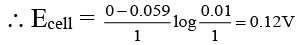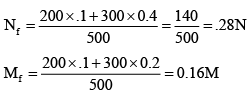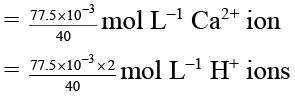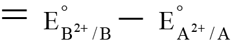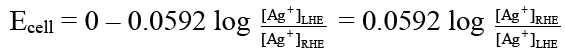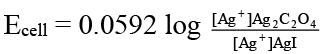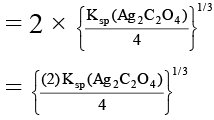JEE Advanced (One or More Correct Option): Electrochemistry | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Which of the following compound (s) do not conduct electricity in their molten state?
(a) MgCl2
(b) BeCl2
(c) BeF2
(d) MgF2
Correct Answer is option (b and c)
The values of E0 of some reactions are given
I2 + 2e- → 2I- E0 = 0.54 volts
Sn+4 + 2e- → Sn2+ E0 = 0.152 volts
Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl- E0 = 1.36 volts
Fe+3 + e- → Fe2+ E0 = 0.76 volts
Ce+4 + e- → Ce3+ E0 = 1.6 volts
Hence
(A) Fe3+ oxidizes Ce+3
(B) Ce4+ can oxidize Fe2+
(C) Sn2+ will reduce Fe3+ to Fe2+
(D) Cl2 will be liberated from KCl by passing I2.
Q.2. Select the correct statement(s) for the concentration cell.
(a) For the cell Cu/CuSO4 (xM) : CuSO4(yM)/Cu material transfers from a more concentrated to diluted solution
(b) ΔG for the overall reaction of concentration cell is the measure of diffusion of electrolyte
(c) Solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt can be measured by setting up a concentration cell
(d) The E.M.F of cell Ag/AgNO3 (0.01M) : AgNO3(1N)/Ag is approx. 0.059V.
Correct Answer is option (a, b and c)
In conc. cell electrical energy is obtained by concentration difference alone without any chemical reaction.
For the cell A/AgNO3(0.01M) : : : Ag(NO3(1M)/Ag
Net cell reaction is
Ag+ (1M) → Ag+ (0.01M)
Q.3. As dilution takes place
(a) Molar conductivity increases
(b) Conductance increases
(c) Ionic mobility increases
(d) Specific conductance increases
Correct Answer is option (a, b and c)
(A), (B) and (C) explain: On dilution the molarity of the solution decreases and hence molar conductivity increases. So choice (A) is correct.
(B) As dilution increases, the conductance of the solution increases because interionic forces of attraction are broken. Hence, choice (b) is correct.
(C) On dilution, ionic mobility increases due to decrease in interionic forces of attraction, hence (C) is correct.
(D) But the conducting power of ions per cubic centimetre decreases, hence specific conductance decreases. As volume of solution increases.
Hence, choice (d) is incorrect.
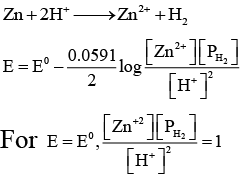
Q.4. In the following electrochemical cell
Zn | Zn2+ || H+ | Pt(H2)
Eocell = Eocell. This will be when
(a) [Zn2+] = [H+] = 1 M and PH2 = 1atm
(b) [Zn2+] = 0.01 M, [H+] = 0.1M and PH2 = 1atm
(c) [Zn2+] = 1 M, [H+] = 0.1 M and PH2 = 0.01atm
(d) [Zn2+] = [H+] = 0.1 M and PH2 = 0.1atm
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
Q.5. In Zn-Cu cell containing K2SO4 in the salt bridge
(a) Electrons flow from Cu to Zn
(b) Conventional current flows from Cu to Zn
(c) SO2–4 ions flow from Cu to Zn
(d) The weight of zinc rod decreases and copper rod increases
Correct Answer is option (b, c and d)
(B), (C) and (D) Explanation: (B), (C) and (D) are correct while (A) is not correct.
(B) is correct because electrons flow from Zn to Cu and conventional current flows from Cu to Zn.
(C) is correct because SO2–4 ions are in excess, therefore, moves from Cu to Zn.
(D) is correct because zinc metal will dissolve and its weight will keep on decreasing and weight of copper rod will keep on increasing.
Q.6. For the reduction of MnO-4 to Mn2+. E° is + 1.51V. The reduction potentials for Zn2+, Ag+, Au+ and Na+ are given as: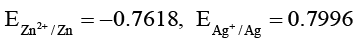
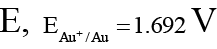 and
and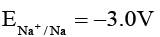
Which of these metals will be oxidized by MnO-4 ion?
(a) Zn
(b) Ag
(c) Au
(d) Na
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
Zn: 1.51V + 0.761 V = 2.27 V > 0
Ag: 1.51V – 0.7956V = 0.710V > 0
Au: 1.51V – 1.692V = –0.18V < 0
Na : 1.51 V + 3.0 V = 4.51 > 0
Q.7. 200 ml of 0.1 M NaOH is mixed with 300 ml of 0.2 M (BaOH )2 then the resulting solution has
(a) molarity = 0.16 M
(b) normality 0.28 N
(c) normality = 1.6 N
(d) molarity = 3.2 N
Correct Answer is option (a and b)
Q.8. A sample of water has a hardness expressed as 77.5 ppm Ca2+. This sample is passed through an ion exchange column and the Ca2+ is replaced by H+. Select correct statement(s)–
(a) pH of the water after it has been so treated is 2.4
(b) Every Ca2+ ion is replaced by one H+ ion
(c) Every Ca2+ ion is replaced by two H+ ions
(d) pH of the solution remains unchanged
Correct Answer is option (a and c)
Ca2+ + RH2 → CaR + 2H+
77.5 ppm = 77.5 g Ca2+ per 106 mL
= 77.5 × 10–3 g L–1 Ca2+
∴ [H+] = 3.875 × 10-3
∴ pH = -log (H+) = 2.4
Q.9. Standard electrode potential of two metals A and B are E01 and E02 respectively. When half cells A2+/A and B2+/B are connected electrons flow from A to B but when A is connected with standard hydrogen electrode electrons flow from A to standard hydrogen electrode. If magnitude of E01 and E02 are 0.25 and 0.34 volt respectively the among the following the correct statement(s) is/are -
(a) E01 for A2+ + 2e → A is -0.25 V
(b) E02 for B2+ + 2e → B is -0.34 V
(c) E0cell of the cell connecting these electrodes is 0.59 V
(d) E02 for B2+ + 2e → B is 0.34 V
Correct Answer is option (a, c and d)
The A is more oxidising than B and A is more oxidising than H2
∴ A → A2+ + 2e E01 = 0.25 V
A2+ + 2e → A E01 = -0.25 V
A → A2+ + 2e
B2+ + 2e → B
A + B2+ → A2+ + B
E0cell = 0.34 + 0.25 = 0.59 V
Q.10. Which of the following expression(s) represent the voltage of cell at 298 K:
Ag (s) | AgI (saturated solution) || Ag2C2O4 (saturated solution) | Ag(s)
(a) 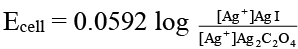
(b) 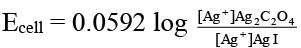
(c) 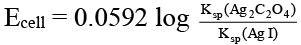
(d) 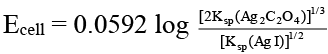
Correct Answer is option (b and d)
The given cell is concentration cell:
Ag → (Ag+) LHE + e
(Ag+) RHE + e → Ag
Net reaction: (Ag+)RHE → (Ag+)LHE
In AgI solution, [Ag+] = Ksp (AgI)1/2
In Ag2C2O4 solution [Ag+]
= [2 Ksp (Ag2C2O4)]1/3
|
446 docs|929 tests
|