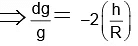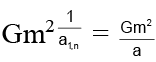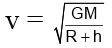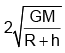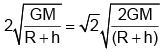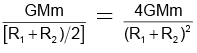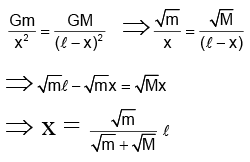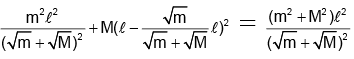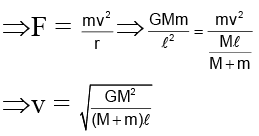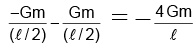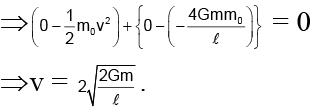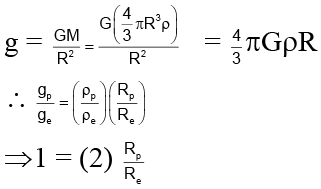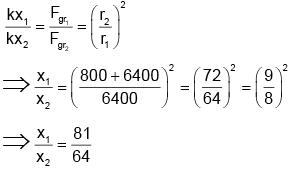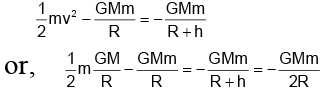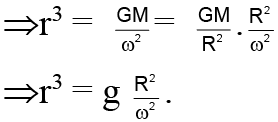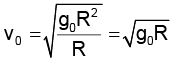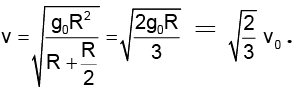JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Gravitation | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. A satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit. The following statements are given
(i) It is moving with a constant velocity.
(ii) It suffers no acceleration.
(iii) Its angular momentum w.r.t. the earth remains conserved.
(iv) Its distance from centre must be equal to 2 times of earth’s radius.
(a) (i) and (ii) are true.
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) are true.
(c) only (iii) is true.
(d) (i) and (iv) are true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
When the earth’s satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit, it is moving with constant speed. It has centripetal acceleration and its angular momentum remains constant as no external torque is present. Thus, its radius need not be equal to the √2Re.
Q.2. The fractional change in the value of free-fall acceleration ‘g’ for a particle when it is lifted from the surface to an elevation h (h<<R) is
(a) h/R
(b) -(2h/R)
(c) 2h/R
(d) none of these.
Correct Answer is option (b)
g = GM/R2 ....(1)
dg/dR = -2GM/R3 putting dR = h we obtain⇒ dg/h = -2GM/R2 1/R . . . (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
⇒ Change is –ve. That means g decreases.
Hence, (B) is correct.
Q.3. A system consists of N identical particles of mass m placed rigidly on the vertices of a regular polygon with each side of length l. If K1 be the kinetic energy imparted to one of the particles so that it just escapes the gravitational pull of the system and thereafter kinetic energy K2 is given by to the adjacent particle to escape, then the difference (K1- K2) is 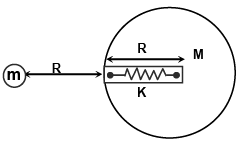 (a) nGm2/a
(a) nGm2/a
(b) GM2/na
(c) 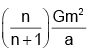
(d) GM2/a
Correct Answer is option (d)
For the first particle, K1 + (-Gm2)= 0
Similarly for the second particle, K2 + (-Gm2)= 0
∴ K1- K2 =
Q.4. A satellite is revolving around the earth at a height h. The satellite explodes into two equal parts, one part has zero velocity after the explosion, and the other moves in the same direction with double the orbital speed of the original satellite. The maximum height reached by the part with double the velocity is (Neglect the gravitational effects between the fragments)
(a) 3h + 4R
(b) 3R + 4h
(c) 3(R +h)
(d) none of these
Correct Answer is option (d)
After the collision, the velocity becomes
Now
∴ The velocity of satellite becomes greater than the escape velocity. Hence, it will escape to infinity.
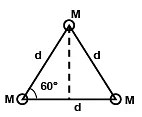
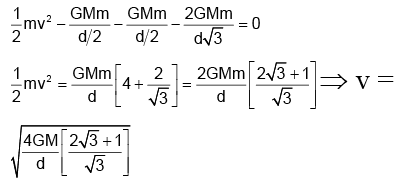
Q.5. Three spheres, each of radiusR are fixed at 3 points such that their centres form an equilateral triangle of side d. With what velocity should a particle of mass ‘m’ be projected from the mid-point of one of the sides of the triangle, so that it escapes the gravitational field of the system? Given that the mass of each sphere is M.
(a) 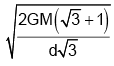
(b) 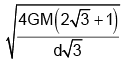
(c) 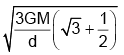
(d) 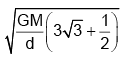
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.6. Consider two thin concentric shells of masses M and 2M and radii R1 and R2 (R1<R2). Magnitude of the gravitational force experienced by a particle of mass m placed at a distance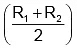 from the common centre will be
from the common centre will be
(a) 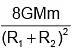
(b) 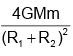
(c) 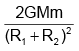
(d) 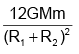
Correct Answer is option (b)
The particle of mass m is located in between the shells
F =
Q.7. Two moving particles collide and stick together on a smooth horizontal surface. The following statements are given below
(i) Mechanical energy is conserved.
(ii) Total energy is conserved.
(iii) Work done by the system is positive
(iv) Work done by the system is negative.
Choose the correct option.
(a) (i) and (iii) are correct.
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct.
(c) (a) and (d) are correct.
(d) (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Correct Answer is option (d)
It is obvious for 2 mass system, whether it is elastic, inelastic or perfectly elastic. Total energy of system will remain conserved. But final kinetic energy will be less than initial K.E. So work done by the system will be negative.
Q.8. When a satellite has an elliptical orbit, the plane of the orbit
(a) Sometimes passes through the centre of earth.
(b) Does not pass through the centre of earth.
(c) Passes through the centre of earth always
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is option (c)
If the plane of the orbit does not pass through the centre of earth there will be a component of Fgr perpendicular to the plane which is not balanced by any force. The orbit would become unstable. Therefore, earth orbit must have to pass through the centre of earth.
Q.9. If the radius of earth were to shrink by one percent, its mass remaining the same, the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface would
(a) Decrease
(b) remains unchanged
(c) Increase.
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (c)
g = GM/R2 ⇒ dg/g = (-2dR/R)
As dR/R = -1% ⇒ dg/g= -2 (-1) = +2 % Thus acceleration due to gravity will increase.
Q.10. Two isolated point masses m and M are separated by a distance l. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis passing through a point where gravitational field is zero and perpendicular to the line joining the two masses, is
(a) 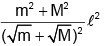
(b) 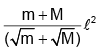
(c) 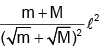
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is option (a)
I = mx2 + M(l - x)2
⇒ l =
Q.11. The earth revolves round the sun in an elliptical orbit. Its speed is
(a) going on decreasing continuously
(b) greatest when it is closest to the sun
(c) greatest when it is farthest from the sun
(d) constant at all the points on the orbit.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Conservation of angular momentum of the planet yields,
mv1r1 = mv2r2 ⇒ v1 r1 = v2 r2
∴ At closest distance, speed is maximum.
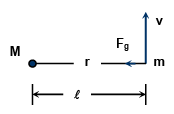
Q.12. Two massive particles of masses M & m (M > m) are separated by a distance l. They rotate with equal angular velocity under their gravitational attraction. The linear speed of the particle of mass m is
(a) 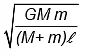
(b) 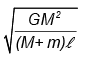
(c) 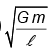
(d) 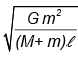
Correct Answer is option (b)
The system rotates about the centre of mass. The gravitational force acting on the particle m accelerates it towards the centre of the circular path, which has the radius R = Ml/M+m
Hence, (b) is correct.
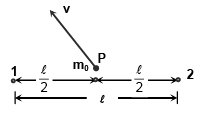
Q.13. A particle is projected from the mid-point of the line joining two fixed particles each of mass m. If the separation between the fixed particles is l, the minimum velocity of projection of the particle so as to escape is equal to
(a) 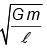
(b) 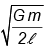
(c) 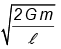
(d) 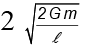
Correct Answer is option (d)
The gravitational potential at the mid-point P,
V = V1 + V2 =
⇒ The gravitational potential energy
U = - 4Gmm0/l, m0 = mass of particle
When it is projected with a speed v, it just escapes to infinity, and the potential & kinetic energy will become zero.
⇒ ΔKE + ΔPE = 0
Hence (d) is correct.
Q.14. A planet has twice the density of earth but the acceleration due to gravity on its surface is exactly the same as on the surface of earth. Its radius in terms of radius of earth R will be
(a) R/4
(b) R/2
(c) R/3
(d) R/8
Correct Answer is option (b)
⇒ RP/Re = ½ ⇒ Rp = R/2
Hence (b) is correct.
Q.15. A particle hanging from a spring stretches it by 1 cm at earth’s surface. Radius of earth is 6400 km. At a place 800 km above the earth’s surface, the same particle will stretch the spring by:
(a) 1 cm
(b) 8 cm
(c) 0.1 cm
(d) 0.79 cm
Correct Answer is option (d)
⇒ x2 =cm = 0.79 cm
Hence (d) is correct.
Q.16. A projectile is launched from the surface of the earth with a very high speed v at an angle q with vertical. What is its velocity when it is at the farthest distance from the earth surface? Given that the maximum height reached by the projectile is equal to the height reached when it is launched perpendicular to earth with a velocity = 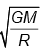 .
.
(a) v cosθ/2
(b) v sinθ/2
(c) 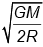
(d) 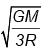
Correct Answer is option (b)
The maximum height reached by the projectile is given by
∴ h = R
Applying conservation of momentum
mu'(R + h) = mv sin θ R∴ u'(2R) = v sin θR
∴ u' = v sinθ/2
Hence, (b) is correct.
Q.17. The mean radius of the earth is R, its angular speed about its own axis is ω and the acceleration due to gravity at the earth surface is g. The cube of radius of orbit of ‘geostationary satellite’ will be:
(a) (R2g/ω)
(b) (R2ω/g)
(c) (Rg/ω2)
(d) (R2g/ω2)
Correct Answer is option (d)
mrω2 = GMm/r2
⇒ rω2 = GM/r2
Hence, (d) is correct.
Q.18. The orbital velocity of an artificial satellite in a circular orbit just above earth’s surface is v0. For a satellite orbiting in a circular orbit at an altitude of half of earth’s radius is
(a) 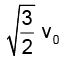
(b) 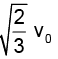
(c) 3/2 v0
(d) 2/3 v0
Correct Answer is option (d)
Orbital velocity =
where R is radius of earth.
If h = 0,
If h = R/2,
Q.19. The dimensional formula for gravitational constant is
(a) [M–1 L3 T–2]
(b) [M3 L–1T–2]
(c) [M–1L2T3]
(d) [M2L3T–1]
Correct Answer is option (a)
M–1 L3T–2
Q.20. The force between a hollow sphere and a point mass at P inside it as shown in the figure
(a) is attractive and constant
(b) is attractive and depends on the position of the point with respect to centre C
(c) is zero
(d) is repulsive and constant.
Correct Answer is option (c)
Since gravitational field inside hollow sphere is zero. Therefore force acting on the particle P is zero.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|