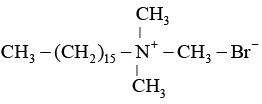JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Surface Chemistry | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. When the molecules of a substance are kept at the surface of a solid or a liquid, what is the name of the process?
(a) Absorption
(b) Adsorption
(c) Sorption
(d) Desorption
Correct Answer is option (b)
Adsorption is the process of a substance’s molecules accumulating in a larger concentration on the surface of a solid or a liquid. Gases, for example, adsorb on the surface of the charcoal.
Q.2. Which one of the following electrolytes will be most effective in coagulation of arsenoussulphide (As2S3) sol?
(a) KCl
(b) NaCl
(c) MgCl2
(d) AlCl3
Correct Answer is option (d)
As2S3 is –vely charged sol. So it can be coagulated by cations. More the charge of cations, more effective will be the coagulation.
Q.3. Which of the following assertions about the extent of physisorption is correct?
(a) Increases with increase in temperature
(b) Decreases with increase in surface area
(c) Decreases with increase in the strength of Van der Waals forces
(d) Decreases with increase in temperature
Correct Answer is option (d)
The process of physisorption is exothermic. A reduction in temperature, according to Le-Chatelier principle favours an exothermic reaction. As a result, as the temperature rises, the amount of physisorption reduces.
Q.4. Which equation represents Freundlisch adsorption isotherm (physical adsorption is basis of this theory):
(a) x/m = k(P)1/n wherex is amount of gas adsorbed on mass ‘m’
at pressure P
(b) 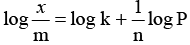
(c) x/m = kP at low pressure and k x/m = k at high pressure
(d) All of these
Correct Answer is option (d)
These are different forms of Freundlich equation.
Q.5. Which of the following is a sorption example?
(a) Sponge in water
(b) Cotton dipped in ink
(c) Water on silica gel
(d) Oxygen on the metal surface
Correct Answer is option (b)
Sorption is a process in which both adsorption and absorption take place at the same time. Cotton dipped in ink is one of the few examples of sorption, which includes both adsorption and absorption.
Q.6. Lyophilic sols have _______ between disperse phase and dispersion medium.
(a) strong attractive interaction.
(b) little attractive interaction.
(c) repulsive interaction.
(d) none of these
Correct Answer is option (a)
To form colloidal solution there should be strong forces of attraction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Q.7. Which of the following is not a lyophobic colloidal example?
(a) Gold solution
(b) Sulphur solution
(c) NaCl solution
(d) Blood
Correct Answer is option (c)
Gold solution, sulphur solution, and blood are colloids in which the dispersed phase has a low affinity for the dispersion medium, and we can’t retrieve the solution directly by combining the two phases once they’ve been separated. As a result, they are classified as lyophobic colloids.
Q.8. Which of the following will have highest coagulating power for As2S3 colloid?
(a) 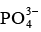
(b) 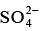
(c) Al3+
(d) Na+
Correct Answer is option (c)
As2S3 sol is negatively charged and hence the ion with maximum positive charge shall be required in minimum concentration to cause its precipitation.
Q.9. Which of the following statements about macromolecular colloids is false?
(a) Protein solution is an example of macromolecular colloids
(b) Man-made macro-molecules like polythene can form such colloids
(c) Silver solution can form macromolecular colloids
(d) These are normally of lyophilic type
Correct Answer is option (c)
Macromolecules dissolve in appropriate solvents, resulting in colloidal particles. These are often lyophilic in nature, with silver solution serving as an example of lyophilic and multi-molecular colloids.
Q.10. The stabilization of the dispersed phase in a lyophobic sol is due to
(a) the viscosity of the medium.
(b) the surface tension of the medium.
(c) affinity for the medium.
(d) the formation of an electrical layer between the two phase.
Correct Answer is option (d)
The stabilization of the dispersed phase is due to adsorption of the ions.
Q.11. A catalyst is a substance which
(a) Increases the equilibrium concentration of the product.
(b) Changes the equilibrium constant of the reaction.
(c) Shortens the time to reach equilibrium.
(d) Supplies energy to the reaction.
Correct Answer is option (c)
A catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of reaction and shortens the time to reach equilibrium.
Q.12. How are different colours used to make gold colloidal solutions?
(a) Different diameters of colloidal gold particles
(b) Variable valency of gold
(c) Different concentrations of gold particles
(d) Impurities produced by different methods
Correct Answer is option (a)
Because the sizes of colloidal gold particles vary, colloidal gold solutions made by different processes have distinct colours. The size of the colloidal particles determines the colour of the solution.
Q.13. The ability of an ion to bring about coagulation of a given colloid depends upon
(a) Its size
(b) The magnitude of its charge only
(c) The sign of its charge
(d) Both the magnitude and the sign of its charge
Correct Answer is option (d)
The ability of an ion to bring about coagulation of a given calloiddepend upon both the magnitude and sign of its charge.
Q.14. Which one of the following is not a surfactant?
(a) 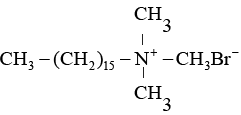
(b) CH3 - (CH2)14 - CH2 - NH2
(c) CH3 - (CH2)16- CH2OSO2- Na+
(d) OHC - (CH2 )14 - CH2 - COO- Na+
Correct Answer is option (b)
Surfactant are those which have charge on their tail e.g., cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide.
Surfactants are those, which dissociate in water to yield positively charged ion.
Q.15. Which of the following slows down the reaction rate?
a) Catalytic promoters
b) Homogeneous catalyst
c) Catalytic poison
d) Heterogeneous catalyst
Correct Answer is option (c)
A catalytic poison is a chemical that, even if present at tiny levels, disrupts the catalyst’s action. For example, any arsenic impurity present in the reacting gas will disrupt the activity of the vanadium pentoxide catalyst in the synthesis of sulphuric acid by contact method.
Q.16. A catalyst is used in a reaction to
(a) Change the nature of reaction products
(b) Increase the reaction yield
(c) Decrease the need for reactants
(d) Decrease the time required for the reaction
Correct Answer is option (d)
A catalyst is used to decrease the time required for the reaction hence it can decease or increase the rate of reaction.
Q.17. What’s the difference between cold cream and vanishing cream?
(a) Vanishing cream is a water-in-oil emulsion whereas cold cream is an oil-in-water emulsion
(b) Both are examples of water-in-oil emulsions
(c) Both are examples of oil-in-water emulsions
(d) Vanishing cream is an oil-in-water emulsion whereas cold cream is a water-in-oil emulsion
Correct Answer is option (d)
Vanishing cream is an oil-in-water emulsion, which means the dispersed phase is oil and the dispersion medium is water. In a water-in-oil emulsion, cold cream, water is the dispersed phase and oil is the dispersion medium.
Q.18. Gold number gives
(a) The amount of gold present in the colloid.
(b) The amount of gold required to break the colloid.
(c) The amount of gold required to protect the colloid.
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (d)
Gold no. is a measure of protective power of a lyophillic colloid.
Q.19. What is the term for a liquid dispersion in another liquid?
(a) Emulsion
(b) Aerosol
(c) Gel
(d) Foam
Correct Answer is option (d)
Gel is the dispersion of a liquid in a solid. Foam is the dispersion of a gas in a liquid media. An emulsion is the dispersion of a liquid in another liquid. Aerosol is the dispersion of a solid or liquid in a gaseous medium.
Q.20. Which of the following forms cationic miscelles above certain concentration
(a) Urea
(b) Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
(c) Sodium dodecyl sulphate
(d) Sodium acetate
Correct Answer is option (d)
Sodium acetate forms cationic micelles in the molecule of soap and detergent the negative ions aggregate to form a micelle of colloidal size. The negative ion has a long hydrocarbon chain and a polar group (-COO-) at one end.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|