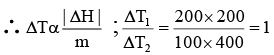JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Thermodynamics | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. A well stoppered thermos flask contains some ice cubes. This is an example of
(a) Closed system
(b) Open system
(c) Isolated system
(d) Non thermodynamics system
Correct Answer is option (c)
It is an isolated system
Q.2. For the reaction C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
(a) △H >△U
(b) △H < △U
(c) △H = △U
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (c)
Here △ng RT = 0 , because reactant and product contain same number of gaseous molecules. So that △H = △U + △ng RT ⇒ △H = △U
Q.3. For an ideal gas, CV and CP are related as:
(a) CV – CP = R
(b) CV + CP = R
(c) CP – Cv = RT
(d) CP – Cv = R
Correct Answer is option (d)
For an ideal gas, CV and CP are related as CP – Cv = R
Q.4. The least random state of the water system is:
(a) ice
(b) liquid water
(c) steam
(d) randomness is same
Correct Answer is option (a)
The least random state of the water system is ice.
Q.5. Considering entropy(S) thermodynamic parameters the criteria for the spontaneity of any process is:
(a) △S system + △S surroundings > 0
(b) △S system – △S surroundings < 0
(c) △S system > 0
(d) △S surroundings > 0
Correct Answer is option (a)
The criteria for the spontaneity of any process is △S system + △S surroundings > 0
Q.6. The enthalpy change in a reaction does not depend upon
(a) The state of reactions and products
(b) The nature of the reactants and products
(c) Different intermediate steps in the reaction
(d) Initial and final enthalpy of the reaction
Correct Answer is option (c)
The enthalpy change is a state function so it doesn’t depend on different intermediate steps in the reaction.
Q.7. The correct relationship between free energy change in a reaction and the corresponding equilibrium constant KC is
(a) -△G = RT lnKC
(b) △G0 = RT lnKC
(c) -△G0 = RT lnKC
(d) △G = RT lnKC
Correct Answer is option (c)
The relationship between free energy change in a reaction and the corresponding equilibrium constant KC is △G0 = – RT lnKC or -△G0 = RT lnKC
Q.8. What is the entropy change (in JK-1 mol-1) when 1 mole of ice is converted into water at 0℃? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol-1 at 0℃)
(a) 20.13
(b) 2.013
(c) 2.198
(d) 21.98
Correct Answer is option (d)
The entropy change; ds = dqrev /T ⇒ ds = 6000J mol-1 / 273K
⇒ ds = 21.978JK-1 mol-1
Q.9. If liquids A and B form an ideal solution
(a) The entropy of mixing is zero
(b) The free energy of mixing is zero
(c) The free energy as well as the entropy of mixing are zero
(d) The enthalpy of mixing is zero
Correct Answer is option (d)
If liquids A and B form an ideal solution the enthalpy of mixing is zero
Q.10. When water is added to quick lime the reaction is
(a) Explosive
(b) Endothermic
(c) Exothermic
(d) Photochemical
Correct Answer is option (c)
When water is added to quick lime the reaction is exothermic
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 △H = -ve
Q.11. A solution of 200 ml of 1 M KOH is added to 200 ml of 1 M HCl and the mixture is well shaken. The rise in temperature T1 is noted. The experiment is repeated by using 100 ml of each solution and increase in temperature T2 is again noted. Which of the following is correct?
(a) T1 = T2
(b) T2 is twice as large as T1
(c) T1 is twice as large as T2
(d) T1 is four times as large T2
Correct Answer is option (a)
|ΔH| = msΔT
⇒ T1 = T2
Q.12. ΔH0f of CO2(g), CO(g), N2O(g) and NO2(g) in kJ/mol are respectively –393, –110, 81 and 34. Calculate the ΔH in kJ of the following reaction:
2NO2(g) + 3CO(g) → N2O(g) + 3CO2(g)
(a) 836
(b) 1460
(c) – 836
(d) –1460
Correct Answer is option (c)
ΔH = 81 + 3 (-393) -2 (34) -3 (-110) = 81 - 1179 - 68 + 330 = – 836 kJ.
Q.13. Heat of combustion of CH4, C2H6, C2H4 and C2H2 are – 212.8, –373.0, –337.0 and –310.5 kcal mol-1 respectively at the same temperature. The best fuel among these gases is (Atomic masses: H = 1, C = 12)
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C2H4
(d) C2H2
Correct Answer is option (a)
Heat of combustion per g is called fuel value. The best fuel is that substance which has a maximum heat of combustion per g.
Q.14. Under same conditions how many ml of 1M NaOH and M/2 H2SO4 solutions should be mixed so that the total volume of the solution is 100 ml and rise in temperature is highest
(a) 67, 33
(b) 33, 67
(c) 60, 40
(d) 50, 50
Correct Answer is option (d)
If 50 ml. of 1(M) NaOH and 50 ml. of M/2 H2SO4 is taken, complete neutralization of acid and base occurs, maximum heat will be released.
Q.15. One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of one litre to 10 litres. The ΔE for this process is (E stands for internal energy)
(a) 16.7 cal
(b) 1381.1 cal
(c) 9 lit atm
(d) Zero
Correct Answer is option (d)
If the gas is ideal, its expansion at constant temperature is called isothermal expansion and it will be accompanied by no change in internal energy. Thus, ΔE = 0.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|