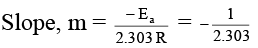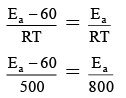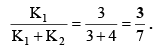JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Chemical Kinetics & Nuclear Chemistry | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. The study of reaction kinetics is called __________.
(a) Rate of reaction
(b) Mechanism of reaction
(c) Factors which affect the rate of reaction
(d) All of the mentioned
Correct Answer is option (d)
Reaction kinetics is the study of reaction rates, mechanisms, and the factors that influence reaction rates.
Q.2. Which of the following is the right temperature coefficient (n) expression?
(a) n = Rate constant at T + 10°/Rate constant at T°
(b) n = Rate constant at T + 20°/Rate constant at T°
(c) n = Rate constant at T + 30°/Rate constant at T°
(d)n = Rate constant at T + 40°/Rate constant at T°
Correct Answer is option (a)
The effect of temperature on a reaction’s pace is commonly stated in terms of the temperature coefficient, which is defined by the equation:
Temperature coefficient (n) = T + 10° (308 K) rate constant/T° rate constant (298 K).
Q.3. Plotting a graph between temperature and reaction rates can reveal the temperature dependence of reaction rates.
(a) Concentration of reactants and temperature
(b) Concentration of products and temperature
(c) Rate constant and temperature
(d) Rate of catalysis and temperature
Correct Answer is option (c)
Plotting a graph between rate constant and temperature for various reactions can be used to investigate the temperature dependence of reaction rates.
Q.4. Only a simple homogeneous reaction requires which of the following methods?
(a) Integration method
(b) Half-life period method
(c) Graphical method
(d) Ostwald’s isolation method
Correct Answer is option (a)
For complex reactions, the integration method leads to incorrect conclusions. But the integration method is suitable for simple homogeneous reactions.
Q.5. In a reaction, what is the driving force?
(a) Energy given
(b) Energy released
(c) Free energy
(d) None of the mentioned
Correct Answer is option (c)
The change in free energy, which is related to the equilibrium constant, is the reaction’s driving force (K).
Q.6. The reaction rate constant can be defined as the rate of reaction when each reactant’s concentration is ___________.
(a) Zero
(b) Unity
(c) Doubled the initial concentration
(d) Infinite
Correct Answer is option (b)
The reaction rate constant can be defined as the rate of the reaction when all of the reactants’ concentrations are unity. The rate of a chemical reaction is quantified by a reaction rate constant, or reaction rate coefficient, k.
Q.7. When the temperature rises, what happens to the peak of the curve in the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution graph?
(a) Shifts forward and upward
(b) Shifts forward and downward
(c) Shifts backwards and upward
(d) Shifts backwards and downward
Correct Answer is option (b)
The peak moves ahead but downward as the temperature rises. This is because when the temperature rises, the most probable kinetic energy rises, while the percentage of molecules with the most probable kinetic energy drops.
Q.8. What effect does temperature have on the half-life of a first-order reaction?
(a) It increases
(b) It decreases
(c) It remains the same
(d) Both increases as well as decrease
Correct Answer is option (b)
For the first-order reaction, the rate constant increases on increasing temperature. But for the half-life of a first-order reaction, the rate constant is inversely proportional to half-life; thus, on increasing temperature, half-life decreases.
Q.9. In 30 minutes, a first-order reaction is 50% complete. Calculate the amount of time it took to complete 87.5 percent of the reaction.
(a) 30 minutes
(b) 60 minutes
(c) 90 minutes
(d) 120 minutes
Correct Answer is option (c)
In 30 minutes, the reaction is 50% complete. As a result, t1/2 = 30 minutes.
In two half-lives, 75% of the process is accomplished. As a result, t = 2 ×30 = 60 minutes.
In three half-lives, 87.5 percent of the reaction is finished.
Hence, t = 3 × 30 = 90 minutes.
Q.10. What is the heat of reaction for ethyl acetate hydrolysis?
(a) Greater than zero
(b) Less than zero
(c) Zero
(d) None of the mentioned
Correct Answer is option (c)
The equilibrium position of ethyl acetate hydrolysis was demonstrated to be temperature independent. Because the bonds broken and created are of the same kind, calculating the heat of reaction using the bond energies technique yields a value of zero.
Q.11. For a first order reaction,
(a) the degree of dissociation is equal to (1 -ekt).
(b) a plot of the reciprocal concentration of the reactant vs time gives a straight line.
(c) the time taken for the completion of 75% reaction is twice the t1/2 of the reaction.
(d) the pre-exponential factor in the Arrhenius equation has the dimension of T.
Correct Answer is option (c)
t3/4 = 2t1/2
Q.12. Figure shows a graph in 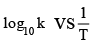 where k is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope,
where k is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope, 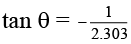 and an intercept of 5 on Y-axis. Thus Ea, the energy of activation is:
and an intercept of 5 on Y-axis. Thus Ea, the energy of activation is: 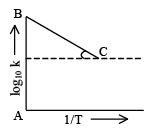
(a) 2.303 x 2 cal
(b) 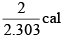
(c) 2 cal
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (c)
∴ Ea = R = 2 cal.
Q.13. If ‘I’ is the intensity of absorbed light and ‘c’ is the concentration of AB for the photochemical process AB + hv → AB* the rate of formation of AB* is directly proportional to:
(a) c
(b) I
(c) I2
(d) c . I
Correct Answer is option (b)
Rate determining step for all photoprimary processes is given as r = k.I
Q.14. The rate constant of a reaction at 500 K, in presence of catalyst is same as that of 800 K in absence of catalyst if use of catalyst lowers down the energy barrier by 60 J then what will be the value of activation energy of uncatalysed reaction?
(a) 120 J
(b) 100 J
(c) 130 J
(d) 160 J
Correct Answer is option (d)
Let in absence of catalyst activation energy to be Ea then in presence of catalyst will be Ea – 60
∵ Kcatalyst = Kwithout catalyst
Ea = 160 J.
Q.15. Decomposition of acetic acid at high temperature takes place by two parallel reactions following first order kinetics as shown below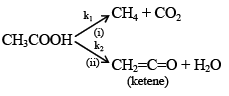
If k1 = 3s–1 and k2 = 4 s–1 then what would be the fraction of acetic acid reacting as per reaction(i)?
(a) 3/4
(b) 3/7
(c) 4/7
(d) none of these
Correct Answer is option (b)
|
446 docs|929 tests
|