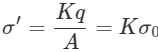JEE Advanced (Assertion-Reason Type): Electrostatics | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Q.1. Assertion: The coulomb force is the dominating force in the universe.
Reason: The coulomb force is weaker than the gravitational force.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
Gravitational force is the dominating force in nature and not coulomb's force. Gravitational force is the weakest force. Also, Coulomb's force >> gravitational force.
Q.2. Assertion: A metallic shield in form of a hollow shell may be built to block an electric field.
Reason: In a hollow spherical shield, the electric field inside it is zero at every point.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
In a hollow spherical shield, the charge is present only on its surface but charge is zero at every point inside the hollow sphere. Hence, the metallic shield in form of hollow shell may be built to block an electric field.
Q.3. Assertion: Electrons move away from a low potential to high potential region.
Reason: Because electrons has negative charge
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Electron has negative charge, in electric field negative charge moves from lower potential to higher potential.
Q.4. Assertion: A parallel plate capacitor is connected across battery through a key. A dielectric slab of constant K is introduced between the plates. The energy which is stored becomes K times.
Reason: The surface density of charge on the plate remains constant or unchanged.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
In the given case V = V0 (constant) Energy stored in the capacitor = 1/2cv2. So energy stored will become A times Q = CV, so Q will become K times of Surface charge density
Q.5. Assertion: Electric lines of force cross each other.
Reason: Electric field at a point superimpose to give one resultant electric field.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (e)
If electric lines of forces cross each other, then the electric field at the point of intersection will have two direction simultaneously which is not possible physically.
Q.6. Assertion: If a proton and an electron are placed in the same uniform electric field. They experience different acceleration.
Reason: Electric force on a test charge is independent of its mass.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Electron and proton have same amount of charge so they have same coulomb force. They have different accelerations because they have different masses (a = F/m). Therefore, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Q.7. Assertion: When charges are shared between any two bodies, no charge is really lost, but some loss of energy does occur.
Reason: Some energy disappears in the form of heat, sparking etc.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Charge is always conserved but energy is lost in the term of heat.
Q.8. Assertion: Annihilation of electron and positron is an example of decay of charges.
Reason: In the process of annihilation an electron and a positron combine to give a gamma particle.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (e)
It is an example of conversation of charges.
Q.9. Assertion: Surface of a symmetrical conductor can be treated as equipotential surface.
Reason: Charges can easily flow in a conductor.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Potential is constant on the surface of a sphere so it behaves as an equipotential surface.
Q.10. Assertion: Surface of a symmetrical conductor can be treated as equipotential surface
Reason: Charges can easily flow in a conductor.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Potential is constant on the surface of a sphere so it behaves as an equipotential surface.
Q.11. Assertion: The capacity of a given conductor remains same even if charge is varied on it.
Reason: Capacitance depends upon nearly medium as well as size and shape of conductor.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Capacitance is basically a geometrical quantity.
Q.12. Assertion: Charge is quantized
Reason: Charge, which is less than 1 C is not possible
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q=±ne and charge lesser than 1 C is possible.
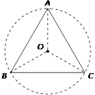
Q.13. Assertion: Three equal charges are situated on a circle of radius r such that they form on equilateral triangle, then the electric field intensity at the centre is zero.
Reason: The force on unit positive charge at the centre, due to the three equal charges are represented by the three sides of a triangle taken in the same order. Therefore, electric field intensity at centre is zero.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Resultant of electric intensity at O due to B and C is equal and opposite to that due to A.
Q.14. Assertion: On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric field decreases at the same rate in both the cases.
Reason: Electric field is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge or an electric dipole.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
The rate of decrease of electric field is different in the two cases. In case of a point charge, it decreases as 1/r2 but in the case of electric dipole it decreases more rapidly, as E ∝ 1/r3
Q.15. Assertion: The whole charge of a conductor cannot be transferred to another isolated conductor.
Reason: The total transfer of charge from one to another is not possible.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
The whole charge of a conductor can be transferred to another isolated conductor, if it is placed inside the hollow insulated conductor and connected with it.
Q.16. Assertion: Conductors having equal positive charge and volume, must also have same potential.
Reason: Potential depends only on charge and volume of conductor.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
Electric potential of a charged conductor depends not only on the amount of charge and volume but also on the shape of the conductor. Hence if their shapes are different, they may have different electric potential.
Q.17. Assertion: At a point in space, the electric field points towards north. In the region, surrounding this point the rate of change of potential will be zero along the east and west.
Reason: Electric field due to a charge is the space around the charge.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Since the electric field is directed from south to north hence rate of change of potential will be along this direction, but it is zero along east and west.
Q.18. Assertion: A point charge is brought in an electric field. The field at a nearby point will increase, whatever be the nature of the charge.
Reason: The electric field is independent of the nature of charge.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
Electric field at the nearby point will be resultant of existing field and field due to the charge brought. It may increase or decrease if the charge is positive or negative depending on the position of the point with respect to the charge brought.
Q.19. Assertion: The lightening conductor at the top of high building has sharp pointed ends.
Reason: The surface density of charge at sharp points is very high resulting in setting up of electric wind.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
A charged cloud induces opposite charge on pointed conductors. At sharp points of the conductor surface density of charge is very high and charge begins to leak from the pointed ends by setting up oppositely charged electric wind. This wind, when comes in contact with the charged cloud, neutralizes some of its charge lowering the potential difference between the cloud and the building. This reduces the chances of lightening striking the building [if the lightening strikes the building, the charge is conducted to the earth and the building remains safe].
Q.20. Assertion: Circuit containing capacitors should be handled cautiously even when there is no current.
Reason: The capacitors are very delicate and so quickly break down.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
A charged capacitor, after removing the battery, does not discharge itself. If this capacitor is touched by someone, he may feel shock due to large charge still present on the capacitor. Hence it should be handled cautiously otherwise this may cause a severe shock.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|