Important Formulas: Whole Numbers | Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 PDF Download
(1) Natural numbers are all the numbers from 1 onwards, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and are used for counting.
(2) Whole numbers are all the numbers from 0 onwards, i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and are used for calculating.
(3) The smallest natural number is 1 and the smallest whole number is 0.
(4) The successor of a whole number is 1 more than the whole number.
(5) The predecessor of a whole number is 1 less than the whole number. There is no predecessor of zero in whole numbers.
(6) A number line is a horizontal line on which there are equally spaced points. These points represent whole numbers starting from zero.
(7) Whole numbers on Number Line:
Addition on a Number Line
To add numbers, we start at one number and make jumps to the right on the number line.
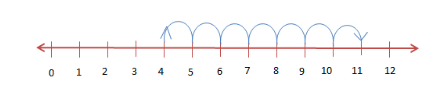
Subtraction on a Number Line
To subtract numbers, we start at one number and make jumps to the left on the number line.
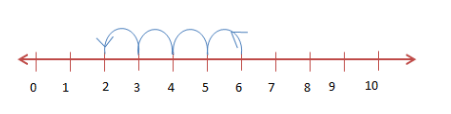
Multiplication on a Number Line
To multiply numbers, we start at 0 and make equal jumps forward on the number line.
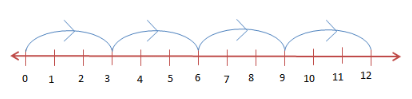
|
92 videos|353 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Whole Numbers - Mathematics (Maths) Class 6
| 1. What are some examples of whole numbers? |  |
| 2. How can whole numbers be used in real life? |  |
| 3. Can whole numbers be negative? |  |
| 4. How are whole numbers different from natural numbers? |  |
| 5. How can whole numbers be used in mathematical operations? |  |


















