large value of Response ratio.
- Now in the ready queue, we have two processes P3 and P5, after the execution of P4 let us calculate the response ratio of P3 and P5
RR (P3) = [(14-5) +8]/8
=2.125
RR (P5) = [(14-8) +5]/5
=2.2
From the above results,it is clear that Process P5 has the Highest Response ratio, so the Process P5 is schedule after P4
- At t = 14, process P5 is executed.
- After the complete execution of P5, P3 is in the ready queue so at time t=19 P3 gets executed.
In the table given below, we will calculate turn around time, waiting time, and completion time for all the Processes.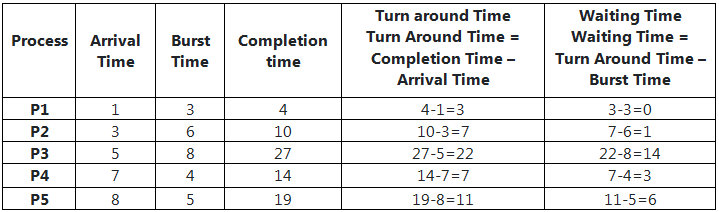
Average waiting time is calculated by adding the waiting time of all processes and then dividing them by no. of processes.
average waiting time = waiting time of all processes/ no.of processes
average waiting time = 0 + 1 + 14 + 3 + 6/5 = 24/5 = 4.8ms
HRRN Scheduling Example in C Language
Given below is the C program for HRRN Scheduling:
// C program for the Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN) Scheduling
#include <stdio.h>
// This structure defines the details of the process
struct process {
char name;
int at, bt, ct, wt, tt;
int complete;
float ntt;
} p[10];
int m;
//The Sorting of Processes by Arrival Time
void sortByArrival()
{
struct process temp;
int i, j;
// Selection Sort applied
for (i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < m; j++) {
// This condition is used to Check for the lesser arrival time
if (p[i].at > p[j].at) {
// Swaping of earlier process to front
temp = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
int i, j, t, sum_bt = 0;
char c;
float avgwt = 0, avgtt = 0;
m = 5;
// the predefined arrival times
int arriv[] = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 8 };
// the predefined burst times
int burst[] = { 3, 7, 8, 4, 2};
// Initialize the structure variables
for (i = 0, c = 'A'; i < m; i++, c++) {
p[i].name = c;
p[i].at = arriv[i];
p[i].bt = burst[i];
// Variable for Completion status
// for Pending = 0
// for Completed = 1
p[i].complete = 0;
// the Variable for the sum of all Burst Times
sum_bt += p[i].bt;
}
// Let us Sort the structure by the arrival times
sortByArrival();
printf("\nName\tArrival Time\tBurst Time\tWaiting Time");
printf("\tTurnAround Time\t Normalized TT");
for (t = p[0].at; t < sum_bt;) {
// Now Set the lower limit to response ratio
float hrr = -9999;
//The Response Ratio Variable
float temp;
// Variable used to store the next processs selected
int loc;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
// Check if the process has arrived and is Incomplete
if (p[i].at <= t && p[i].complete != 1) {
// Calculating the Response Ratio
temp = (p[i].bt + (t - p[i].at)) / p[i].bt;
// Checking for the Highest Response Ratio
if (hrr < temp) {
// Storing the Response Ratio
hrr = temp;
// Storing the Location
loc = i;
}
}
}
// Updating the time value
t += p[loc].bt;
// Calculation of the waiting time
p[loc].wt = t - p[loc].at - p[loc].bt;
// Calculation of the Turn Around Time
p[loc].tt = t - p[loc].at;
// Sum of Turn Around Time for the average
avgtt += p[loc].tt;
// Calculation of the Normalized Turn Around Time
p[loc].ntt = ((float)p[loc].tt / p[loc].bt);
// Updating the Completion Status
p[loc].complete = 1;
// Sum of the Waiting Time to calculate the average
avgwt += p[loc].wt;
printf("\n%c\t\t%d\t\t", p[loc].name, p[loc].at);
printf("%d\t\t%d\t\t", p[loc].bt, p[loc].wt);
printf("%d\t\t%f", p[loc].tt, p[loc].ntt);
}
printf("\nThe Average waiting time:%f\n", avgwt / m);
printf("The Average Turn Around time:%f\n", avgtt / m);
}
Output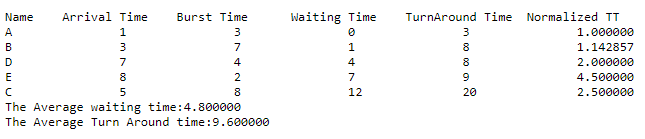
Advantages of HRNN Scheduling
The advantages of the HRNN scheduling algorithm are as follows:
- HRRN Scheduling algorithm gives better performance than the shortest job first Scheduling.
- With this algorithm, there is a reduction in waiting time for longer jobs and also it encourages shorter jobs.
- With this algorithm, the throughput increases.
Disadvantages of HRNN Scheduling
The disadvantages of the HRNN scheduling algorithm are as follows:
- The Practical implementation of HRRN scheduling is not possible because we cannot know the burst time of every process in advance.
- In this scheduling, there may occur overhead on the processor.
|
10 videos|144 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN) Scheduling Algorithm - Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is the Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN) scheduling algorithm? |  |
| 2. How does the HRRN algorithm improve upon traditional scheduling methods? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using the HRRN scheduling algorithm? |  |
| 4. Are there any disadvantages to the HRRN scheduling algorithm? |  |
| 5. In what scenarios is the HRRN scheduling algorithm most effective? |  |
















