JEE Advanced (Fill in the Blanks): Probability | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. For a biased die the probabilities for the different faces to turn up are given below :
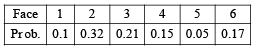
This die is tossed and you are told that either face 1 or face 2 has turned up. Then the probability that it is face 1 is ................... (1981 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let E1 ≡ face 1 has turned up,E2 ≡ face 1 or 2 has turned up.
By the given data P (E2) = 0.1 + 0.32 = 0.42, P (E1 ∩ E2) = P(E1) = 0.1
Given that E2 has happened and we have to find the probability of happening of E1.
∴ By conditional probability theorem, we have

Q.2. P( A ∪ B) = P( A∩B) if and only if th e relation between P(A) and P(B) is ................... (1985 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Given that P (A ∪ B) = P (A ∩ B) ⇒ P (A) + P (B) – P (A ∩ B ) = P (A ∩ B)
⇒ [P (A) – P (A ∩ B)] + [P(B) – P (A ∩ B)] = 0
But P (A) – P (A ∩ B), P (B) – P (A ∩ B) ≥ 0 [Q P (A ∩ B) ≤ P (A), P (B)]
⇒ P (A) – P (A ∩ B) = 0 and P (B) – P (A ∩ B) = 0 [Q Sum of two non-negative no’s can be zero only when these no’s are zeros]
⇒ P (A) = P (B) = P (A ∩ B)
Q.3. A box contains 100 tickets numbered 1, 2, ... .., 100. Two tickets are chosen at random. It is given that the maximum number on the two chosen tickets is not more than 10. The minimum number on them is 5 with probability ................... (1985 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let A be the event that max. number on the two chosen tickets in not more than 10, and B is the event that min. number on them is 5. We have to find P (B / A).
We know that 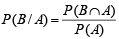
Total ways to select two tickets out of 100 = 100C2.
Number of ways favourable to A = number of ways of selecting any 2 numbers from 1 to 10 = 10C2 = 45
A ∩ B contains one number 5 and other greater than 5 and ≤ 10
So ways favourable to A ∩ B = 5C1 = 5 Therefore, 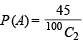 and
and 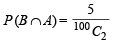
Thus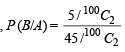
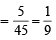
Q.4. If 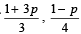
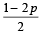 are the probabilities of three mutually exclusive events, then the set of all values of p is ................... (1986 - 2 Marks)
are the probabilities of three mutually exclusive events, then the set of all values of p is ................... (1986 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let 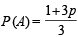 ,
, 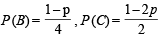
As A, B and C are three mutually exclusive events
∴ P (A) + P (B) + P (C) ≤ 1
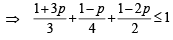
⇒ 4 + 12p + 3 – 3p + 6 – 12p ≤ 12
⇒ 3p ≥ 1 ⇒ p ≥ 1 /3 … (i)
Also 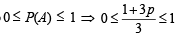
⇒ 0 ≤ 1 + 3p ≤ 3
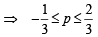 … (ii)
… (ii)
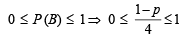
⇒ 0 ≤ 1 – p ≤ 4
⇒ – 3 ≤ p ≤ 1 … (iii)
0 ≤ P (C) ≤ 1 ⇒ 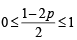
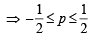 … (iv)
… (iv)
Combining (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get 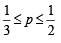
Q.5. Urn A contains 6 red and 4 black balls and urn B contains 4 red and 6 black balls. One ball is drawn at random from urn A and placed in urn B. Then one ball is drawn at random from urn B and placed in urn A. If one ball is now drawn at random from urn A, the probability that it is found to be red is ................... (1988 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. There may be following cases: Case I : Red from A to B and red from B to A then prob. of
drawing a red ball from 
Case II : Red from A to B and black from B to A then prob. of drawing a red from 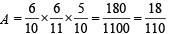
Case III : Black from A to B and red from B to A then prob. of drawing red from 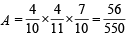
Case IV : Black from A to B and black from B to A then prob. of drawing red from 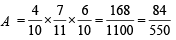
∴ The required prob 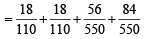
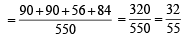
Q.6. A pair of fair dice is rolled together till a sum of either 5 or 7 is obtained. Then the probability that 5 comes before 7 is ................... (1989 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Probability of getting a sum of 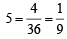 = P(A) as favourable cases are {(1, 4), (4, 1), (2, 3), (3, 2) } Similarly favourable cases of getting a sum of 7 are {(1, 6), (6, 1), (2, 5), (5, 2), (3, 4), (4, 3)} = 6
= P(A) as favourable cases are {(1, 4), (4, 1), (2, 3), (3, 2) } Similarly favourable cases of getting a sum of 7 are {(1, 6), (6, 1), (2, 5), (5, 2), (3, 4), (4, 3)} = 6
∴ Prob. of getting a sum of 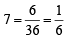
∴ Prob. of getting a sum of 5 or 7
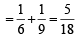 [as events are mutually exclusive.]
[as events are mutually exclusive.]
∴ Prob of getting neither a sum of 5 nor of 7 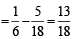
Now we get a sum of 5 before a sum of 7 if either we get a sum of 5 in first chance or we get neither a sum of 5 nor of 7 in first chance and a sum of 5 in second chance and so on.
Therefore the required prob. is
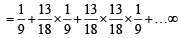
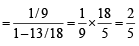
Q.7. Let A and B be two events such that P (A) = 0.3 and P ( A ∪ B) = 0.8. If A and B are independent events then P (B) = ................... (1990 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. P (A ∪ B) = 0.8
⇒ P (A ∪ B) = P (A) + P (B) – P (A ∩ B)
⇒ P (A ∪ B) = P (A) + P (B) – P (A) P (B)
[As A and B are independent events]
⇒ 0.8 = 0.3 + P (B) – 0.3 P (B)
⇒ 0.5 = 0.7 P (B) ⇒ P (B) = 5/7
Q.8. If the mean and the variance of a binomial variate X are 2 and 1 respectively, then the probability that X takes a value greater than one is equal to ................... (1991 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. For a binomial distribution, we know, mean = np and variance = npq
∴ np = 2; npq = 1 ⇒ q = 1/2 ⇒ p = 1/2 and n = 4
∴ P (X > 1) = P (X = 2) + P (X = 3) + P (X = 4)
= 1– P (X = 0) – P (X = 1)
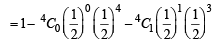
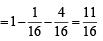
Q.9. Three faces of a fair die are yellow, two faces red and one blue. The die is tossed three times. The probability that the colours, yellow, red and blue, appear in the first, second and the third tosses respectively is .....................(1992 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Sample space = {Y, Y,Y, R, R, B} where Y stands for yellow colour, R for red and B for blue.
Prob. that the colours yellow, red and blue appear in the first second, and third tosses respectively 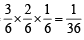
Q.10. If two events A and B are such that P(Ac) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.4 and P ( A ∩B c) = 0.5, then P(B/(A ∪ Bc)] = ................... (1994 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Given that P (Ac) = 0.3, P (B) = 0.4 and P (A ∩ Bc) = 0.5 then P [B/ (A ∩ Bc)] = 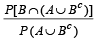
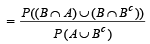
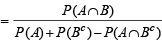
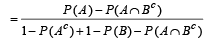
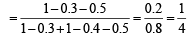
|
481 docs|964 tests
|





















