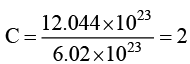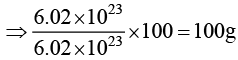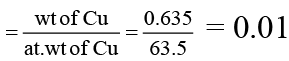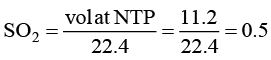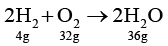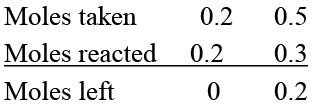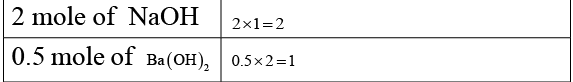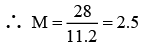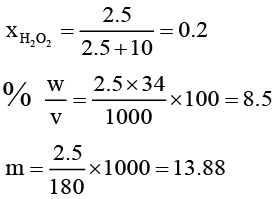JEE Advanced (One or More Correct Option): Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. In which of the following statements is/are correct?
(a) Weight of 12.044 × 1023 atoms of carbon is 24g.
(b) Weight of 6.022 × 1023 molecules of CaCO3 is 100 g.
(c) Number of moles of 0.635 g of Cu is 2. (At wt of Cu = 63.5)
(d) The number of molecules in 11.2 litre of SO2 gas at NTP is 0.5.
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
For (A) → The number of moles of
Wt of C-atm = 2 × 12 = 24g
For (B) weight of CaCO3 = number of moles × mol.wt
For (C) number of moles of Cu
Hence it is wrong.
For (D) number of
Q.2. 4g of hydrogen is ignited with 4 g oxygen. Following reaction takes place
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Select the correct statement(s).
(a) Oxygen is limiting reactant
(b) Hydrogen is limiting reactant
(c) 4g of hydrogen reacts with 2g oxygen
(d) 4.5 g of water will be formed
Correct Answer is option (a and d)
4 g of H2 will completely react with 32 g of O2 , but only 4 g of O2 is present.
Hence, O2 is limiting reactant.
Since, 32 g of O2 produces 36g of H2O
Hence 4 g of O2 will produce 36/32 × 4 = 4.5g of H2O
Q.3. 0.2 mole of Na3PO4 and 0.5 mole of Ba (NO3)2 are mixed in one litre of solution. Which of the following is/are correct.
(a) 0.2 mole of Ba3 (PO4)2 is obtained
(b) 0.1 mole of Ba3 (PO4)2 is obtained
(c) Molarity of Ba3 (PO4)2 in solution is 0.1 M
(d) Molarity of Ba3 (PO4)2 in solution is 0.2 M
Correct Answer is option (b and c)
2Na3PO4 + 3Ba (NO3)2 → Ba3 (PO4)2 + 6NaNO3
Na3PO4 is limiting reactant.
∴ Moles of Ba3(PO4)2 formed = 0.1
Molarity of Ba3 (PO4)2 = 0.1/1 = 0.1M
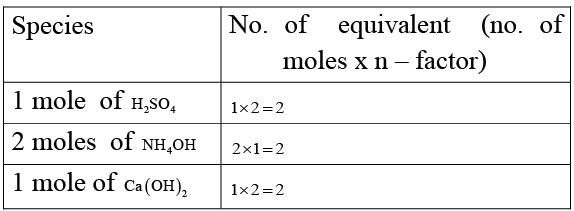
Q.4. 1 mole of H2SO4 will exactly neutralise
(a) 2 moles of NH4OH
(b) 1 mole of Ca (OH)2
(c) 2 moles of NaOH
(d) 0.5 mole of Ba (OH)2
Correct Answer is option (a, b and c)
Equal number of equivalents of acid and base neutralises.
Q.5. 200 ml of 0.3 M Ca(OH)2 will be completely neutralized by
(a) 1200 ml of 0.1 M HCl
(b) 600 ml of 0.1 M H2SO4
(c) 400 ml of 0.1 M H3PO4
(d) 600 ml of 0.2 M HNO3
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
m eq of Ca(OH)2 ⇒ 200 × 0.3 × 2 ⇒ 120 (nf = n-factor)
(A) 1200 × 0.1 = 120 M eq of HCl HCl nf = 1
(B) 600 × 0.1 × 2 = 120 M eq of H2SO4 H2SO4 nf = 2
(C) 400 × 0.1 × 3 = 120 M eq of H3PO4 H3PO4 nf = 3
(D) 600 × 0.2 × 1 = 120 M eq of HNO3 HNO3 nf = 1
Q.6. 100 ml of 0.1 M H2SO4 is mixed with 200 ml of 0.2 M HCl then resulting mixture will be neutralized by
(a) 600 ml of 0.1 M NaOH
(b) 300 ml of 0.1 M Ca(OH)2
(c) 200 ml 0.1 M of Al(OH)3
(d) 400 ml of 0.1 M KOH
Correct Answer is option (a, b and c)
m eq of H2SO4 + m eq of HCl
⇒ 100 × 0.1 × 2 + 200 × 0.2 × 1
⇒ 20 + 40 = 60 m eq of Acid
(A) 600 × 0.1 = 60 m eq of NaOH
(B) 300 × 0.1 × 2 = 60 m eq of Ca(OH)2
(C) 200 × 0.1 × 3 = 60 m eq of Al(OH)3
(D) 400 × 0.1 × 1 = 40 m eq of KOH
Q.7. 1 molar of 1 litre of H2SO4 will exactly neutralize
(a) 2 molar of 1 litre NH3
(b) 1 molar of 1 litre Ca (OH)2
(c) 0.5 molar of 1 litre Ba (OH)2
(d) 2 molar of 1 litre NaOH
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
n-factor for H2SO4 = 2
Equivalent of H2SO4 = 2
Equivalence of NH3 = 2 × n - factor = 2 × 1 = 2
Equivalence of Ca(OH)2 = 1 × 2 = 2
Equivalence of Ba(OH)2 = 0.5 × 2 = 1
Equivalence of NaOH =2 × 1 = 2
Q.8. 10 moles of SO2 and 4 moles of O2 are mixed in a closed vessel. Following reaction takes place 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g). Select the correct statement(s).
(a) SO2 is limiting reactant
(b) O2 is limiting reactant
(c) 8 moles of SO3 are formed
(d) 10 moles of SO3 are formed
Correct Answer is option (b and c)
2SO + O2 → 2SO3
Moles taken initially 10 moles 4 moles 0
Moles involved in reaction 8 4 8
Final moles 2 0 8
O is limiting reactant. SO2 is excess reactant as 2 moles of SO2 remains unreacted. 8 moles of SO3 are produced.
Q.9. Which of following contains the same number of moles?
(a) 1g of O2 and 2 g of SO2
(b) 1 g of O2 and 1 g of O3
(c) 1 g of CO2 and 1g of N2O
(d) 11.2 L of CO2 at STP and 1 g H2
Correct Answer is option (a, c and d)
Moles in 1 g O2 = 1/32
Moles in 2 g SO2 = 2/64 = 1/32
Moles in 1 g O3 =1/48
Moles in 1 g CO2 = 1/44
Moles in 1g N2O = 1/44
Moles in 11.2 L CO2 (STP) = 11.2/22.4 = 1/2
Moles in 1g H2 = 1/2
Q.10. A sample of H2O2 solution labelled as “28 volume” has density of 26.5 g/L. Mark the correct option(s) representing concentration of same solution in other units:
(a) H2O2 M = 2.5
(b) %w/v = 17
(c) Mole fraction of H2O2 = 0.2
(d) m H2O2 = 13.88
Correct Answer is option (a, c and d)
Vstrength = 56
∴ 1 L contain 2.5 moles of H2O2
Or 2.5 × 34 = 85g H2O2
Wt. of 1 litre solution = 265 g (∵ d = 265g/L)
∴ wH2O = 180g or moles of H2O = 10
|
446 docs|929 tests
|