JEE Advanced (Fill in the Blanks): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Fill in the Blanks
Q.1. Formic acid when heated with conc. H2SO4 pr oduces ............... . (1983 - 1 Mark)
Ans. CO
Solution. 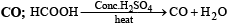
Q.2. Fehling’s solution ‘A’ consists of an aqueous solution of copper sulphate, while Fehling’s solution ‘B’ consists of an alkaline solution of .............. (1990 - 1 Mark)
Ans. sodium potassium tartarate
Solution. sodium potassium tartarate.
Q.3. The structure of the intermediate product, formed by the oxidation of toluene with CrO3 and acetic anhydride, whose hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde is ............... (1992 - 1 Mark)
Ans. C6H5CH(OCOCH3)2
Solution. C6H5CH(OCOCH3)2 benzylidene acetate
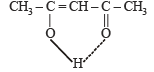
Q.4. The structure of the enol form of CH3–CO–CH2–CO–CH3 with intramolecular hydrogen bonding is .................. (1993 - 1 Mark)
Ans.
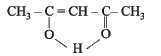
Solution.
True / False
Q.1. Benzaldehyde undergoes aldol condensation in an alkaline medium. (1982 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Benzaldehyde has no a-hydrogen atom hence it does not undergo aldol condensation but undergoes Cannizzaro reaction.
Q.2. Hydrolysis of an ester in presence of a dilute acid is known as saponification. (1983 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Saponification is alkaline hydrolysis of esters.
Q.3. The yield of ketone when a secondary alcohol is oxidized is more than the yield of aldehyde when a primary alcohol is oxidized. (1983 - 1 Mark)
Ans. T
Solution. True : Aldehydes (from primary alchols) may further be oxidised easily to acids as compared to ketones (from secondary alcohols).
Q.4. The reaction of methyl magnesium iodide with acetone followed by hydrolysis gives secondary butanol. (1987 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Grignard reagents react with ketones to form teralcohols; hence here ter-butanol will be formed.
Q.5. The boiling point of propionic acid is less than that of n-butyl alcohol, an alcohol of comparable molecular weight. (1991 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : H-bonding in propionic acid is stronger (carboxylic acids can form dimers) than that in butanol.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















