Important Questions: Electricity: Circuits and their Components | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
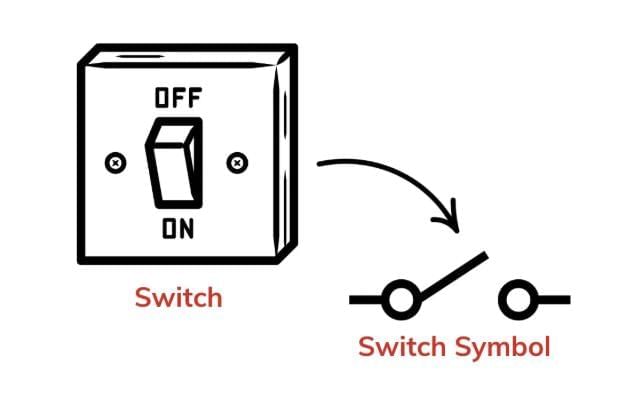
Q1: What is the function of a switch in an electrical circuit?
a) To produce light
b) To control current flow
c) To store energy
d) To insulate wires
Answer: b
Q2: Which material is a good conductor of electricity?
a) Plastic
b) Rubber
c) Copper
d) Wood
Answer: c
Q3: What happens to an incandescent lamp when its filament breaks?
a) It glows brighter
b) It stops glowing
c) It changes color
d) It uses less current
Answer: b
Q4: Which terminal of an LED must connect to the battery’s positive terminal for it to glow?
a) Shorter wire
b) Longer wire
c) Either wire
d) Neither wire
Answer: b
Q5: What type of current is produced by batteries?
a) Alternating Current (AC)
b) Direct Current (DC)
c) Static Current
d) Variable Current
Answer: b
Q6: Which component of a torchlight provides electrical energy?
a) Lamp
b) Switch
c) Electric cell
d) Wires
Answer: c
Q7: What is the negative terminal of an electric cell usually made of?
a) Plastic
b) Flat metal disc
c) Metal cap
d) Glass
Answer: b
Q8: Why is copper commonly used for electrical wires?
a) It is an insulator
b) It is a good conductor and cost-effective
c) It is lightweight
d) It prevents shocks
Answer: b
Q9: Which organization sets standard symbols for circuit diagrams?
a) World Health Organization
b) International Electrotechnical Commission
c) United Nations
d) Indian Space Research Organisation
Answer: b
Q10: Why should you avoid touching electrical switches with wet hands?
a) The human body is an insulator
b) The human body conducts electricity
c) Water is a conductor
d) Both b and c
Answer: d
Q11: What is an electric circuit, and why is it important?
Answer: An electric circuit is a closed path that allows electric current to flow from a power source through a device and back. It is important because it enables devices like lamps to work by providing a complete path for current flow.
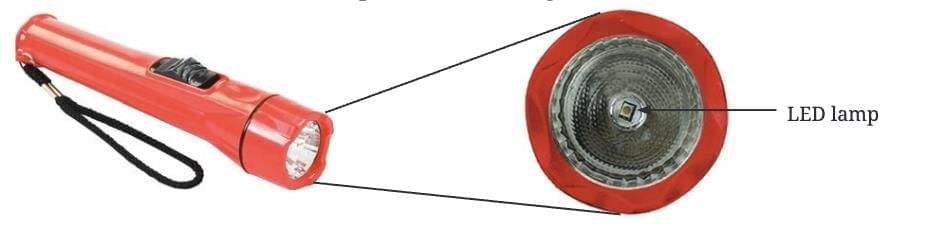
Q12: How does an LED lamp differ from an incandescent lamp in a torchlight?
Answer: An LED lamp has no filament, glows only when correctly connected (positive to positive terminal), and is more efficient, while an incandescent lamp has a filament that glows regardless of terminal connections but is less efficient.
Q13: Define conductors and insulators, and give one example of each.
Answer: Conductors allow electric current to flow easily, e.g., copper. Insulators block current flow, e.g., plastic.
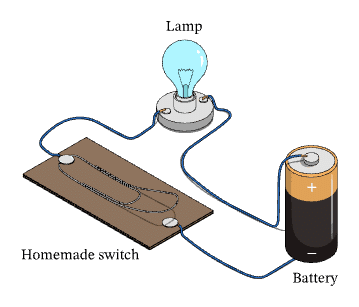
Q14: What is the role of a cell holder in a circuit?
Answer: A cell holder securely places the electric cell in a circuit, ensuring proper connection of the cell’s terminals to wires for current flow.
Q15: Why is a circuit diagram useful?
Answer: A circuit diagram uses standard symbols to represent components, making it easy to understand, draw, and build electrical circuits accurately.
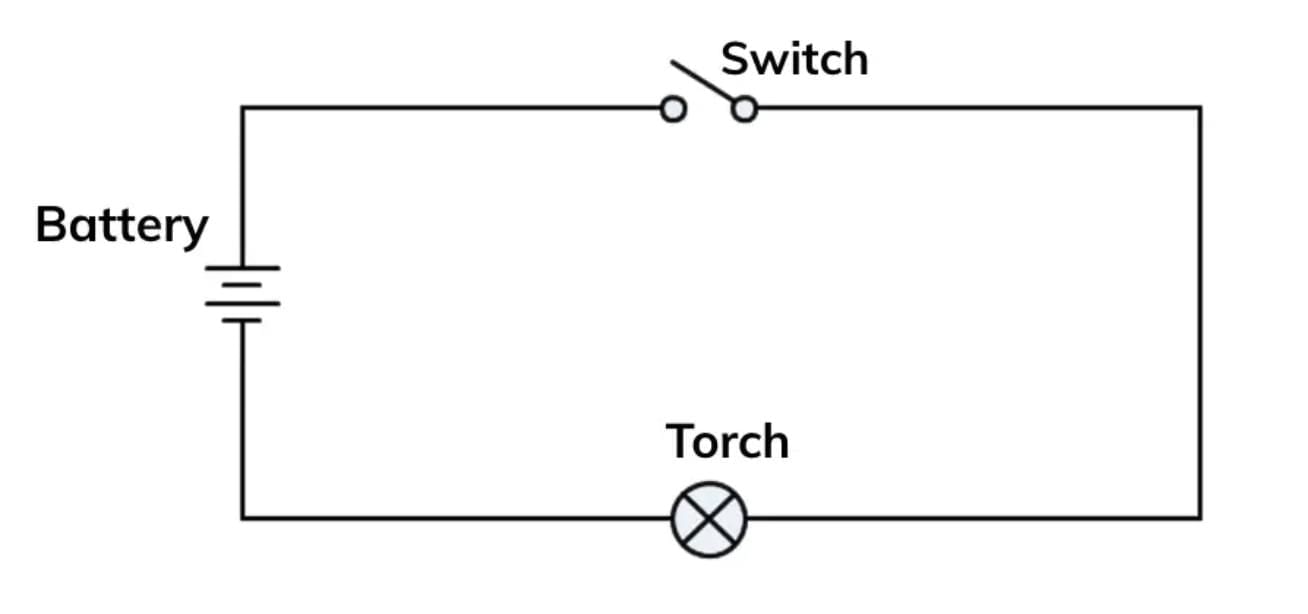
Q16: Explain how a torchlight works, describing the role of its main components.
Answer: A torchlight produces light using a simple electrical circuit with key components:
Electric Cells: Provide electrical energy through a chemical reaction, with a positive (+) and negative (-) terminal.
Lamp: An incandescent lamp or LED that glows when current flows through it. Incandescent lamps have a filament that heats up, while LEDs require correct terminal alignment.
Switch: Controls current flow by closing (ON) or opening (OFF) the circuit. When ON, it connects the cells to the lamp, allowing current to flow; when OFF, it breaks the circuit, stopping the light.
Wires: Connect the components, allowing current to flow from the negative terminal of the cell, through the lamp, and back to the positive terminal.
When the switch is ON, the circuit is complete, and current flows from the cells through the lamp, making it glow. This portable design makes torchlights useful for seeing in the dark, as explored by Nihal’s class.
Q17: Describe the differences between conductors and insulators, and their uses in electrical circuits, with examples.
Answer: Conductors and insulators differ in their ability to handle electric current:
Conductors: Materials like copper, silver, and aluminum allow current to flow easily due to their structure. They are used in wires (e.g., copper wires in circuits), switches, and plugs to carry current efficiently. Copper is preferred for its conductivity, cost, and availability.
Insulators: Materials like plastic, rubber, and glass block current flow, preventing unwanted electrical movement. They are used to cover wires (e.g., plastic insulation), make plug tops, and switches to protect users from shocks. Rubber gloves are another example used for safety.
In circuits, conductors ensure current reaches devices like lamps, while insulators prevent shocks and short circuits. For example, in a torchlight, copper wires (conductors) connect the cell to the lamp, and a plastic body (insulator) encases the circuit, ensuring safe operation, highlighting their complementary roles in electrical safety and functionality.
Q18: Discuss the importance of circuit diagrams and the role of switches in controlling electrical circuits, with examples.
Answer: Circuit diagrams and switches are crucial in electrical circuits:
Circuit Diagrams
- These are drawings using standard symbols (set by organizations like IEC) to represent components like cells, lamps, and wires.
- They simplify complex circuits, making them easy to understand, design, and build globally.
- For example, a diagram for a torchlight shows a cell (long/short lines), lamp (circle with loop), and switch (break in line), guiding Nihal’s class to visualize how current flows.
Switches
- A switch controls current by closing (ON) or opening (OFF) the circuit.
- When ON, it completes the path, allowing current to flow (e.g., turning on a torchlight’s lamp).
- When OFF, it breaks the path, stopping current (e.g., turning off the lamp).
- Switches can be placed anywhere in the circuit, as seen in home light switches or torch sliders.
Together, circuit diagrams help plan circuits accurately, while switches provide practical control, ensuring devices work only when needed, enhancing safety and efficiency in applications like Nihal’s torchlight or household lighting.
Q19: Draw a neat circuit diagram of a torchlight, labeling the electric cell, lamp, switch, and wires.
Answer:
Q20: Draw a diagram of a battery made of two electric cells, labeling the positive and negative terminals and showing their connection.
Answer: Diagram of a battery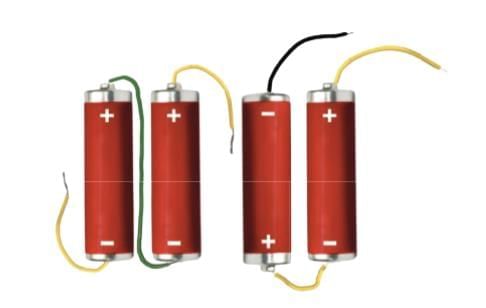
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Electricity: Circuits and their Components - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What is an electric circuit and what are its main components? |  |
| 2. How does a series circuit differ from a parallel circuit? |  |
| 3. What is the role of a switch in an electric circuit? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to use conductors and insulators in electrical circuits? |  |
| 5. What is Ohm's Law and why is it significant in understanding electric circuits? |  |