Important Questions & Answers: Human Memory | Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q.1. In the experiment on forgetting when the subject is asked to recall words from list
1. she/he can recall words from the list
2. Identify the kind of interference.
proactive (forward moving)
Q2: What happens during the encoding stage?
During encoding, our brain takes in information and makes it meaningful. This is the first step where we pay attention and create signals in our brain to remember things later.
Q3: Why is deep processing important for memory?
Deep processing is important for memory because it helps us remember information for a longer time. When we think about the meaning of what we learn, we are more likely to keep it in our memory and not forget it easily.
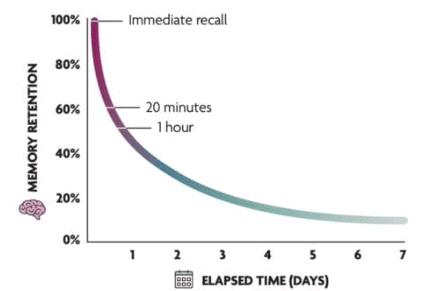
Q4: What does the "Forgetting Curve" show us?
The Forgetting Curve shows that we forget things very quickly at first, especially within the first hour. After that, we still forget, but not as fast. This means that most forgetting happens soon after we learn something.
Q.5. State the features of Sensory memory.
The incoming information first enters the sensory memory.Following are important features of Sensory Memory.
- Sensory memory has a large capacity. However, it is of very short duration, i.e. less than a second.
- It is a memory system that registers information from each of the senses with reasonable accuracy.
- Often this system is referred to as sensory memories or sensory registers because information from all the senses are registered here as an exact replica of the stimulus.
- An example that you can relate to is if you have experienced visual after-images (the trail of light that stays after the bulb is switched off) or when you hear reverberations of a sound when the sound has ceased, then you are familiar with iconic (visual) or echoic (auditory) sensory registers.
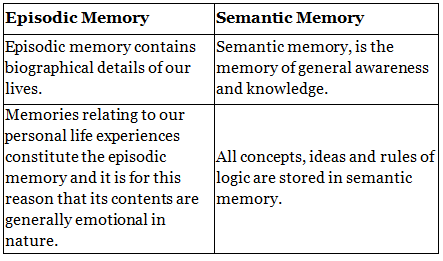
Q.6. Give two points of difference between Episodic and Semantic memory.
Q7: Discuss the importance of memory in everyday life. How do the processes of encoding, storage, and retrieval contribute to our ability to function in daily activities?
Memory is a vital aspect of our everyday life that significantly impacts our ability to function effectively. The processes of encoding, storage, and retrieval are essential for various daily activities, from simple tasks to complex decision-making.
- Facilitates Learning: Memory allows us to learn new information and skills. For instance, when a student learns a new concept in class, encoding helps them grasp the information meaningfully. Without effective encoding, the information may not be retained, leading to difficulties in understanding subsequent lessons. Thus, strong memory skills are fundamental for academic success.
- Enables Daily Tasks: Everyday tasks, such as remembering a grocery list or following a recipe, rely heavily on memory. Encoding helps us remember the items we need to buy, while storage keeps this list accessible until we are ready to use it. Efficient retrieval allows us to recall the list or recipe when needed, demonstrating how these memory processes support our daily routines.
- Supports Social Interactions: Memory is crucial for building and maintaining relationships. Remembering names, faces, and personal details about friends and family strengthens social bonds. For instance, encoding someone's name at a party helps in later retrieval during conversations, fostering a sense of connection and attentiveness.
- Aids Decision-Making: Memory plays a key role in decision-making processes. When faced with choices, we often rely on past experiences stored in our memory to guide our decisions. This retrieval of previous outcomes helps us evaluate potential consequences and make informed choices, whether it concerns personal life or professional matters.
- Preserves Identity: Our memories contribute to our sense of self and identity. The stored memories of our past experiences shape who we are and how we view the world. They influence our beliefs, values, and behaviors, providing continuity in our lives. This connection between memory and identity highlights the importance of memory in understanding ourselves and our place in society.
Thus , memory is fundamental to our ability to learn, perform daily tasks, interact socially, make decisions, and preserve our identity. The processes of encoding, storage, and retrieval work together seamlessly to ensure we can navigate our lives effectively.
Q8: Discuss the implications of the levels of processing theory for effective learning strategies. How can students apply deep processing techniques to enhance their understanding and retention of new information?
The levels of processing theory has important implications for how students can approach their learning. By understanding the differences between shallow, intermediate, and deep processing, students can adopt strategies that enhance their understanding and retention of new information. Here are several effective learning strategies based on deep processing techniques:
- Focus on Meaning: Students should aim to understand the significance of the information they are learning. Instead of memorizing facts, they should ask themselves questions about why the information is important and how it connects to what they already know. This approach fosters deeper engagement with the material, leading to better retention.
- Elaborate on Concepts: When faced with new material, students should take the time to elaborate on the meanings of the concepts. This could involve writing summaries, creating mind maps, or discussing the material with peers. By relating new information to existing knowledge or personal experiences, students can create a richer context for the information, making it easier to recall later.
- Use Mnemonics and Analogies: Creating mnemonic devices or analogies can help students relate new information to familiar concepts. For example, linking the characteristics of a cat to a person's own pet can create memorable connections that enhance understanding. This strategy taps into deep processing by fostering meaningful associations.
- Teach What You Learn: One of the most effective ways to reinforce understanding is to teach the material to someone else. This process forces students to organize their thoughts and express the information clearly, promoting deep processing. Teaching others helps solidify the knowledge and creates a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Reflect and Review: After learning new information, students should take time to reflect on what they have learned. This could involve journaling about the key takeaways or discussing them in study groups. Regular review sessions that encourage deep processing rather than rote memorization can significantly enhance retention and understanding.
Q9: Discuss the factors that can significantly influence memory improvement. Include details on how each factor affects memory retention and recall.
Memory improvement is not just about using specific techniques; it involves understanding and addressing several factors that impact how we remember information. Here are five key factors that play a crucial role in enhancing memory:
- Health Status: Physical health greatly affects cognitive functions, including memory. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep are essential for optimal brain function. For instance, exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promoting the growth of new brain cells. A healthy diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamins can protect brain cells from damage. Moreover, sleep is vital for memory consolidation, where information is processed and stored during different sleep stages.
- Interest and Motivation: Having a genuine interest in the subject matter greatly enhances memory retention. When individuals care about what they are learning, they are more likely to engage with the material, which leads to better understanding and recall. Motivation drives people to use various strategies, such as visualization or mnemonic devices, making the learning process more effective and enjoyable.
- Familiarity with the Subject Matter: Familiarity can significantly ease the process of memory recall. When learners already have a foundation of knowledge in a certain area, new information can be linked to existing knowledge, making it easier to remember. This method, known as "chunking," helps break down complex information into manageable pieces, facilitating better retention.
- Environmental Factors: The environment in which learning occurs can influence memory retention. A quiet, comfortable space with minimal distractions allows for better concentration and information absorption. Conversely, a noisy or chaotic environment can hinder focus and make it more challenging to remember what has been learned. Personalizing the learning environment, such as using specific colors or scents, can also enhance memory through associative learning.
- Practice and Repetition: Regularly reviewing and practicing information strengthens memory pathways. Techniques such as spaced repetition, where information is reviewed at increasing intervals, can significantly enhance long-term retention. Active recall, where learners test themselves on the material, also reinforces memory by encouraging deeper processing and understanding of the subject matter.
In conclusion, a comprehensive approach to memory improvement involves considering various factors, including health, motivation, familiarity, environment, and practice. By addressing these areas, individuals can enhance their memory retention and improve their overall learning outcomes.
Q10: Explain the role of motivation and interest in the process of memory improvement. How can individuals enhance these factors to support their learning?
Motivation and interest are critical components of effective learning and memory improvement. When individuals are motivated and interested in what they are learning, they are more likely to engage deeply with the material, leading to better retention and recall. Here are five ways motivation and interest influence memory and strategies to enhance these factors:
- Engagement with Material: When learners are motivated, they actively engage with the content, using various strategies such as summarizing, questioning, and connecting new information to existing knowledge. This engagement promotes deeper processing, which is essential for long-term memory. To enhance engagement, individuals can choose topics that excite them or relate learning to personal interests and goals.
- Goal Setting: Setting specific, achievable goals can boost motivation. Goals provide a clear direction and purpose, making learning more meaningful. For instance, rather than aiming to "study history," a student could set a goal to "learn about World War II and its impact on modern society." This specificity can increase motivation and make the learning process feel more rewarding. Individuals can enhance their motivation by breaking larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks that can be achieved step by step.
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewarding oneself for reaching study milestones can significantly enhance motivation. This could involve treating oneself to something enjoyable, such as a favorite snack or a break to watch a favorite show after completing a study session. By creating a system of rewards, individuals can associate learning with positive feelings, making it more likely they will stay motivated in the long term.
- Connecting Learning to Real Life: Making connections between the material and real-life experiences can increase interest. When students see practical applications of what they are learning, they are more likely to find it relevant and engaging. For example, relating mathematical concepts to everyday budgeting or scientific principles to current events can enhance understanding and interest. Individuals can enhance interest by seeking out real-world examples and applications of the concepts they are studying.
- Social Learning: Collaborating with peers can enhance motivation and interest in learning. Group discussions, study groups, or collaborative projects allow learners to share insights and perspectives, making the learning experience more interactive and dynamic. Engaging with others can also provide support and encouragement, making the process feel less daunting. To enhance motivation through social learning, individuals can seek out study partners or join learning communities that share their interests.
|
43 videos|88 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions & Answers: Human Memory - Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is human memory and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of memory? |  |
| 3. How does the process of memory encoding work? |  |
| 4. What factors can affect human memory? |  |
| 5. How can individuals improve their memory? |  |