Integer Answer Type Questions: Motion | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. A train is moving along a straight line with a constant acceleration ‘a’. A boy standing in the train throws a ball forward with a speed of 10 m/s, at an angle of 60° to the horizontal. The boy has to move forward by 1.15 m inside the train to catch the ball back at the initial height. The acceleration of the train, in m/s2, is
Ans. 5
Solution. From t h e perspective of observer A, consider in g vertical motion of the ball from the point of throw till it reaches back at the initial height.
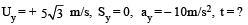
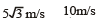
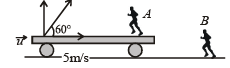
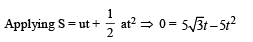
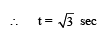
Considering horizontal motion from the perspective of observer B. Let u be the speed of train at the time of throw.
The horizontal distance travelled by the ball = (u + 5) √3 .
The horizonal distance travelled by the boy
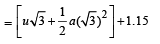
As the boy catches the ball therefore
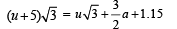
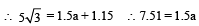
∴ a ≈5 m/s2
Q.2. Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertical plane at angles 30° and 60° with respect to the horizontal respectively as shown in figure. The speed of A is 100 √3 m/s. At time t = 0 s, an observer in A finds B at a distance of 500 m. The observer sees B moving with a constant velocity perpendicular to the line of motion of A. If at t = t0, A just escapes being hit by B, t0 in seconds is (JEE Adv. 2014)
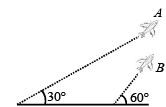
Ans. 5
Solution. 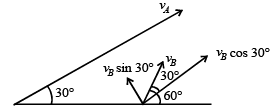
Here
vA = vB cos 30°

∴vB = 200 ms–1
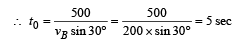
Q.3. A rocket is moving in a gravity free space with a constant acceleration of 2 m/s2 along +x direction (see figure). The length of a chamber inside the rocket is 4 m. A ball is thrown from the left end of the chamber in +x direction with a speed of 0.3 m/s relative to the rocket. At the same time, another ball is thrown in –x direction with a speed of 0.2 m/s from its right end relative to the rocket. The time in seconds when the two balls hit each other is (JEE Adv. 2014)
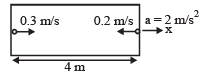
Ans. 8
Solution. 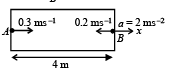
For ball A
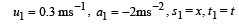
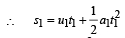
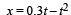 ...(1)
...(1)
For ball B
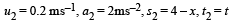
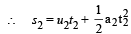
4 – x = 0.2 t + t2 ...(2)
From (1) and (2) t = 8 sec
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Integer Answer Type Questions: Motion - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What is motion in physics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of motion? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |
| 4. What is acceleration? |  |
| 5. What are the equations of motion? |  |