JEE Advanced (Matrix Match & Integer Answer):Thermodynamics | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
DIRECTION : Question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :

If the correct matches are A-p, s and t; B-q and r; C-p and q; and D-s then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the given.
Q.1. Match the transformations in column I with appropriate options in column II (2011)
Column-I Column-II
(A) CO2 (s) → CO2 (g) (p) phase transition
(B) CaCO3 (s) → CaO(s)+ CO2 (g) (q) allotropic change
(C) 2Hg → H2 (g) (r) ΔH is positive
(D) P(white, solid) → P(red, solid) (s) ΔS is positive (t) ΔS is negative
Ans. Sol. A – p, r, s ; B – r, s ; C – t ; D – p, q, t
(A) CO2 (s) → CO2 (g) It is phase transition. The process is endothermic (sublimation). Gas is produced, so entropy increases.
(B) On heating CaCO3 decomposes. So, process is endothermic.
The entropy increases as gaseous product is formed.
(C) 2H• → H2(g) Entropy decreases as number of gaseous particles decreases.
(D) It is phase transition.
White and red P are allotropes.
Red P is more stable than white.
So ΔH is –ve.
DIRECTION : Question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :
Q.2. Match the thermodynamic processes given under Column-I with the expressions given under Column-II. (JEE Adv. 2015)
Column-I Column-II
(A) Freezing of water at 273 K and 1 atm (p) q = 0
(B) Expansion of 1 mol of an ideal gas into a vacuum under isolated conditions (q) w = 0
(C) Mixing of equal volumes of two ideal gases at constant temperature and pressure (r) ΔSsys < 0 in an isolated container
(D) Reversible heating of H2(g) at 1 atm from 300 K to 600 K, followed by reversible (s) ΔU = 0 cooling to 300 K at 1 atm
(t) ΔG = 0
Ans. Sol. A- (r, t); B -(p, q, s); C -(p, q, s); D- (p, q, s, t) (A) → r,t
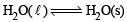
It is at equilibrium at 273 K and 1 atm So ΔSsys is negative As it is equilibrium process so ΔG = 0
(B) → p, q, s
Expansion of 1 mole of an ideal gas in vacuum under isolated condition
Hence, w = 0 and qp = CpdT (∵dT = 0) ⇒ q = 0
ΔU = CvdT (∵dT = 0) ΔU = 0
(C) → p, q, s
Mixing of two ideal gases at constant temperature
Hence, DT = 0
∴ q = 0; ΔU = 0 also w = 0
(ΔU = q + w)
(D) → p, q, s, t
Reversible heating and cooling of gas follows same path also initial and final position is same.
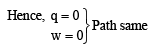

|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















