Important Compounds of Sodium | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Sodium carbonate is an inorganic chemical compound. Sodium carbonate is what is commonly known as Soda ash. Soda ash is extracted from trona. Trona is a double salt containing sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate formed as a result of the series of evaporation processes taking place at lakes.
Sodium carbonate often called washing soda or soda ash is the most important of all basic heavy chemicals. Its great advantage over sodium hydroxide is that it is no-corrosive and is, therefore, safer to handle.
Sodium Carbonate Formula
Sodium carbonate is a diazonium salt of carbonic acid with chemical formula Na2CO3. It is also known as Soda crystals, soda ash, washing soda. This inorganic compound is water-soluble and when dissolved in water, it forms carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide. In its pure form, it is white powder and odourless. It is a strong base and acts as an antacid.
Sodium carbonate can be produced by four processes – “Solvay process, Labnac process, Dual-process, Electrolytic process”. Since it is a weak acid it is slightly soluble in ethanol and insoluble in alcohol. One of the important uses of Na2CO3 is as a water softener. pH is about 10.52
Synthesis of Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Sodium carbonate is now exclusively manufactured by the Solvay process. In this process carbon dioxide and ammonia are passed into a cold saturated solution of sodium chloride. In the reactions which occur sodium hydrogen carbonate is formed which is only very slightly soluble in the presence of sodium ions, is almost completely precipitated. It is removed by filtration and ignited to produce sodium carbonate.
The ingredients of this process are readily available and inexpensive. These are salt brine (NaCl), ammonia (NH3) and limestone (CaCO3). In this process, CaCl2 is an important by-product obtained.
The reactions can be represented by the following equation.
2NH3 + H2O + CO2 → (NH4)2CO3
(NH4)2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NH4HCO3
Addition of common salt to the solution containing NH4+ and HCO3– results in the precipitation of NaHCO3 which is least soluble. It is then filtered off.
NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Sodium bicarbonate is then heated to give Na2CO3.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
The CO2 gas evolved can be reused again.
Anhydrous sodium carbonate is dissolved in water and recrystallizes to get washing soda crystals containing 10 molecules of water of crystallization.
Properties of Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)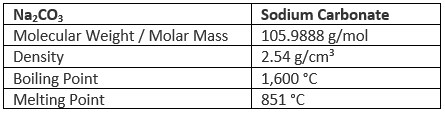
Chemical Properties of Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
- Anhydrous sodium carbonate is stable towards heat. It melts without decomposition at 852ºC.
- Aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate are mildly alkaline due to hydrolysis which releases OH–(aq) ions.
Na2CO3(s) + 2H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) - Aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate absorb carbon dioxide from the air forming sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Na2CO3(aq) + H2O + CO2(g) → 2NaHCO3(aq) - Sodium carbonate reacts with acids like weak vegetable acids, such as lime juice liberating carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3(aq) + 2H+(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Sodium Carbonate Structure (Na2CO3)
The structure of sodium carbonate molecules is illustrated below. It can be noted that each molecule of sodium carbonate contains 2 sodium atoms, 3 oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. Each sodium cation holds a charge of +1 whereas the polyatomic carbonate anion holds a net charge of magnitude -2. Sodium carbonate is, therefore, a neutrally charged molecule.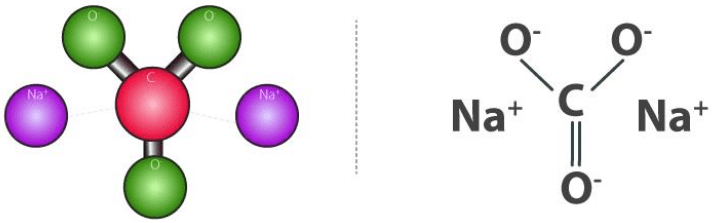 Sodium Carbonate Structure
Sodium Carbonate Structure
Uses of Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
The uses of sodium carbonate are listed below:
- It is used in the manufacture of detergents, soaps, paper.
- Also used in the manufacture of water glass (sodium silicate), borax, sodium phosphate, and many other sodium compounds.
- It is used in as a wetting agent in brick industry.
- It is used as an abrasive and foaming agent in toothpaste.
- It is used as a pH modifier.
- It is used as water softener – Hard water which consists of magnesium and calcium ions are precipitated by carbonate.
- As a laboratory reagent to standardize acids and as an analytical reagent.
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Sodium Chloride is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl.
Sodium Chloride is also known as salt. It occurs in oceans and sea waters. It is also found as rock salt. About 1% to 5 % of seawater is made of NaCl. It is a crystalline solid, white. In its aqueous form, it is called a saline solution.
The molecular weight of NaCl is 58.44g/mol
This compound is water-soluble and consists of sodium cation and chloride anion. The sodium and chloride ion are present in the ratio 1 : 1. It is widely known as table salt and is mostly used in the food industry for preservation and flavouring. The pH of sodium chloride is 7.
Properties of Sodium Chloride (NaCl)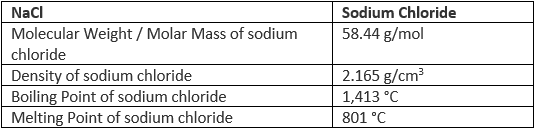
Structure of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Structure of Sodium Chloride
Structure of Sodium Chloride
Uses of Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- It is used in medicine – Saline solution in nasal spray
- It is used in fire extinguishers
- It is used in cleansers like shampoo, toothpaste
- It is used in the soda ash industry to produce sodium carbonate through Solvay process
- It is used in the paper industry, textile industry and in the construction of roads
- It is used in water softening
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium Hydroxide is a solid ionic compound. It is also known as caustic soda, Iye, sodium hydrate or soda lye.
It is a co-product of chlorine production. In its pure form, it is crystalline solid, colourless in nature. This compound is highly water-soluble and consists of sodium cations and hydroxide anions. NaOH absorbs moisture from the air. It is highly corrosive and can cause severe skin burn and irritation to eyes and other body parts.
It generates a high level of heat and so is always created by mixing the compound into the water, not the vice versa. In cosmetics, this inorganic compound is used as a buffering agent. It can also control the PH levels. The PH of sodium chloride is 13.
Properties of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium Hydroxide is a white, translucent crystalline solid. It is commonly referred to as caustic soda due to its corrosive action on many substances it decomposes proteins at room temperatures and may cause chemical burn to human bodies. Although it does not occur in nature, sodium hydroxide has been manufactured on large scale for many years from readily obtainable raw material and is used in numerous industrial processes.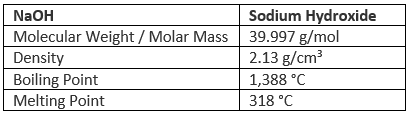
Sodium Hydroxide Structure (NaOH)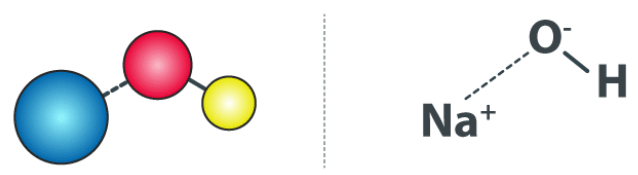 Sodium Hydroxide Structure (NaOH)
Sodium Hydroxide Structure (NaOH)
NaOH Uses (Sodium Hydroxide)
- It is used in the manufacturing of detergents and soaps
- It is used in the production of bleach-like chlorine
- It is used in drain cleaners
- It is used in the removal of heavy metals from the water by the municipal water treatment facility
- It is used in food preservatives to prevent bacteria and mould growth
- It is used for canning It is used in papermaking and paper recycling process
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Sodium bicarbonate or Sodium hydrogen carbonate has a monoclinic crystalline structure. Nicolas Leblanc a French chemist produced sodium carbonate in the year 1791. In the year 1846 Austin Church and John Dwight, bakers of New York started the first factory to produce baking soda. It is a white solid crystalline chemical compound usually in its powder form. This salt is composed of sodium ions and bicarbonate ions. Its molecular formula is NaHCO3. It is a weak base. It is commonly called as baking soda and is used in cooking. PH value is about 8.31.
Properties of Sodium Bicarbonate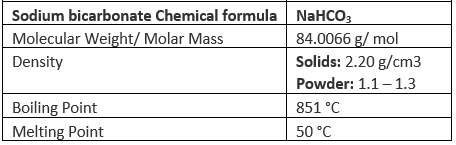
A few other important properties of sodium hydrogen carbonate are listed below:
- NaHCO3 has a white, crystalline appearance.
- This compound is insoluble in ethanol and slightly soluble in methanol and acetone.
- At a temperature of 20 degrees celsius, the solubility of this compound in water corresponds to 96 grams per litre.
- Sodium bicarbonate crystallizes in a monoclinic crystal lattice.
Sodium Bicarbonate Structure (NaHCO3)
Sodium bicarbonate molecules feature one sodium cation and one bicarbonate anion. Here, an ionic bond is formed between the positively charged sodium ion and the negatively charged oxygen (which is singly bonded to the central carbon and not bonded to a hydrogen atom).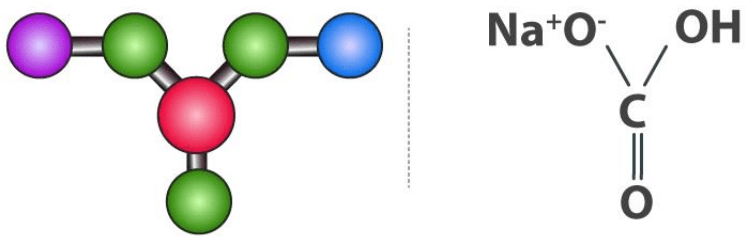 Sodium Bicarbonate Structure
Sodium Bicarbonate Structure
Uses of Sodium Bicarbonate
- It is used as pest control to kill cockroaches and controlling fungal growth
- It is used as a disinfectant
- It is used to protect armpits from bad smell and irritation
- It is used in cooking especially to bake food items
- It is used in medicine to be injected intravenously to the prevention of chemotherapy side effects
- It is used to wash kitchen products due to its antibacterial properties
- It is used to have clean teeth and mouth
|
366 videos|833 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Important Compounds of Sodium - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are some important compounds of sodium? |  |
| 2. What is the chemical formula for sodium chloride? |  |
| 3. What is the common household use of sodium hydroxide? |  |
| 4. How is sodium carbonate used in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What is the role of sodium bicarbonate in baking? |  |





















