Internet Basics: Chapter Notes | Computer Application: Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Some Networking Devices |

|
| Applications of the Internet |

|
| Connecting Your PC to the Internet (Using Broadband) |

|
| Some Important Internet Terminologies |

|
| Web Client |

|
Introduction
The Internet is the most commonly used term in today’s world and plays a very important role in people's everyday lives. The Internet completely revolutionized communication and technology across the Globe. Initially, computerized devices were only used for large industries, but later, their usage increased massively.
It is also mandatory for people to know that a single person can't develop something as broad and wide as the Internet all by himself/herself. The Internet was discovered through the combined effort of multiple researchers and programmers.
Internet: A global system of interconnected computers, using a standardised Internet Protocol suite for communication and sharing information is called the Internet
 Internet
Internet
History of internet
The Internet originated in 1969 with the U.S. Department of Defense’s ARPANET, designed to connect computers for research and military use. Its growth accelerated in the 1970s with the creation of TCP/IP, a standardized communication protocol. In the 1980s, networks like BITNET expanded their reach, connecting educational institutions worldwide. The 1990s marked the Internet’s public and commercial boom, driven by the rise of the World Wide Web. Today, it’s a central part of daily life, reshaping communication, business, and information access globally.
Communication and Working on the Internet
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that enables worldwide communication and resource sharing through various connection methods, such as cables and satellites. Communication relies on protocols, which create a unified platform for interaction.
Protocols
Protocols are rules for secure communication between devices. Common protocols include TCP/IP and FTP, which standardize data exchange on the Internet.
Address of Your Computer Over the Internet
Every device on the Internet has a unique IP address. When connected through an ISP, users receive a temporary IP address, allowing them to communicate and access resources online.
Some Networking Devices
Modem and Its Working
A modem (short for Modulator-Demodulator) is a device used to convert data signals, enabling computers to send and receive data over a network. Computers store data digitally, while telephone lines transmit it as analog signals. A modem converts between these two forms:
- Modulation: Converts digital data to analog form for transmission.
- Demodulation: Converts analog data back to digital form for computer processing.
Router
A router is a small physical device that connects multiple networks, directing data between them and allowing different networks to communicate.
Repeater
A repeater is a network device that amplifies a received signal, retransmitting it with greater power to cover a larger area. Repeaters extend the reach of a network by expanding its coverage area.

Who Manages the Internet?
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): The W3C is the main international organization responsible for setting standards for the World Wide Web. Founded by Tim Berners-Lee at MIT, it ensures the web's structure and protocols remain universally accessible and standardized.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF): The IETF aims "to make the Internet work better" by standardizing protocols and technologies from an engineering standpoint, ensuring seamless Internet functionality.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN): ICANN manages the Internet’s unique identifiers, such as domain names and IP addresses, ensuring they are unique, secure, and globally coordinated.
Applications of the Internet
E-mail: Enables instant communication worldwide, allowing messages to be sent in seconds.
Social Networking: Sites like Facebook and Instagram allow people to connect, communicate, and share experiences with others worldwide.
E-Commerce (Online Shopping): Online shopping platforms, such as Amazon, eBay, and Flipkart, allow consumers to purchase products from home.
Entertainment: Offers various forms of entertainment, such as streaming movies, playing games, and accessing music.
Information: The Internet provides access to information on nearly any topic, with resources from universities, banks, and global organizations.
Business Tools: Supports online tools for business management, such as online banking and productivity applications, enhancing efficiency and accessibility for users.

Accessing the Internet
Dial-up Connection:
A dial-up connection connects a computer to the Internet using a public switched telephone network (PSTN). This type of connection is temporary and requires dialing a phone number to establish a connection.
Features of a Dial-up Connection:
- Ties up the telephone line: Using the Internet blocks the phone line, making it unavailable for calls.
- Low speed: Maximum speed is around 56 Kbps.
- Limited connectivity: The Internet connection is not continuous and must be dialed each time.
- Good availability: Only requires a standard telephone line, with no additional infrastructure needed.
- Not suitable for high-speed activities: Lacks the speed necessary for online gaming or video chat.
Broadband Connection
High-speed Internet that combines "broad" and "bandwidth," delivering speeds of 512 Kbps or more, allowing faster page loading than dial-up.
Features of a Broadband Connection:
- High-speed data transfer: Supports large data volumes quickly.
- Faster than dial-up: Delivers much higher speeds.
- Continuous connection: Stays connected without needing to redial, with no extra charges.
- Simultaneous phone use: Allows phone calls during Internet use.
- Lower running costs: More economical for regular users than dial-up.
- Flexible plans: Options tailored for continuous users and businesses.
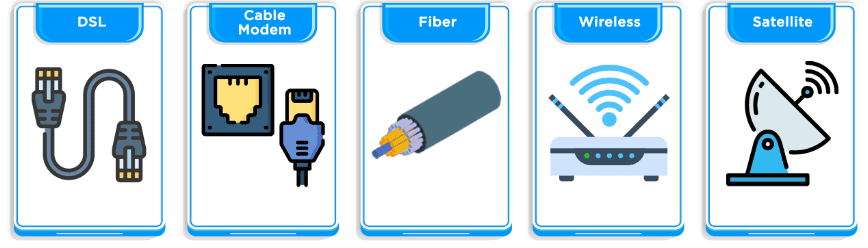
 Types of Broadband Connection
Types of Broadband Connection
Wireless Connection
Data transfer using Wi-Fi signals (radio frequency waves), requiring no physical cables. Devices need a wireless adapter to connect to Wi-fi.
Advantages of Wireless Connection:
- Access: Simplifies device mobility; devices can connect anywhere within the Wi-Fi range.
- Tidiness: Reduces cable clutter; supports shared access to printers and other devices.
- Easier upgrading: Adding new devices is simpler and more affordable than in wired networks.
- Connect on the go: Laptops with data cards can access the Internet while traveling, enhancing mobility.
Connecting Your PC to the Internet (Using Broadband)
Requirements:
- ISP subscription
- Modem (DSL or similar)
- Ethernet/phone cables
- Installation/PC suite disc (if needed)

Steps:
- Plug the modem into an electrical outlet.
- Connect the phone line: Plug one end of the phone cable into the WAN port on the modem and the other end into the wall jack (no DSL filter for DSL users).
- Connect the modem to the computer: Use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem’s LAN port to the computer (skip this step for wireless).
- Open the Connect to the Internet wizard: Go to Start > Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Set up a connection or network.
- Follow the instructions to complete the setup.
Some Important Internet Terminologies
WWW
World Wide Web is a set of programs, standards, and protocols that allows multimedia and hypertext files to be created, displayed, and linked on the Internet. It was proposed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991.
The Internet is the physical network of computers all over the world. The World Wide Web is a virtual network of websites connected by hyperlinks (or “links”). Websites are stored on servers on the Internet, so the World Wide Web is a part of the internet.
Web Server
A web server is a computer that stores websites on the Internet and delivers web pages to viewers upon request.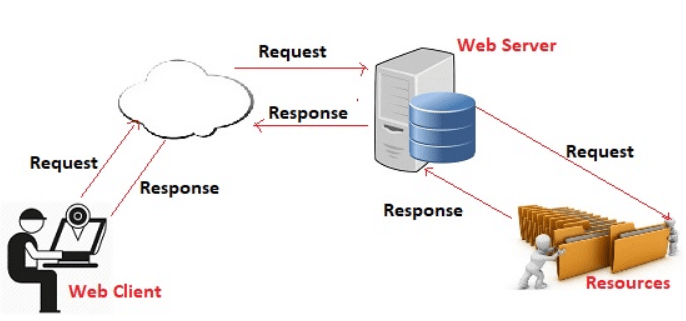
Website
A website is a collection of web pages belonging to a particular person or organization. The first page is called the homepage. From the homepage, we can visit all pages on the site. Static websites have pre-stored information while dynamic websites customise themselves frequently.
Web browser
A web browser is a piece of software that enables the user to access web pages and web apps on the internet. There are a range of browsers available, and they are usually free to download and install.
Some popular web browsers are:
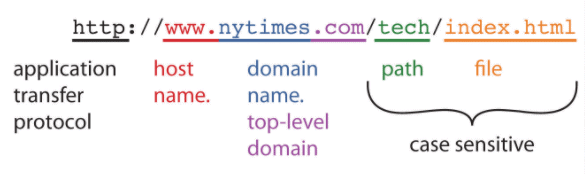
Web address
The web address allows us to identify a computer on the network. There are two systems used for identification:
- Domain Name System (DNS): A domain name is a readable computer address that identifies the location of a computer on the internet.
- Internet Protocol Addressing: A unique 32-bit address is assigned to each computer that is connected to the internet.
Example: 5.230.50.50 === www.abc.com
HTML is a computer language devised to allow website creation.
Email address: It is a unique identifier used to send and receive mail in an electronic format.
Newsgroups are similar to e-mails except that instead of sending our message to someone’s mailbox, the message is posted on a bulletin board where anyone can read it and respond.
A blog is a type of website usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of news on a particular subject, description of events, graphics or videos.
Using a newsgroup, people can share their views on any topic according to their interests. Blogs are virtual diaries created by individuals and stored on the Internet.
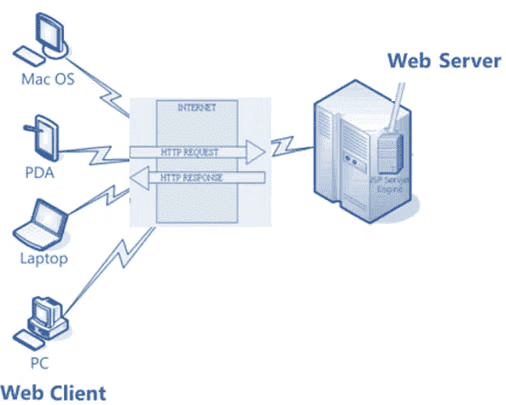
Web Client
A web client is an application that communicates with a web server using the HTTP protocol. It receives and sends information to the server.
Example: A web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox).
Characteristics: Also called a thin browser because it doesn't perform heavy tasks like querying databases or executing complex operations.Components:
- Dynamic Web Page: Generated by components running on the web server.
- Web Browser: Displays the web pages received from the server.

Know the Terms
- Hypertext: Text linked together in a complex web of associations in which the user can browse through related topics.
- Modem: A device that allows a computer to transmit information over a telephone line.
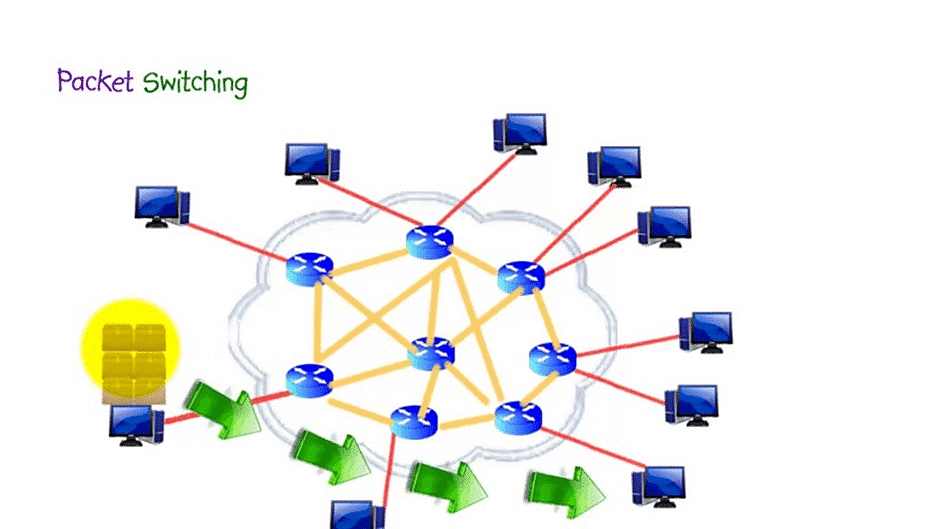
- Packet: A block of data transmitted.
- Uploading: Uploading is the transmission of data or files from a local computer to a remote computer.
- Downloading: Downloading is transmitting data or file from a remote computer to a local computer.
- ARPANET: Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
- NSF: National Science Foundation
- ISP: Internet Service Provider
- HTML: Hypertext Markup Language
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- DNS: Domain Name System

|
11 videos|49 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Internet Basics: Chapter Notes - Computer Application: Class 10
| 1. What is the Internet and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of Internet connections? |  |
| 3. What is a web browser and what are its functions? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a website and a web page? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of Internet security? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|