Important Graphs of Periodic Properties | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Trends in Periodic Properties |

|
| Alkali Metals |

|
| CARBON FAMILY |

|
| CHALCOGENS |

|
| POINTS TO REMEMBER |

|
Trends in Periodic Properties
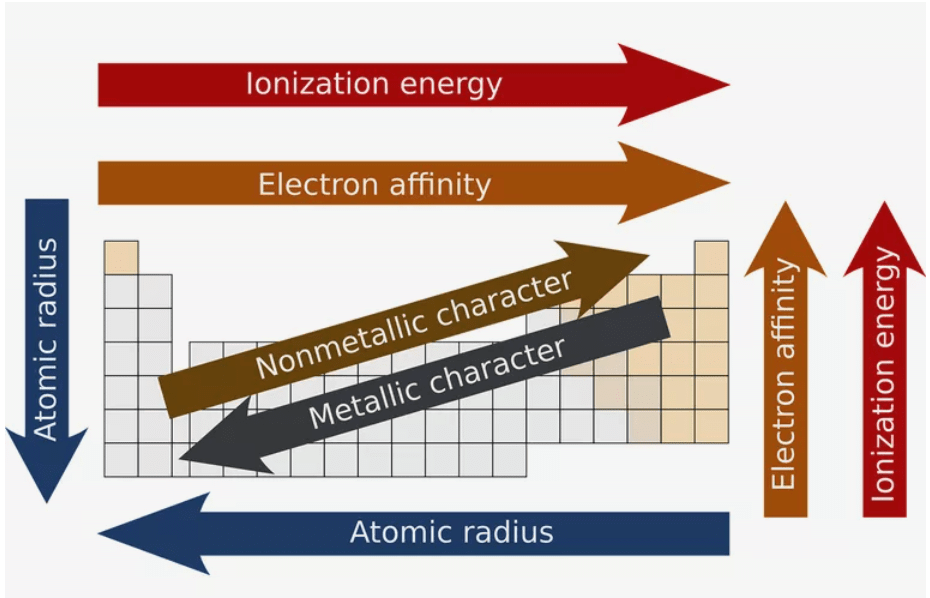
Alkali Metals
CARBON FAMILY
CARBON FAMILY
CHALCOGENS
3-D SERIES
POINTS TO REMEMBER
1. The basis of Mendeleev's periodic table was his periodic law. According to it the physical and chemical properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
2. According to Moseley, that a plot of v (where v is frequency of X-Rays emitted) against atomic number (Z) gave a straight line and not the plot of ~ vs atomic mass. Therefore, he concluded that atomic number (Z) instead of atomic mass was a better fundamental property of an element and atomic number instead of atomic mass should be basis of the classification of the elements.
3. Long form of periodic table contains seven periods (horizontal rows) and eighteen groups (vertical columns).
4. In the modern periodic table, the period indicates the value of principle quantum number.
5. The number of elements in each period is twice the number of atomic orbitals available in the energy level that is being filled. 6. Group consists of a series of elements having similar valence shell electronic configuration.
7. In modern periodic table each block (s, - p, - d - and f -) contains a number of columns equal to the numbers of electrons that can occupy that sub-shell.
8. The 4f - (i.e., actinides) and 5f - (i.e., lanthanides) inner transition series of element are placed separately in the periodic table to maintain its structure and to preserve the principle of classification.
9. Metals comprise more than 78% of all known elements and appear on the left side of the periodic table. Silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, selenium and tellurium all are semi - metals or metalloids.
10. The combined effect of attractive force due to nucleus and repulsive force due to intervening electrons, acting on the valence electrons is that the valence - electron experiences less attraction from the nucleus. This is called shielding or screening effect.
11. Covalent radius < metallic or crystal radius < Van der Waal's radius.
12. Species having same number of electrons but different in the magnitude of their nuclear charges are called as isoelectronic species and their size is inversely proportional to their effective nuclear charge.
13. The smaller the ionisation energy, the easier it is for the neutral atom to change in to a positive ions in gaseous state . IE1 < IE2 < IE3 .........•
14. The greatest increase in ionization enthalpy is experienced on removal of electrons from core noble gas configuration. End of valence electrons is marked by a big jump in ionization enthalpy. 15. Electron gain enthalpy provides a measure of the ease with which an atom adds an electron to form anion:
16. The negative value of electron gain enthalpy of Cℓ > F (similarly S > 0) because there is weak electron electron repulsion in the bigger 3p subshell of Cℓ as compared to compact 2p - subshell of F.
17. Noble gases have larger positive electron gain enthalpies because the electron has to enter the next higher energy level.
18. Addition of 2nd electron to an anion is opposed due to electrostatic repulsion and thus requires the absorption of energy e.g in case of the formation of S2–, O2– etc.
19. The relative reactivity of metals increases with the decrease in their ionisation energies. Similarly the relative reactivity of non-metals increases with increases in the negative value of electron gain enthalpy.
20. According to Pauling, the electronegativity difference between two atoms is equal to 0.208 √Δ where L is the extra bond energies in K cal mol-1. The acidic character of oxides increases when electronegativity difference decreases between element and oxygen (E - O).
|
366 videos|847 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Important Graphs of Periodic Properties - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the trends in periodic properties for alkali metals? |  |
| 2. How do the periodic properties of the carbon family vary? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of chalcogens in terms of periodic trends? |  |
| 4. What are some important graphs of periodic properties? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions about periodic properties in exams? |  |





















