Humidity: Relative Humidity & Dew point | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download
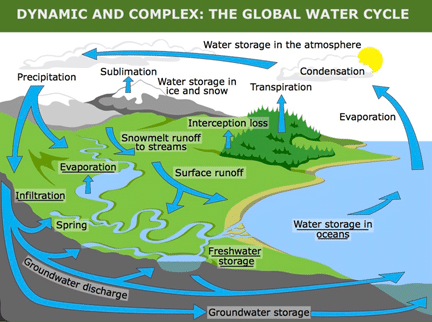
WATER CYCLE – HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE
- There is a continuous exchange of water between the atmosphere, the oceans and the continents through the processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation and precipitation.
- The moisture in the atmosphere is derived from water bodies through evaporation and from plants through transpiration (evapotranspiration).
- Evaporated water undergoes condensation and forms clouds.
- When saturation is reached, clouds give away water in the form of precipitation.
- Since the total amount of moisture in the entire system remains constant, a balance is required between evapotranspiration and precipitation. The hydrological cycle maintains this balance.
WATER VAPOUR IN ATMOSPHERE
- Water vapour in air varies from zero to four per cent by volume of the atmosphere (averaging around 2% in the atmosphere). Amount of water vapour (Humidity) is measured by, an instrument called Hygrometer.
Significance of Atmospheric Moisture
- Water vapour absorbs radiation—both incoming and terrestrial. It thus plays a crucial role in the earth’s heat budget.
- The amount of water vapour present decides the quantity of latent energy stored up in the atmosphere for development of storms and cyclones.
- The atmospheric moisture affects the human body’s rate of cooling by influencing the sensible temperature.
Evaporation
- The oceans covering 71% of the earth’s surface hold 97% of all the earth’s water reserves.
- Evapotranspiration may be taken as the starting point in the hydrological cycle. The oceans contribute 84% of the annual total and the continents 16%.
- The highest annual evaporation occur in the sub-tropics of the western North Atlantic and North Pacific because of the influence of the Gulf Stream and the Kurishino Current, and in the trade wind zone of the southern oceans.
- The land maximum occurs in equatorial region because of high insolation and luxuriant
HUMIDITY
- Water vapour present in the air is known as Humidity.
➢ Absolute Humidity
- The actual amount of the water vapour present in the atmosphere is known as the absolute humidity.
- It is the weight of water vapour per unit volume of air and is expressed in terms of grams per cubic metre.
- The absolute humidity differs from place to place on the surface of the earth.
- The ability of the air to hold water vapour depends entirely on its temperature (Warm air can hold more moisture than cold air).
➢ Relative Humidity
- The percentage of moisture present in the atmosphere as compared to its full capacity at a given temperature is known as the relative humidity.
Relative Humidity = [Actual amount of water vapor in air (absolute humidity)/humidity at saturation point (the maximum water vapor air can hold at a given temperature)] X 100
- With the change of air temperature, the capacity to retain moisture increases or decreases and the relative humidity is also affected.
- Relative humidity is greater over the oceans and least over the continents (absolute humidity is greater over oceans because of greater availability of water for evaporation).
- The relative humidity determines the amount and rate of evaporation and hence it is an important climatic factor.
- Air containing moisture to its full capacity at a given temperature is said to be ‘saturated’. At this temperature, the air cannot hold any additional amount of moisture. Thus, relative humidity of the saturated air is 100%.
- If the air has half the amount of moisture that it can carry, then it is unsaturated and its relative humidity is only 50%.
Relative humidity can be changed in either of the two ways—
1. By adding moisture through evaporation (by increasing absolute humidity): If moisture is added by evaporation, the relative humidity will increase and vice versa.
2. By changing temperature of air (by changing the saturation point): A decrease in temperature (hence, decrease in moisture-holding capacity/decrease in saturation point) will cause an increase in relative humidity and vice versa.
- Consider 1 m3 of air at a temperature ‘T’.
- Let us assume that saturation occurs when 0.5 kg of water vapor is present in 1 m3 of air.
- That is, relative humidity will be 100% if 1 m3 of air contains 0.5 kg of water vapor at temperature T (saturation temperature or saturation point).
- Assume that 1 m3 of air at a given time consists of 0.2 kg of water vapor at a temperature ‘T’.
- Now the relative humidity = 40 % ===> 0.2 kg of water vapor per 1 m3 of air ===> the air can still hold 0.3 kg of water vapor since saturation occurs at 0.5 kg.
Here,
Absolute Humidity = 0.2 kg/ m3 and
Relative Humidity = 40 %
- So, relative humidity is expressed as % whereas absolute humidity is expressed in absolute terms.
- Now to make the air saturated (100 % relative humidity),
(i) We can add that additional 0.3 kg of water vapor by evaporation. OR
(ii) We can decrease the temperature. - If we decrease the temperature, the saturation point will come down.
- Let us assume that the temperature of 1 m3 of air is decreased by 2 °C. The water holding capacity will fall due to decrease in temperature. Let us assume that the water holding capacity decreases by 0.1 kg per m3 of air per 1 °C fall in temperature.
- So, for 2 °C fall in temperature, the fall in water holding capacity is 0.2 kg/m3 of air (0.1 kg/m3 x 2).
- Hence the new saturation point occurs at 0.3 kg/m3 of air [0.5 kg/m3 – 0.2 kg/m3].
- That is, the ‘new saturation point’ (relative humidity = 100%)” occurs when the water vapor content is 0.3 kg per 1 m3 of air.
- So now we can saturate 1 m3 of air by adding just 0.1 kg instead of 0.3 kg as in the earlier case.
[because, initially, we assumed that 1 m3 of air at a given time consists of 0.2 kg of water vapor at a temperature ‘T’.]
Dew point
- The air containing moisture to its full capacity at a given temperature is said to be saturated.
- It means that the air at the given temperature is incapable of holding any additional amount of moisture at that stage.
- The temperature at which saturation occurs in a given sample of air is known as dew point.
- Dew point occurs when Relative Humidity = 100%.
Specific Humidity
- It is expressed as the weight of water vapour per unit weight of air.
- Since it is measured in units of weight (usually grams per kilogram), the specific humidity is not affected by changes in pressure or temperature.
Absolute Humidity and Relative Humidity are Variable whereas Specific Humidity is a constant.
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Humidity: Relative Humidity & Dew point - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What is relative humidity and how is it measured? |  |
| 2. What is the dew point and why is it important in understanding humidity? |  |
| 3. How does relative humidity affect human comfort and health? |  |
| 4. How does relative humidity impact the weather and natural phenomena? |  |
| 5. How can relative humidity be controlled indoors for optimal comfort? |  |





















