Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Mathematics Olympiad Class 7 > Infographics: Types of Fractions
Infographics: Types of Fractions | Mathematics Olympiad Class 7 PDF Download
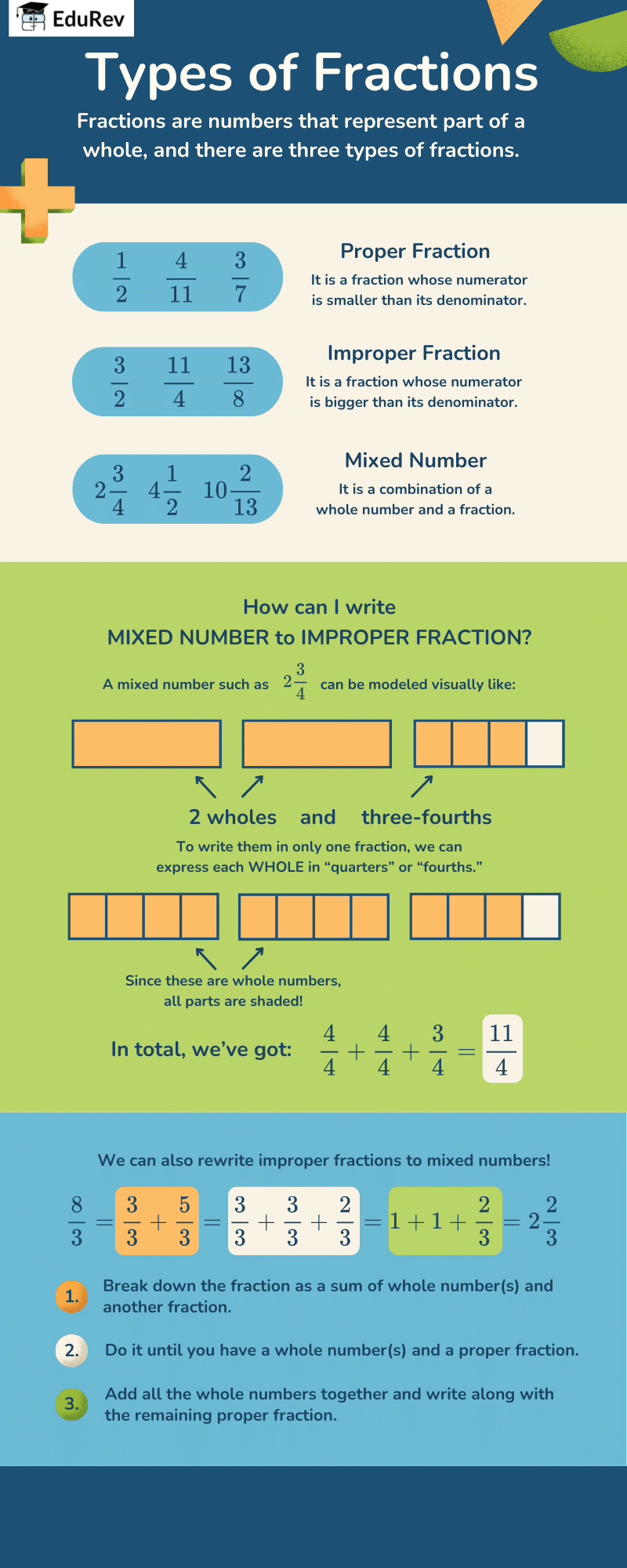
The document Infographics: Types of Fractions | Mathematics Olympiad Class 7 is a part of the Class 7 Course Mathematics Olympiad Class 7.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
28 videos|89 docs|91 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Types of Fractions - Mathematics Olympiad Class 7
| 1. What are the different types of fractions? |  |
Ans. The different types of fractions include proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed numbers. Proper fractions are those where the numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., 3/4). Improper fractions have numerators that are greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/3). Mixed numbers combine a whole number with a proper fraction (e.g., 2 1/2).
| 2. How do you convert an improper fraction to a mixed number? |  |
Ans. To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the proper fraction part. For example, to convert 9/4, divide 9 by 4, which gives 2 with a remainder of 1. So, 9/4 can be written as 2 1/4.
| 3. How do you add fractions with different denominators? |  |
Ans. To add fractions with different denominators, first find a common denominator, which is usually the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators. Then, convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with the common denominator. Finally, add the numerators and keep the common denominator. For example, to add 1/3 and 1/4, the common denominator is 12. Thus, 1/3 becomes 4/12 and 1/4 becomes 3/12, so 4/12 + 3/12 = 7/12.
| 4. What is the difference between a proper fraction and an improper fraction? |  |
Ans. The difference between a proper fraction and an improper fraction lies in their numerators and denominators. In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., 2/5), while in an improper fraction, the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 7/4). This distinction affects how they are represented and used in mathematical operations.
| 5. How can you simplify a fraction? |  |
Ans. To simplify a fraction, divide both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For example, to simplify the fraction 6/8, find the GCD of 6 and 8, which is 2. Then, divide both by 2: 6 ÷ 2 = 3 and 8 ÷ 2 = 4. Thus, 6/8 simplifies to 3/4.
Related Searches





















