Introduction to 3D Geometry | Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics PDF Download
Understanding the 3D Geometry
We can understand any 3D space in terms of 3 coordinates- x, y, and z.
Vectors
Vectors are the Fundamental Unit of 3D Operations. In physics, Vectors are quantities having both magnitude and distance. In mathematics, especially in 3D geometry, a vector is a directed entity that connects 2 or more points. A position vector is a special type of vector that connects the origin O(0,0,0) to the point, as shown below:
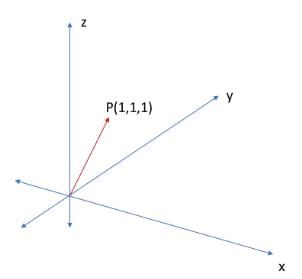
Here, we have the position vector P, defined by an arrow from O(0,0,0) to P(1,1,1). Note that the starting point of the vector is defined as the tail of the vector, and the ending point of the vector is defined as the head of the vector. The direction of any vector is always from tail to head.
In physics, we have a special kind of vector known as a displacement vector. A displacement vector is used to quantify the vector between 2 points. A position vector is actually a special kind of displacement vector.
Magnitude of a Vector
The magnitude of a vector is a measure of how long a vector is. Consider a vector whose tail is given by T(x1, y1, z1) and whose head is given by H(x2, y2, z2). If we define this vector as V, then the magnitude of the vector is denoted as |V|, where:
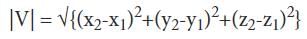
Example: Calculate the magnitude of a vector whose tail is given by (1,2,3), and whose head is given by (4,5,6)
Solution: In the given example, we have:
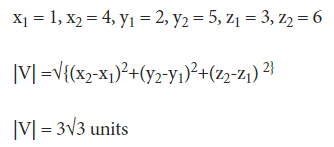
Example: Calculate the magnitude of a vector whose tail is (-1,-4,3), and whose head is (4,7,-2)
Solution: In the given example, we have:
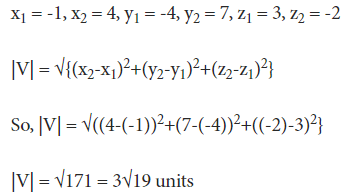
A unit vector is any vector that has a magnitude of 1.
Components of a Vector
If we consider a Cartesian coordinate system, any vector can be defined in terms of 3 components. We can define the notation of any vector as:
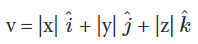
Where 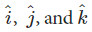 are the unit vectors along the x, y and z-axes respectively, and |x|, |y|, and |z| denote the length of the components of the vector along these axes respectively. The magnitude of a vector V, is
are the unit vectors along the x, y and z-axes respectively, and |x|, |y|, and |z| denote the length of the components of the vector along these axes respectively. The magnitude of a vector V, is 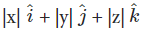 can be denoted as |V|, where,
can be denoted as |V|, where,
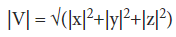
Example: Calculate the x, y, and z components of the vector 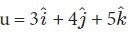 as well as the magnitude of the vector.
as well as the magnitude of the vector.
Solution: In the above problem, we have |x| = 3, |y| = 4, and |z| = 5
x-component = 3, y-component = 4, z-component = 5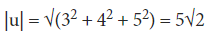
More Solved Examples for You
Question: The point (0, -2, 5) lies on the:
X-axis
Y-axis
XY-plane
YZ-plane
Solution: Option D. Given Point is (0, -2, 5). The X co-ordinate of the point is 0. Thus, the point lies in the YZ-plane.
|
2 videos|44 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to 3D Geometry - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics
| 1. What is 3D geometry in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are some common 3D geometric shapes? |  |
| 3. How is 3D geometry different from 2D geometry? |  |
| 4. How is 3D geometry used in real life? |  |
| 5. What are some key concepts in 3D geometry? |  |






















