GMAT Exam > GMAT Notes > Quantitative for GMAT > Important Formulas: Statistics
Important Formulas: Statistics | Quantitative for GMAT PDF Download
Statistics is a mathematical field focused on numbers and the analysis of data. It involves the examination, interpretation, presentation, and arrangement of data. Within statistical theory, a statistic is defined as a function applied to a sample, and this function remains unaffected by the distribution of the sample.
The important statistics formulas are listed in the chart below: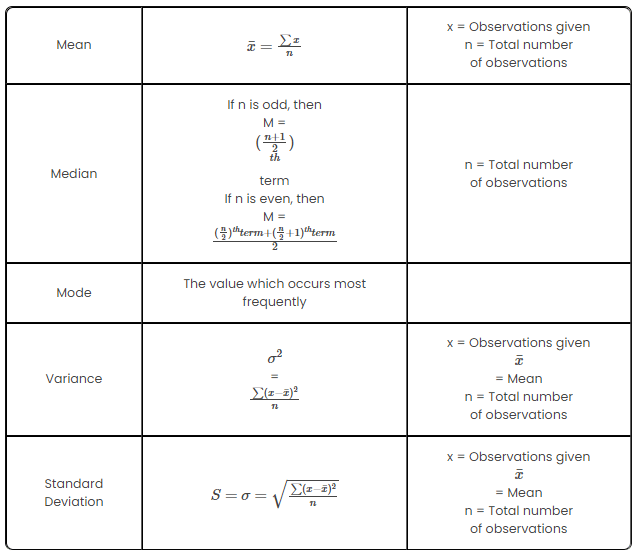
1. Mean:
- The arithmetical mean is the sum of a set of numbers separated by the number of numbers in the collection, or simply the mean or the average.
- To calculate the mean of a given data set, we use the following formula,
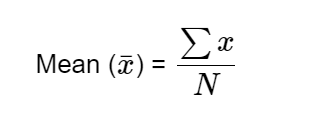
2. Median:
- In a sorted, ascending or descending, list of numbers, the median is the middle number and may be more representative of that data set than the average.
- In the case of the median, we have two different formulas. If we have an odd number of terms in the data set we use the following formula,
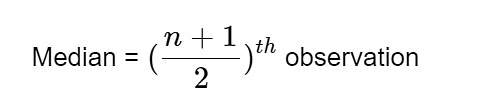
- If an even number of terms are given in the data set, we use the following formula,
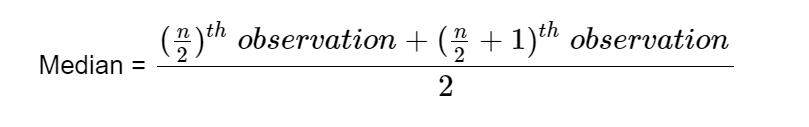
3. Mode:
- The mode is the value that most frequently appears in a data value set.
- In the case of clustered frequency distributions, it is not possible to calculate the mode simply by looking at the frequency. We measure the modal class in order to evaluate the data mode in such situations. Inside the modal class, the mode lies.
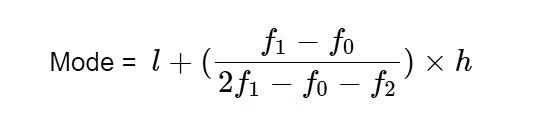
4. Standard Deviation:
- A calculation of the amount of variance or dispersion of a set of values is the standard deviation.
- By evaluating the deviation of each data point relative to the mean, the standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance.
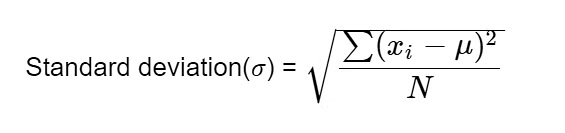
5. Variance:
- The expectation of the square deviation of a random variable from its mean is variance.
- The variance is defined as the total of the square distances from the mean (μ) of each term in the distribution, divided by the number of distribution terms (N).
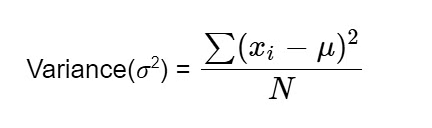
The document Important Formulas: Statistics | Quantitative for GMAT is a part of the GMAT Course Quantitative for GMAT.
All you need of GMAT at this link: GMAT
|
121 videos|148 docs|111 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Statistics - Quantitative for GMAT
| 1. What are some important formulas in probability and statistics? |  |
Ans. Some important formulas in probability and statistics include the formula for calculating probability: P(A) = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes. Other important formulas include the mean (average) formula: μ = Σx / n, where Σx is the sum of all the values and n is the total number of values. The formula for calculating variance is: σ^2 = Σ(x - μ)^2 / n, where σ^2 represents the variance, Σ(x - μ)^2 is the sum of the squared differences from the mean, and n is the total number of values.
| 2. How do you calculate the probability of an event? |  |
Ans. To calculate the probability of an event, you can use the formula: P(A) = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes. The number of favorable outcomes refers to the number of outcomes that satisfy the desired condition or event, while the total number of outcomes refers to the total number of possible outcomes. By dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of outcomes, you can determine the probability of that event occurring.
| 3. What is the mean (average) and how is it calculated in statistics? |  |
Ans. The mean, also known as the average, is a measure of central tendency in statistics. It represents the typical value in a set of data. To calculate the mean, you add up all the values in the data set and then divide the sum by the total number of values. The formula for calculating the mean is: μ = Σx / n, where Σx represents the sum of all the values and n is the total number of values. The mean provides a useful measure to understand the average value of a dataset.
| 4. What is variance and how is it calculated in statistics? |  |
Ans. Variance measures the dispersion or spread of a dataset. It quantifies how much the values in a dataset deviate from the mean. To calculate the variance, you need to subtract the mean from each value, square the result, sum up all the squared differences, and then divide by the total number of values. The formula for calculating variance is: σ^2 = Σ(x - μ)^2 / n, where σ^2 represents the variance, Σ(x - μ)^2 is the sum of the squared differences from the mean, and n is the total number of values.
| 5. How are probability and statistics related? |  |
Ans. Probability and statistics are closely related fields. Probability deals with the likelihood of events occurring, while statistics involves the collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data. Probability theory provides a foundation for statistical analysis by quantifying uncertainty and randomness. Statistical methods, on the other hand, utilize probability concepts to make inferences, draw conclusions, and estimate parameters based on observed data. Probability and statistics are essential for understanding and predicting various phenomena in the real world, including in fields such as finance, medicine, and social sciences.
Related Searches





















