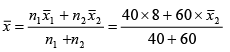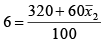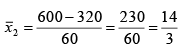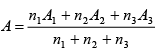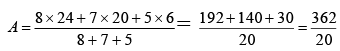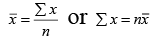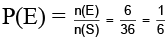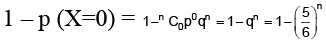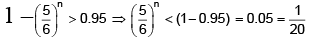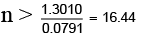Integer Answer Type Questions for JEE: Probability | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Mean of 100 items is 49. It was discovered that three items which should be 60, 70, 80 were wrongly read as 40, 20, 50 respectively. The correct mean is
Ans. 50
Sum of 100 items = 49 x 100 = 4900
Sum of items added = 60+ 70 + 80 = 210
Sum of items replaced = 40 + 20 + 50 = 110
New sum = 4900 - 110 + 210 = 5000
∴ New Mean = 5000 / 100 = 50
Q.2. A form of readymade garments make both men’s and women’s shirts. Its profit average is 6% of sales. Its profits in men’s shirts average 8% of sales and women’s shirts comprise 60% of output. What would be the average profit per sales rupee in women’s shirts.
Ans. 4.66
Assuming that
, we know that
⇒
⇒
= 4.66
This the average profit in women’s shirt is 4.66% of sale or Rs. 0.0466 per sale rupee.
Q.3. In a family, there are 8 men, 7 women and 5 children whose mean ages separately are respectively 24, 20, and 9 years what is mean age of the family?
Ans. 18.1
Here we have three collections for which A1 = 24, n1 = 8, A2 = 20, n2 = 7 and A3 = 6, n3 = 5.
Their combined mean is the required mean.
By the formula,
= 18.1
∴ The mean age of the family = 18.1 years
Q.4. Mean of 25 observations was found to be 78.4. But later on it was found that 96 was misread as 69. The correct mean is
Ans. 79.48
We know that the mean is given by
Here= 78.4, n = 25
∴ ∑x = 25 x 78.4 = 1960
But this ∑x is incorrect as 96 was misread as 69
Correct ∑x = 1960 - 69 = 1987
∴ Current Mean = 1987 / 25 = 79.48
Q.5. The median of the items 6, 10, 4, 3, 9, 11, 22, 18, is
Ans. 9.5
Let s arrange the items in ascending order 3, 4, 6, 9,9 10, 11, 18, 22.
In this data the number of items is n = 8, which is even.
∴ Median = M = average of (n/2)th and (n/2 + 1)th terms.
= Average of (8/2)th and (8/2 + 1)th terms.
= Average of 4th and 5th terms
= 9 + 10/2 = 19/2 = 905
Q.6. Find the minimum number of tosses of a pair of dice so that the probability of getting the sum of the digits on the dice equal to 7 on at least one toss is greater than 0.95. (log10 2 = 0.3010, log10 3 = 0.4771).
Ans. 17
Let S be the sample space and E be the event of occurrence of a total of 7 when a pair of dice is tossed.
Then n(S) = 6 ´ 6 = 36 and E = {(1, 6), (2, 5), (3, 4), (4,3), (5, 2), (6, 1)}
∴ n (E) = 6
∴
Let occurrence of event E be called a success and X denote the number of successes.
Here p = P(E) = 1/6 and q = 1 - p= 5/6
Let n = number of trials = number of tosses
Probability of at least one success = 1 – probability of no success
=
∴
∴ n [log105-log106] < log10 1-log1020
or n[log10 10 - log10 2 - log10 2 - log10 3] < - log10 2 - log10 10
or n [1 - 2 log10 2 - log10 3] < -1 - log10 2
or – 0.0791 n < – 1.3010
∴
Hence, the least number of trials = 17.
Q.7. India play two matches each with West Indies and Australia .In any match the probabilities of India getting points 0, 1 and 2 are 0.45, 0.05 and 0.50 respectively. Assuming that the outcomes are independent, the probability of India getting at least 7 points is
Ans. 0.0875
Probability of getting at least seven points = Probability of getting 7 points or 8 points = probability of getting 7 points + probability of getting 8 points.
Seven points in four matches can be obtained in the following four different ways: (2, 2, 2, 1) ; (2, 2, 1, 2); (2, 1, 2, 2); (1, 2, 2, 2)
Hence, probability of getting 7 points = 4. (0.50)3 (0.05) = 0.0250
Eight points in four matches can be obtained only in one way i.e. 2, 2, 2, 2,
Hence, probability of getting 8 points = (0.50)4 = 0.0625
Thus, the required probability = 0.0250 + 0.0625 = 0.0875.
Q.8. Two events A and B have probabilities 0.25 and 0.50 respectively. The probability that both A and B occur simultaneously is 0.14. Then the probability that neither A nor B occurs is
Ans. (.39)
P(A) = .25, P (B) = .50, P ( A ∩ B) = .14
P (A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B) = .25 + .50 - .14 = .61
= 1 – .61 = .39
Q.9. A speaks truth in 60% cases and B speaks truth in 70% cases. The probability that they will say the same thing while describing single event is
Ans. 0.54
They will say same thing in two ways i.e. either both speak truth or both tell a lie.
So, probability = (.6 x .7) + (1 – .6) (1 – .7) = .42 + .12 = 0.54 .
Q.10. A, B, C are events such that P(A) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.4, P(C) = 0.8, P(A ∩ B) = 0.08,
P(A ∩ C) = 0.28,
P(A ∩ B ∩ C) = 0.09.
If 0.75 ≤ P(A ∪ B ∪ C) ≤ 1, then P(B ∩ C) may be
Ans. 0.48
P(A ∪ B ∪ C) = =P(A) + P(B) + P(C)-P(A ∩ B) -P(B ∩ C) - P(A ∩ C) + P(A ∩ B ∩ C).
= 0.3 + 0.4 + 0.8 - 0.08 - P(B ∩ C) - 0.28 + 0.09
= 1.23 - P(B ∩ C)
Now, 0.75 ≤ 1.23 - P(B ∩ C) ≤ 1
⇒ 0.23 ≤ P(B ∩ C) ≤ 0.48.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|