Q.1. What is the meaning of uploading? Give some guidelines for safe downloads. (2 Marks)
Ans: Uploading: Uploading is the transmission of data or file from a local computer to a remote computer, as from your PC to a website you are constructing. It allows users to easily exchange files over networks.
Guidelines for safe downloads:
- While downloading any file close all the applications that are running on your computer, let only one set-up file run at a time of downloading.
- Close all the important applications in order to be safe if something goes wrong while downloading. Set firewalls, and antivirus to actively scan all the files you download.
- Scan all the files after you download whether from websites or links received from e-mails.
- Always use updated antivirus, spam filter and spyware to help detect and remove virus, spyware from the application you want to download.
Q.2. Why do we need computer networks? (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) Networks enable resource sharing across the globe.
(ii) Networks provide high reliability by having alternate copies of data. Presence of multiple CPUs means that if one goes down, the others may be able to take over its work. This ability to work in the face of hardware problems is of atmost importance in military, banking, air traffic control, nuclear reactor safety, etc.
(iii) Networks enable a client/server model with clients as small computers, one per user, with data kept on one or more shared file server machines. Eg. Software installation can be on server and this can save cost of buying license for every machine.
Q.3. How are files downloaded? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Downloading is transmitting data or file from a remote computer to a local computer.
- Downloading enables users to save files on their own computers. These files are downloaded using FTP (File Transfer Protocol).
- We can also use HTTP to download files from the web.
- From the internet client/user’s point of view, to download a file is to request it from another computer or from a web page on another computer and then receive or retrieve it.
Q.4. What is LAN? (2 Marks)
Ans: A LAN (Local Area Network) connects network devices over a relatively short distance. A networked office building, school, or home usually contains a single LAN, though sometimes one building will contain a few small LANs (perhaps one per room), and occasionally a LAN will have span a group of nearby buildings.
In addition to operating in a limited space, LANs are also typically owned, controlled, and managed by a single person or organisation. They also tend to use certain connectivity technologies, primarily, Ethernet and Token Ring.
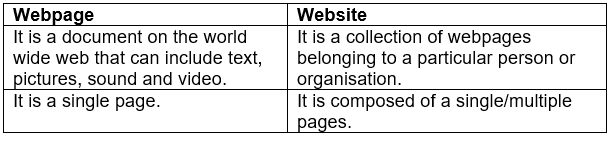
Q.5. What are the differences between a webpage and website? (2 Marks)
Ans:

Q.6. What is WAN? (2 Marks)
Ans: A WAN (Wide Area Network) spans a large physical distance. The Internet is the largest WAN, spanning the Earth.
A WAN is a geographically-dispersed collection of LANs. A network device called a router connects LANs to a WAN. In IP networking, the router maintains both a LAN address and a WAN address.
WANs tend to use technology like ATM, Frame Relay and X.25 for connectivity over the longer distances.
Q.7. What is the structure of a URL? (2 Marks)
Ans: The URL contains 4 parts :
(i) The type of service that the resource is served by HTTP, FTP, etc.
(ii) The domain name of the site.
(iii) The internet port number of the service.
(iv) The location of the resource in the directory structure of the server.
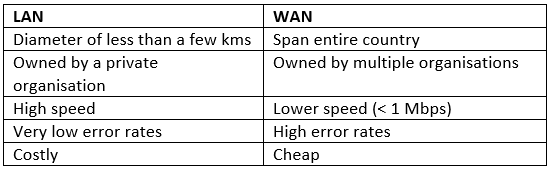
Q.8. Differentiate between LAN and WAN. (2 Marks)
Ans:

Q.9. List some advantages of blogs. (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) Blog sites can be developed with the help of simple procedures.
(ii) A blog can be read by anyone.
(iii) It improves writing skills of blogger.
(iv) It allows us to get feedback on our thoughts.
Q.10. What is MAN? (2 Marks)
Ans: A MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) is a network spanning a physical area larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, such as a city. A MAN is typically owned and operated by a single entity such as a government body or large corporation. This is often the case for hospitals that need to connect treatment facilities, out-patient facilities, doctor’s offices, labs, and research offices for access to centralized patient and treatment information.
Q.11. List some disadvantages of blogs. (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) It involves a lot of time.
(ii) Sometimes, people just blog with sloppy writing.
(iii) There is no confidentiality as it is a public forum.
(iv) Some people might give negative feedback in a harsh way.
Q.12. What is an IP address? (2 Marks)
Ans: Every machine in a network has a unique identifying number, called its IP Address. An IP address is a group of four bytes (or 32 bits) each of which can be a number from 0 to 255. A typical IP address looks like this: 59.177.134.72
Q.13. What are the different types of newsgroups? (2 Marks)
Ans: The three major types of newsgroups are:
(i) Standard newsgroups: These include highquality discussions which cannot be established without a formal voting procedure. Hierarchies – Comp, Sci, Soc, News, Rec, Talk, Misc.
(ii) Alt Newsgroups: These include the discussions which can be established by anyone with the requisite technical knowledge.
(iii) Biz Newsgroups: These include the discussions on commercial uses.
Q.14. What is a Website? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Website is a set of related web pages containing content such as text, images, video, audio, etc.
- A website is hosted on at least one web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local area network through an Internet address known as a Uniform Resource Locator.
- All publicly accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web.
Q.15. What are the types of IP addresses? (2 Marks)
Ans: IP addresses are of two types:
(i) Static IP Address: Static IP addresses are those types of IP address that never change once they are assigned to a device on a network. No doubt this type of addressing is cost effective but could have a high security risk. Static IP addresses are mostly used by web, email and gaming servers who don’t care much about hiding their locations.
(ii) Dynamic Address: A Dynamic IP address changes each time the device logs into a network. This kind of IP address is very tough to trace and are used by companies and business firms.
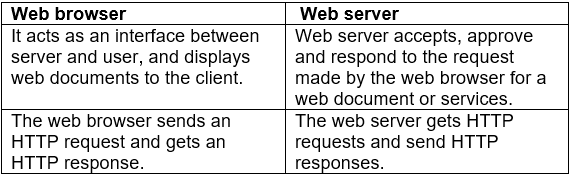
Q.16. Differentiate between Web browser and Web server. (2 Marks)
Ans: Differences between Web browser and Web server are as follows:

Q.17. Write a short note on MAC address. (2 Marks)
Ans: Each NIC (Network Interface Card) has a universally unique address assigned to it by its manufacturer. This address is known as the MAC (Media Access Control) address of the card. It means that a machine with a NIC can be identified uniquely through its NIC’s MAC address.
MAC address of an NIC is permanent and does never change. MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal (6 bytes or 48 bit) numbers. By convention, MAC addresses are usually written in one of the following two formats:
MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
MM-MM-MM-SS-SS-SS
Q.18. What is Web Hosting? (2 Marks)
Ans: A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service that allows individuals and organizations to make their website accessible via the World Wide Web.
Web hosts are companies that provide space on a server, owned or leased, for use by clients, as well as providing internet connectivity, typically in a data center.
There are 4 major types of web hosting:
(a) Free hosting
(b) Virtual or Shared hosting
(c) Dedicated hosting
(d) Colocation hosting
Q.19. What is DNS? (2 Marks)
Ans: It is practically impossible for a person to remember the IP addresses of all the computers one may have to communicate with. Therefore, a system has been developed which assigns names to some computers (web servers) and maintains a database of these names and corresponding IP addresses. These names are called Domain Names. Example: cbse.nic.in, sikkimipr.org, indianrailway.gov.in.
Q.20. Differentiate between a website and a web portal. (2 Marks)
Ans: Website is a location on the Internet, publicly accessible with a unique URL (web address). Webportal is a private location on the Internet, accessible with a unique URL (web address) and unique username and password.
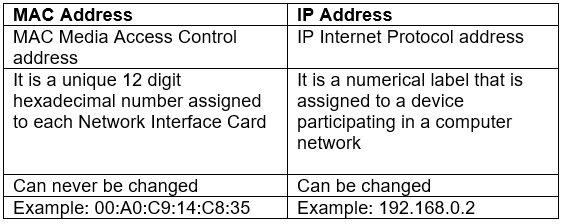
Q.21. Distinguish between MAC address and IP address with the help of example of each. (2 Marks)
Ans: