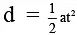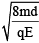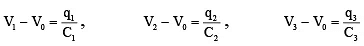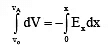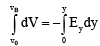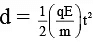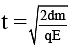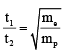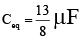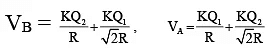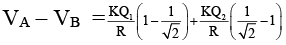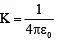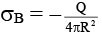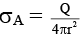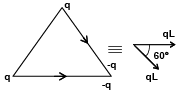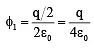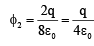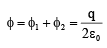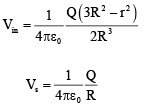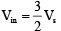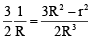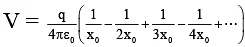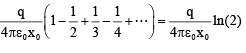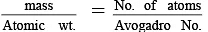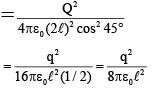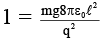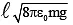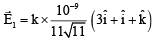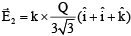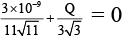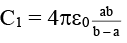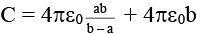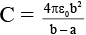JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Electrostatics | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. The wedge-shaped surface in figure is in a region of uniform electric field E0 along x axis. The net electric flux for the entire closed surface is
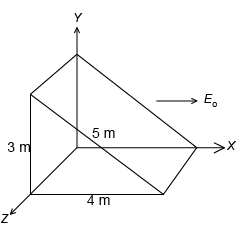 (a) 9 E0
(a) 9 E0
(b) 15 E0
(c) 12 E0
(d) zero
Correct Answer is option (d)
Since, field is uniform, the net flux for the closed surface is zero.
Q.2. A block of mass m carrying a positive charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table, which ends in a vertical wall situated at a distance d from block. An electric field E is switched on towards right. Assuming elastic collisions, find the time period of resultant oscillation.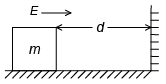 (a)
(a) 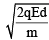
(b) 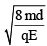
(c) 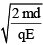
(d) 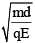
Correct Answer is option (b)
Acceleration of the block a = qE / m
Required time = 2t =
Q.3. Three uncharged capacitors of capacities C1 , C2 , C2 are connected as shown in figure to one another and to points A, B and C at potentials V1 , V2 and V3 . Then the potential at O will be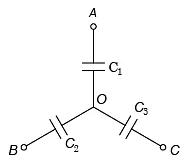 (a)
(a) 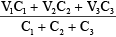
(b) 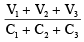
(c) 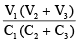
(d) 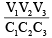
Correct Answer is option (a)
Taking into account the relation between capacitance, voltage and charge of a capacitor, we can write the following equations for the three capacitors.
where C1, C2 and C3 are the capacitances of corresponding capacitors and q1, q2 and q3 are charges on the plates. According to charge conservation law, q1 + q2 + q3 = 0 and hence the potential V0 of the common point is.
Q.4. Following operations can be performed on a capacitor.
A: connect the capacitor to a battery of emf E.
B: Disconnect the battery.
C: Reconnect the battery with polarity reversed.
D: Insert a dielectric slab into the capacitor. Now choose the incorrect option (s)
(a) in action ABC (perform A, then B and then C), the stored electric energy remains unchanged and no thermal energy is developed.
(b) the charge appearing on capacitor is greater after the action ADB than after the action ABD.
(c) the electric energy stored in the capacitor is greater after the action DAB than the action ABD.
(d) the electric field in the capacitor after the action AD is same as that after the action DA.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Use the concept of capacitor, charging, discharging etc.
Q.5. Gauss’s law is frequently written in the following form: 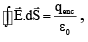
Where, the symbols have their usual meanings
(a) this law is true for all closed surfaces
(b) it is true only in vacuum
(c) it is true only when the charge distribution is symmetric
(d) it is true only when the electric field is symmetric
Correct Answer is option (a)
Gauss’s law is true for all closed surface.
Q.6. If Vo be the potential at origin in an electric field 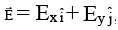 , then the potential at point P(x, y) is
, then the potential at point P(x, y) is
(a) 
(b) 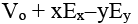
(c) 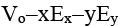
(d) 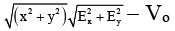
Correct Answer is option (c)
Ex = -dV/dx and Ey = -dV/dy
Taking x-component
Vp - V0 = -Ex(x)
Taking y-component
VB - V0 = -Ey(y)
Adding, VB = V0 - xEx - yEy
Q.7. An electron of mass me, initially at rest, moves through a certain distance in a uniform electric field in time t1. A proton of mass mp, also initially at rest, takes time t2 to move through an equal distance in this uniform electric field. Neglecting the effect of gravity, the ratio t2/t1 is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 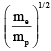
(c) 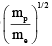
(d) 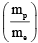
Correct Answer is option (c)
Acceleration in uniform electric field
a = qE/m
If t is time for a distance d,
or
so,
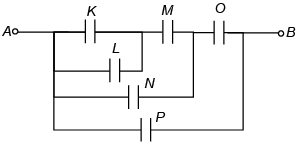
Q.8. The effective capacitance between A and B is ( each capacitor is of 1 μF)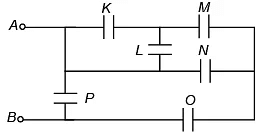 (a) 15 / 2 μF
(a) 15 / 2 μF
(b) 17 / 3 μF
(c) 13 / 8μF
(d) 19 / 8 μF
Correct Answer is option (c)
Circuit can be redrawn as
∴
Q.9. Two identical thin rings, each of radius R metres are coaxially placed at a distance R metres apart. If Q1 and Q2 charges are spread uniformly on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q from the centre of one ring to that of the other is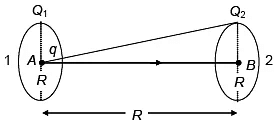 (a) zero
(a) zero
(b) 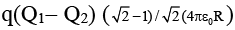
(c) 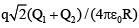
(d) 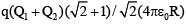
Correct Answer is option (b)
∴
∴, where
∴ W = q (VA – VB)
Q.10. A and B are two concentric spheres If A is given a charge Q while B is earthed as shown in figure, then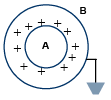 (a) the charge densities of A and B are same
(a) the charge densities of A and B are same
(b) the field inside and outside A is zero
(c) the field between A and B is not zero
(d) the field inside and outside B is zero
Correct Answer is option (c)
Since, B is grounded, therefore VB = 0(R = radius of shell B)
QB = - QA
Now take
QA = Q
But
∴ (A) is not correct
Apply Gauss's theorem. Only (C) is correct.
Q.11. Electric charges q, q and -2q are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side L. The magnitude of electric dipole moment of the system is
(a) qL
(b) 2qL
(c) (√3)qL
(d) 4qL
Correct Answer is option (c)
As shown the three charges are equivalent to two dipoles of magnitude q L.
∴ Equivalent dipole moment == √3qL
Q.12. If charges q/2 and 2q are placed at the centre of face and at the corner of a cube, then the total flux through the cube will be
(a) 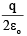
(b) 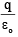
(c) 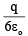
(d) 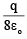
Correct Answer is option (a)
Flux through the cube when q/2 is placed at the centre of face
Flux through the cube when 2q is placed at the corner of cube is
Now, total flux through the cube
Q.13. A solid insulating sphere of radius R is given a charge Q. If at a point inside the sphere the potential is 1.5 times the potential at the surface, this point will be
(a) at a distance of 2R/3 from the centre
(b) at the centre
(c) at a distance of 2R/3 from the surface
(d) data insufficient
Correct Answer is option (b)
Given
⇒
or r = 0
Q.14. A charge +q is fixed at each of the points x = x0, x = 3x0, x = 5x0, . . .,∞ on the x-axis and a charge -q is fixed at each of the points x = 2x0, x = 4x0, x = 6x0, . . ., ∞. Here, x0 is a positive quantity. Take the electric potential at a point due to charge Q at a distance r from it to be 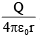 Then, the potential at origin due to the above system of charges is
Then, the potential at origin due to the above system of charges is
(a) 0
(b) ∞
(c) 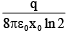
(d) 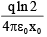
Correct Answer is option (d)
=
Q.15. Find the charge on an iron particle of mass 2.24 mg, if 0.02% of electrons are removed from it.
(a) -0.01996 C
(b) 0.01996 C
(c) 0.02 C
(d) 2.0 C
Correct Answer is option (b)
As,
∴ No. of atoms = 24 x 1018 atoms
= 24 x 1018 x 26 electrons.
n = No. of electrons removed = 24 x 1018 x 26 x 0.01/100 = 1248 x 1014 electron
∴ Q = ne = (+ve charge) = 0.01996 C
Q.16. Two small metallic spheres each of mass ‘m’ are suspended together with strings of length ‘l’ and placed together. When a quantum of charge ‘q’ is transferred to each, the strings make an angle of 90° with each other. The value of ‘q’ is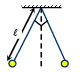
(a) 
(b) 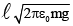
(c) 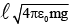
(d) 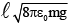
Correct Answer is option (d)
T cos 45° = FE
T sin 45° = mg
∴ q =
Q.17. Two connected charges of +q and -q are at a fixed distance AB apart in a non-uniform electric field, whose lines of force are shown in the figure. The resultant effect on the two charges is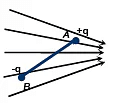 (a) a torque in the plane of the paper and no resultant force.(b) a resultant force in the plane of the paper and no torque.
(a) a torque in the plane of the paper and no resultant force.(b) a resultant force in the plane of the paper and no torque.
(c) a torque normal to the plane of the paper and no resultant force.
(d) a torque normal to the plane of the paper and a resultant force in the plane of the paper.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Change in potential energy = gain in kinetic energy =
Q.18. A ring of radius R carries a charge +q. A test charge -q0 is released on its axis at a distance 3R from its centre. How much kinetic energy will be acquired by the test charge when it reaches the centre of the ring?
(a) 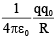
(b) 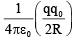
(c) 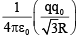
(d) 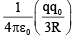
Correct Answer is option (c)
Electric field due to 10–9 C at (3, 1, 1)
Electric field due to Q at (3, 1, 1)
Ex = 0
⇒
⇒ Q = – 4.3 x 10–10C
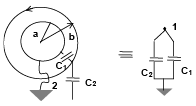
Q.19. The figure shows a spherical capacitor with inner sphere earthed. The capacitance of the system is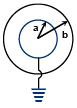 (a)
(a) 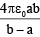
(b) 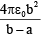
(c) 4 πε0 (b + a)
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is option (b)
The potential on the outer sphere is V (assume). Thus we can consider two capacitors between the outer sphere and inner sphere C1 and outer sphere and earth C2. These two capacitors are in parallel.
Thus,
C2 = 4πε0 b
∴
Q.20. The figure shows a charge q placed inside a cavity in an uncharged conductor. Now if an external electric field is switched on then: (a) only induced charge on outer surface will redistribute.
(a) only induced charge on outer surface will redistribute.
(b) only induced charge on inner surface will redistribute.
(c) Both induced charge on outer and inner surface will redistribute.
(d) force on charge q placed inside the cavity will change
Correct Answer is option (a)
The distribution of charge on the outer surface, depends only on the charges outside, and it distributes itself such that the net electric field inside the outer surface due to the charge on outer surface and all the outer charges is zero. Similarly the distribution of charge on the inner surface, depends only on the charges inside the inner surface, and it distributes itself such that the net, electric field outside the inner surface due to the charge on inner surface and all the inner charges is zero. Also the force on charge inside the cavity is due to the charge on the inner surface. Hence answer is option (A).
|
446 docs|929 tests
|