Year 3 Exam > Year 3 Notes > Year 3 Computing > How do search engines work?
How do search engines work? | Year 3 Computing PDF Download
Searching the world wide web
- The World Wide Web consists of nearly 2 billion websites.
- Each website has a unique URL, or web address.
- You are familiar with the URLs of some of your favorite webpages, which you use to visit them.

What are search engines?
- A search engine is a program that locates webpages on the internet.
- You enter the words you want information about.
- The search engine searches for webpages containing that information.
Question for How do search engines work?Try yourself: What is a search engine?View Solution
How do search engines work?
- A search engine is similar to a librarian.
- At the library, you can ask a librarian to find books on your favorite topic.
- The librarian searches through an index to locate the books.
- The index contains key details about each book in the library.
- The librarian then provides you with the titles of the books they found.
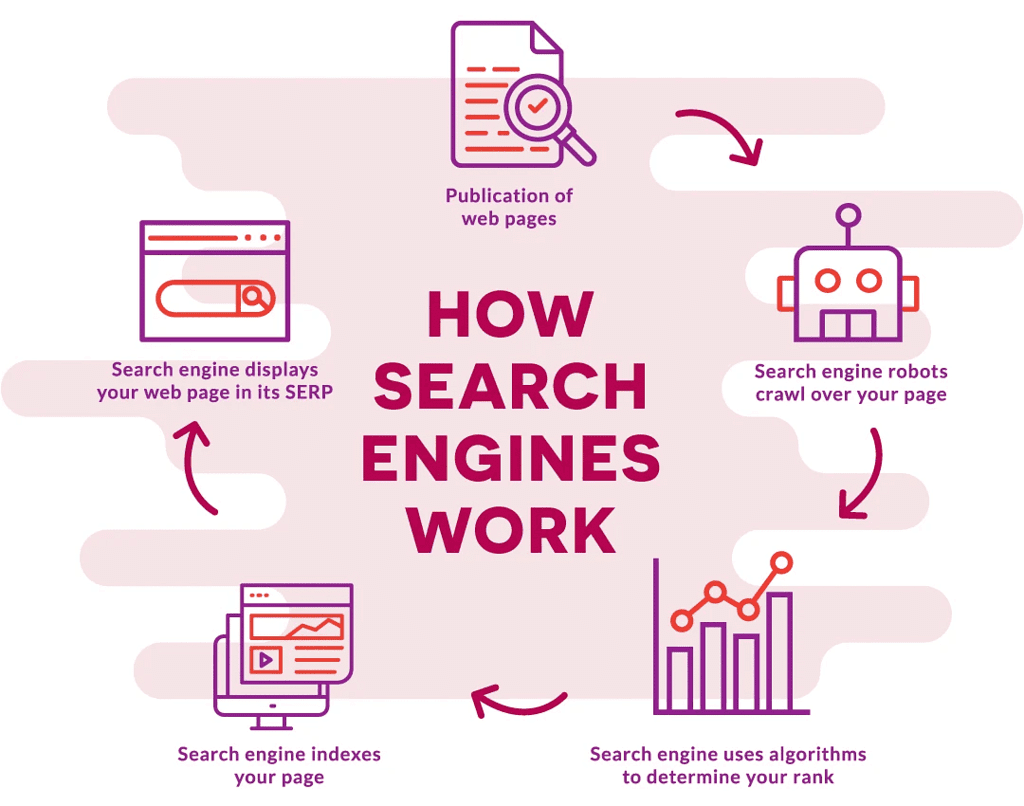
How a search engine works?
- You enter keywords or a question into the search engine.
- The program searches the index for webpages related to your keywords or question.
- The program determines which pages are most useful to you.
- The program ranks the webpages, placing the most useful at the top.
- The search engine displays the webpages it has found for you.
Are all search engines the same?
- Function of Search Engines: Search engines play a vital role in helping us find information on the internet. They work by allowing users to input keywords or questions, which the search engine then uses to locate relevant webpages.
- Diversity Among Search Engines: Not all search engines are identical; they have individual features and specialties. Some search engines focus on specific types of content like news, facts, or images, while others cater to a younger audience by filtering out inappropriate material.
- Search Strategies: Effective searching involves using the right keywords. For instance, searching for "Wellington" could yield results related to the capital city of New Zealand, Wellington boots, or a type of food.
- Capital city of New Zealand
- Wellington boots
- Type of food
- Enhancing Search Precision: To refine search results, additional keywords can be added. For example, typing "Wellington, New Zealand" can provide more accurate and targeted information.
- Specialized Search Engines: Some search engines are designed for specific purposes, such as searching for news, images, or educational content. These specialized search engines can provide tailored results based on the user's needs.
How Search Engines Create an Index?
- A search engine creates an index using a web crawler.
- A web crawler is an automated program that browses the web and collects information about the webpages it visits.
- Each time a web crawler visits a webpage, it copies the page and adds the URL to the index.
- It also includes details of the page content, keywords, and types of media.
- When you enter words into a search engine, it searches its index for matches to your words.

Question for How do search engines work?Try yourself: How do search engines create an index of webpages?View Solution
How do search engines order results?
- Search engines use algorithms to rank the list of webpages they return.
- The webpages at the top of the list are typically the most useful to you. All these webpages have been visited by the search engine’s web crawlers.
- So, when you use a search engine to find information, remember that web crawlers created an index and an algorithm ranked the results.
The document How do search engines work? | Year 3 Computing is a part of the Year 3 Course Year 3 Computing.
All you need of Year 3 at this link: Year 3
|
13 videos|26 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on How do search engines work? - Year 3 Computing
| 1. What are search engines? |  |
Ans. Search engines are software programs that help users find information on the internet by searching for keywords or phrases and returning relevant websites or documents.
| 2. How do search engines work? |  |
Ans. Search engines work by crawling the web to find content, indexing that content, and then ranking it based on relevancy to a user's search query. They use algorithms to determine the most relevant results.
| 3. Are all search engines the same? |  |
Ans. No, not all search engines are the same. Different search engines may use different algorithms, have different crawlers, and prioritize results differently, leading to variations in search results.
| 4. How do search engines create an index? |  |
Ans. Search engines create an index by crawling the web, analyzing the content of websites, and then storing that information in a database. This index is used to quickly retrieve relevant results for user queries.
| 5. How do search engines order results? |  |
Ans. Search engines order results based on a combination of factors, including the relevance of the content to the search query, the authority of the website, and the quality of the content. The most relevant and trustworthy results are usually displayed at the top of the search results page.
Related Searches















