Important Questions & Answers: Sensory, Attentional, & Perceptual Processes | Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q.1. When we go to a matinee show, on entering the theatre we find it difficult to see things around. However, after spending about 15-20 minutes there, we are able to see almost everything. What is this phenomenon called?
visual adaptation.
Q.2. _____________ help flattens the lens to focus the distant objects.
ciliary muscles
Q.3. With the help of an example explain Size Constancy.
- The size of an image on our retina changes when the distance of the object from our eye changes.
- The far it is, the smaller is the image.
- On the other hand, our experience shows that within limits the object appears to be about the same size irrespective of its distance.
- This tendency of the size of objects to remain relatively unchanged with changes in their distance from the observer and the size of the retinal image is called size constancy.
An example is, when you approach your friend from a distance, your perception of the friend’s size does not change much despite the fact that the retinal image (image on retina) becomes larger.
Q.4. The process of organising visual field into meaningful wholes is known as _____________.
form perception.
Q.5. Artist mostly use _____________ to create an impression of depth on a flat surface.
Monocular cues
Q.6. Explain the term Illusion.
Our perceptions are not always truthful. Sometime we fail to interpret the sensory information correctly. This results in a mismatch between the physical stimuli and its perception. These misperceptions resulting from misinterpretation of information received by our sensory organs are generally known as illusions.
Illusions are are experienced more or less by all of us.
They result from an external stimulus situation and generate the same kind of experience in each individual.Illusions are also called "primitive organisations".
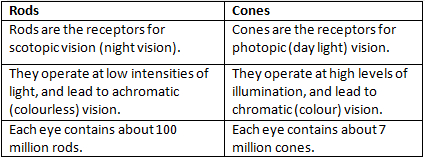
Q.7. State three points of difference between Rods and Cones.
Q.8. Explain the concept of sensory modalities and their role in perception.
Sensory modalities refer to the different ways our sense organs perceive stimuli from the environment. The primary modalities include vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch, each associated with specialized receptors that detect specific types of stimuli.
- Vision: Detects light and color, allowing us to perceive shapes and distances.
- Hearing: Processes sound waves, enabling us to recognize tones and patterns.
- Taste: Involves chemical receptors that identify flavors.
- Smell: Detects airborne chemicals, contributing to flavor perception.
- Touch: Senses pressure, temperature, and pain through skin receptors.
These modalities work together to form a coherent perception of our surroundings. They are crucial for interpreting sensory information, guiding attention, and influencing our interactions with the world. The integration of these modalities enhances our cognitive processes, allowing us to respond appropriately to various stimuli.
Q.9. Explain the concept of span of attention and its significance.
The concept of "span of attention," also known as "perceptual span," refers to the limited capacity of human attention to process stimuli at any given moment. It indicates the number of objects one can effectively attend to during a brief exposure, typically lasting a fraction of a second. Research, particularly by Miller, suggests that this span is generally around seven items, plus or minus two, often referred to as the "magic number." This means that individuals can typically focus on five to seven distinct pieces of information simultaneously, although this can extend under optimal conditions.
- Measurement: The span of attention can be assessed using tools like the tachistoscope.
- Practical Implications: Understanding this span is crucial in various fields, such as traffic management, where number plates are designed to be easily recognizable.
- Vigilance: Sustained attention, or vigilance, is vital in high-stakes environments like air traffic control, where constant monitoring is essential.
- Influencing Factors: Factors such as sensory modality and clarity of stimuli can significantly affect attention performance.
Q.10.Describe the Gestalt psychologists' principle of figure-ground segregation.
The principle of figure-ground segregation, as described by Gestalt psychologists, refers to the ability to distinguish an object (the figure) from its background (the ground). This process is fundamental to how we perceive visual stimuli in an organized manner.
- Definite Form: The figure has a clear, defined shape, while the background is more formless.
- Organization: The figure is perceived as more structured compared to the background.
- Contour: The figure has a distinct outline, whereas the background lacks clear contours.
- Depth Perception: The figure appears closer and more defined, while the background seems distant and vague.
This principle illustrates that our perception is geared towards recognizing organized wholes rather than isolated parts.
|
43 videos|88 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions & Answers: Sensory, Attentional, & Perceptual Processes - Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the main components of sensory, attentional, and perceptual processes? |  |
| 2. How do sensory processes affect our perception of the world? |  |
| 3. What role does attention play in perceiving stimuli? |  |
| 4. Can perceptual processes be influenced by past experiences? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between bottom-up and top-down processing in perception? |  |