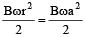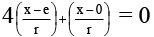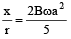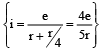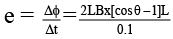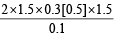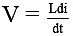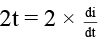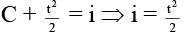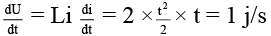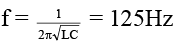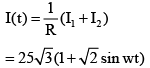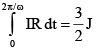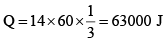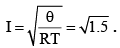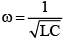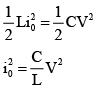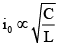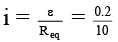JEE Advanced (One or More Correct Option): Moving Charges & Magnetism | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
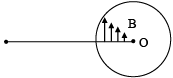
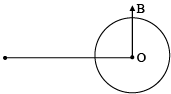
Q.1. A rectangular wire frame rotates with a constant velocity around one of its sides parallel to a current carrying & rectilinear conductor nearly as shown in diagram – (a) When rectangular wire frame is in the plane passing through rectilinear conductor flux linked through rectangular wire frame is minimum.
(a) When rectangular wire frame is in the plane passing through rectilinear conductor flux linked through rectangular wire frame is minimum.
(b) When rectangular wire frame is in the plane passing through rectilinear conductor emf induced in rectangular wire frame is minimum.
(c) When rectangular wire frame is in plane perpendicular to the plane passing through conductor then, emf is maximum.
(d) When rectangular wire frame is in plane perpendicular to the plane passing through conductor then, flux is minimum.
Correct Answer is options (b, c, d)
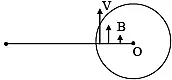
Top view
Flux is maximum
B & V are parallel so no induced emf
Flux is zero
Angle between B & V is 90°.
So max. induced emf.
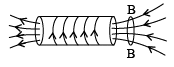
Q.2. An aluminium ring B faces an electromagnet A. The current i through A can be altered -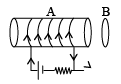 (a) If i increase, A will repel B
(a) If i increase, A will repel B
(b) If i increases, A will attract B
(c) If i decreases, A will attract B
(d) If i decreases, A will repel B
Correct Answer is options (a, c)
When i is increased flux through B increased therefore according to Lenz law current induced in B will produced in such a way that it will go away from electromagnet, similarly when current is decreased then B will come near to A.
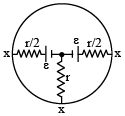
Q.3. In the figure shown, 'R' is a fixed conducting fixed ring of negligible resistance and radius 'a'. PQ is a uniform rod of resistance r. It is hinged at the centre of the ring and rotated about this point in clockwise direction with a uniform angular velocity ω. There is a uniform magnetic field of strength 'B' pointing inwards, 'r' is a stationary resistance, then -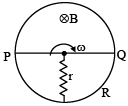 (a) Current through 'r' is zero
(a) Current through 'r' is zero
(b) Current through 'r' is 2Bωa2 / 5r
(c) Direction of current in external 'r' is from centre to circumference.
(d) Direction of current in external 'r' is from circumference to centre.
Correct Answer is options (b, d)
Equivalent circuit
Induced emf e =
(Θ Radius = a)
By nodal equation, nodal
5 x = 4e
x = 4e/5 and i =
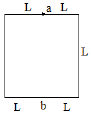
Q.4. The wire as shown in figure is bent in the shape of a tent, with θ = 60º and L = 1.50 m and is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.300 T perpendicular to the table top. The wire is rigid but hinged at points a and b. If the tent is flattened out on the table in 0.100 sec, then-
(a) Average induced emf in the wire during this time is 6.75 V.
(b) Average induced emf in the wire during this time is clockwise.
(c) Average induced emf in the wire during this time is anticlockwise.
(d) Average induced emf in the wire during this time is 2.75 V .
Correct Answer is options (a, b)
ϕi = 2Lx cos θ × B
ϕf = 2L2B
∆ϕ = 2L2B [cos θ – 1]
=
= – 6.75 volt clockwise
Q.5. A variable voltage V = 2t is applied across an inductor of inductance L = 2 Henry as shown in figure. Then -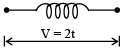 (a) current versus time graph is a parabola.
(a) current versus time graph is a parabola.
(b) energy stored in magnetic field at t = 2s is 4 joule.
(c) potential energy at time t = 1 s in magnetic field is increasing at a rate of 1 J/s.
(d) energy stored in magnetic field is zero all time.
Correct Answer is options (a, b, c)
⇒
(A) is correct= 4 joule
(B) is correct
(C) is correct
Q.6. In the circuit shown, resistance R=100Ω , inductance L=2/πH and capacitance C = 8/πμF are connected in series with an ac source of 200 volt and frequency 'f '. If the readings of the hot wire voltmeters V1 and V2 are same then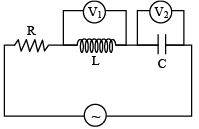 (a) f = 125 Hz
(a) f = 125 Hz
(b) f = 250 πHz
(c) current through R is 2A
(d) V1 = V2 = 1000 volt
Correct Answer is options (a, c, d)
V1 = V2 ⇒ XL= XC
⇒Θ X = 0 ∴ Z = R
I0 = 2A
V1= V2 = I = IωL= 2 × 2π × 125 × 2/π = 1000volt
Q.7. In the circuit shown in the figure R = 50Ω, E1 = 25 √3 volt and E2 = 25 √6 sin (ωt) volt where ω = 100 πs–1. The switch is closed at t = 0 and remains closed for 14 minutes, then it is opened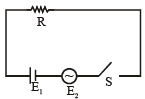
(a) The amount of heat produced in the resistor is 63000 J.
(b) The amount of heat produced in the resistor is 7000 J.
(c) If total amount of heat produced is used to heat 3 kg of water at 20ºC, the final temperature will be 25ºC.
(d) The value of direct current that will produce same amount of heat in same time through same resistor will be √1.5 A.
Correct Answer is options (a, c, d)
Heat produced in one cycle
Heat produced in 14 minutes
∴Q = ms ∆θ
∆θ = 5ºC
∴ Tf = 5 + 20 = 25ºC
and heat produced by direct current I2RT=Q
∴
Q.8. An LC circuit has capacitance C1 = C and inductance L1 = L. A second circuit has C2 = C/2 and L2 = 2L and a third circuit has C3 = 2C and L3 = L/2 . All the three capacitors are charged to the same potential V and then made to oscillate. Then:
(a)Angular frequency of oscillation is same for all the three circuits.
(b) Maximum current is greatest in first circuit.
(c) Maximum current is greatest in second circuit.
(d) Maximum current is greatest in third circuit.
Correct Answer is options (a, d)
Angular frequency
Product of L and C is same for all the three circuits. Therefore, angular frequency is same for all the three circuits.
From conservation of energy
i.e., maximum current
C/L is maximum for third circuit. Therefore, maximum current is greatest for third circuit.
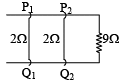
Q.9. In the diagram shown, the wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are made to slide on the rails with same speed of 5 m/s-1. In this region a magnetic field of 1 T exists. The electric current in 9 Ω resistor is–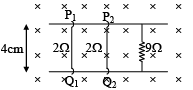 (a) zero if both wires slide towards left.
(a) zero if both wires slide towards left.
(b) zero if both wires slide in opposite direction.
(c) 20 mA if both wires move towards left.
(d) 20 mA if both wires move in opposite direction.
Correct Answer is options (b, c)
ε = Bλv = 1 × 0.04 × 5
ε = 0.2 volt
i = 0.02 A
i = 2 × 10–2A
= 20 mA
Q.10. Two contours whose planes are parallel to each other and are separated by a certain distance. Both are carrying current in the same direction. A is fixed & B can be positioned in different manner with respect to the first.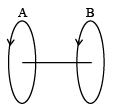 Different positions are such that the plane of B tuned by 90º, or by 180º, and in third case it is just moved parallel to itself over a certain distance. One has to do work to bring B in any of above positions. These works are W1 for 90º, W2 for 180º and for third case W3. Among W1 W2, W3 -
Different positions are such that the plane of B tuned by 90º, or by 180º, and in third case it is just moved parallel to itself over a certain distance. One has to do work to bring B in any of above positions. These works are W1 for 90º, W2 for 180º and for third case W3. Among W1 W2, W3 -
(a) W1 is maximum & W3 is minimum
(b) W2 is maximum & W3 is minimum
(c) W3 is minimum
(d) W2 > W1 > W3
Correct Answer is options (b, c, d)
That
W = I (ϕ2 – ϕ1)
φ2 is final flux & φ1 is initial flux
W1 = – Iϕ1, W2 = – 2Iϕ1, W3 = I (ϕ2 – ϕ1)
|
446 docs|929 tests
|