JEE Advanced (Matrix Match & Integer Answer): Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles & Technique | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :
If the correct matches are A-p, s and t; B-q and r; C-p and q; and D-s then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the given.

Q.1. Given below are certain matching type questions, where two columns (each having 4 items) are given. Immediately after the columns the matching grid is given, where each item of Column I has to be matched with the items of Column II, by encircling the correct match(es). Note that an item of Column I can match with more than one item of Column II. All the items of Column II must be matched. Match the following :
Column I Column II
(A) C6H5CH2CD2Br on reaction with C2H5O– gives (p) E1 reaction
C6H5–CH=CD2
(B) PhCHBrCH3 and PhCHBrCD3, both react with (q) E2 reaction
the same rate
(C) C6H5CH2CH2Br on treatment with C2H5O– and (r) E1cB reaction
C2H5OD gives C6H5CD=CH2
(D) C6H5CH2CH2Br reacts faster than C6H5CD2CH2Br (s) First order reaction
on reaction with C2H5O– in ethanol
Ans. (A) - (q), (B) - (p, s), (C) - (r, s), (D) - (q)
Solution. E1 mechanisms are encountered only with tertiary or secondary substrates and in presence of either a weak base or a base in low concentration. So primary substrates will follow E2 mechanism, i.e. (A) → E2 and (D) → E2.
Further E1 mechanism (similar to SN1) proceeds by first order kinetics and is determined by the slower (first) step of the formation of carbocation. Hence (B)→E1 and first order reaction.
NOTE THIS STEP : Reaction of C6H5CH2CH2Br on treatment with C2H5O– in presence of C2H5OD gives C6H5CD = CH2.
This reaction follows E1CB (Elimination unimolecular conjugate base) mechanism. This 2 step mechanism follows the following path :
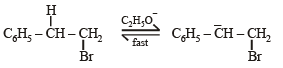
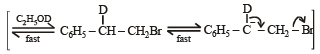
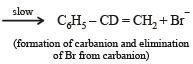
Although this mechanism involves 2 steps the overall rate of the reaction is limited to the slower second step and hence the rate of reaction depends only on the concentration of the carbanion, i.e. first order reaction. Hence, (C) → (r), (s).
Q.2. Match the compounds/ions in Column I with their properties/reactions in Column II. Indicate your answer by darkening the appropriate bubbles of the 4 × 4 matrix given in the ORS.
Column I Column II
(A) C6H5CHO (p) gives precipitate with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
(B) CH3C ≡ CH (q) gives precipitate with AgNO3
(C) CN– (r) is a nucleophile
(D) I– (s) is involved in cyanohydrin formation
Ans. (A) - (p, s); (B) - (q); (C) - (q, r, s); (D) - (q, r )
Solution. (A) C6H5CHO forms ppt. of 2, 4-dibromophenylhydrazone (p), forms silver mirror with ammonical silver nitrate – Tollen's reagent (q), forms cyanohydrin with CN– (s).
(B) CH3C ≡ CH gives ppt. with AgNO3 (q)
(C) CN– reacts with AgNO3 to form ppt. of AgCN (q), it is a nucleophile (r) and forms cyanohydrin (s)
(D) I– gives ppt. of AgI with AgNO3 (q), and it is a nucleophile (r)
Q.3. Match each of the compounds given in Column-I with the reaction(s), that they can undergo, given in Column-II.
Column-I Column-II
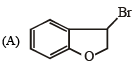 (p) Nucleophilic substitution
(p) Nucleophilic substitution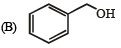 (q) Elimination
(q) Elimination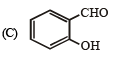 (r) Nucleophilic addition
(r) Nucleophilic addition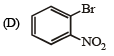 (s) Esterification with acetic anhydride
(s) Esterification with acetic anhydride
(t) Deh ydrogenation
Ans. (A) - (p,q,t); (B) - (p,s,t); (C) - (r,s); (D) - (p)
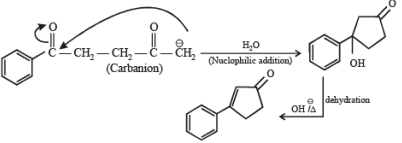
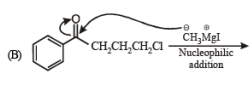
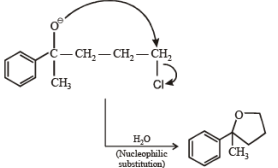
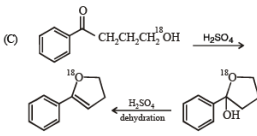
Solution.
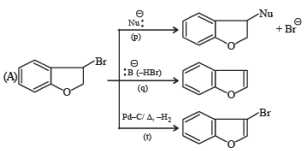
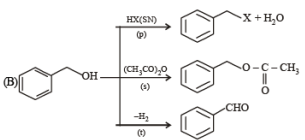
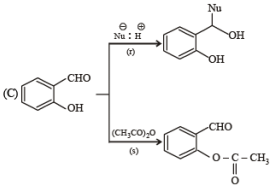
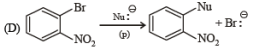
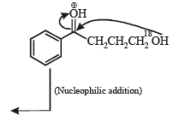
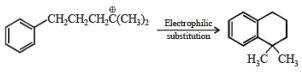
Q.4. Match the reactions in Column I with appropriate types of steps/reactive intermediate involved in these reactions as given in Column II.
Column I Column II
 (p) Nucleophilic substitution
(p) Nucleophilic substitution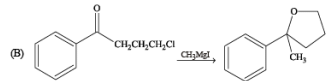 (q) Electrophilic substitution
(q) Electrophilic substitution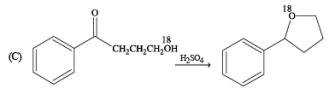 (r) Dehydration
(r) Dehydration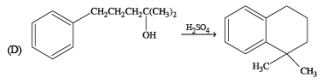 (s) Nucleophilic addition
(s) Nucleophilic addition
(t) Carbanion
Ans. (A) - (r,s,t); (B) - (p,s); (C) - (r,s); (D) - (q,r)
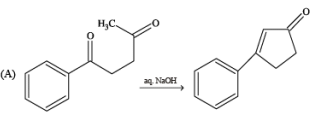
Solution.
(A)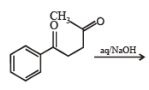
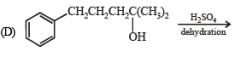
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















