JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
13. 3,3-Dimethylbutan-2-ol loses a molecule of water in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid to give tetramethylethylene as a major product. Suggest a suitable mechanism. (1996 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
The steps involved in the suggested mechanism are as follows.
(a) The protonation of hydroxyl group.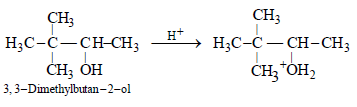
(b) The removal of H2O to form a secondary (2o) carbonium ion
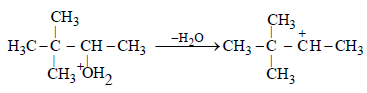
(c) The conversion of 2o carbonium to the more stable 3o carbonium ion by the shift of CH3 group
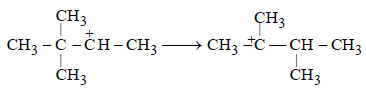
(d) The removal of H+ to form a double bond
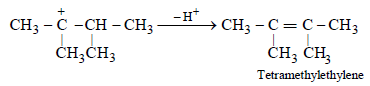
14. A compound D (C8H10O) upon treatment with alkaline solution of iodine gives a yellow precipitate. The filtrate on acidification gives a white solid E (C7H6O2). Write the structures of D and E and explain the formation of E. (1996 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
NOTE :
The reaction of D (C8H10O ) with alkaline solution of iodine is an iodoform reaction. This reaction is possible if the compound D has 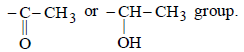
The high carbon content in D indicates that D is an aromatic compound containing a benzene ring. To account for the given formula, the compound D may be C6H5CH(OH)CH3 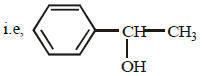
The given reactions are
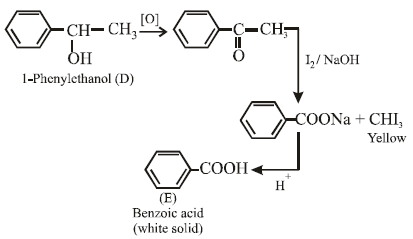
15. An optically active alcohol A (C6H10O) absorbs two moles of hydrogen per mole of A upon catalytic hydrogenation and gives a product B. The compound B is resistant to oxidation by CrO3 and does not show any optical activity. Deduce the structures of A and B. (1996 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
(a) Since (B) is resistant to oxidation, it must be ter-alcohol.
(b) Since (B) is optically inactive, it must have at least two alkyl groups similar.
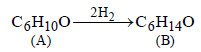
Thus the five carbon atoms can be adjusted into three alkyl groups (of which two are similar) either as –CH3, –CH3, and –C3H7, or as –C2H5, –C2H5 and –CH3,
Thus the possible structure of alcohol (B) is either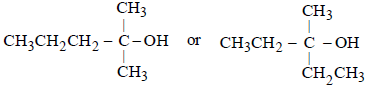
Hence the corresponding compound (A) is either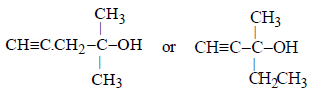
However, the compound (A) is optically active, so (A) and hence also (B) should have right side structure.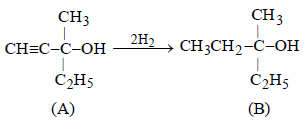
16. Predict the structures of the intermediates/products in the following reaction sequence : (1996 - 2 Marks)
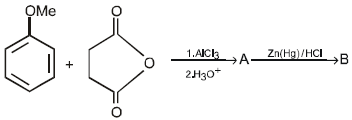
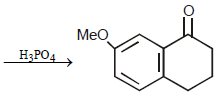
Solution :
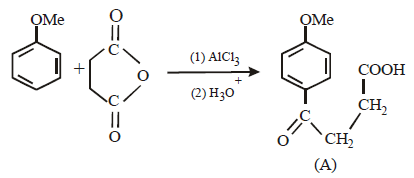
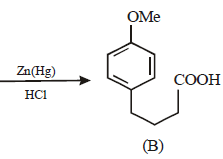
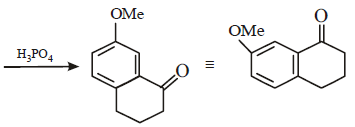
17. 2, 2-Dimethyloxirane can be cleaved by acid (H+). Write mechanism. (1997 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
The oxirane ring is cleaved via SN2 mechanism
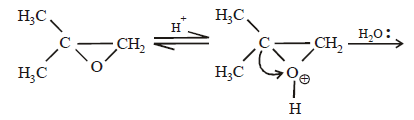
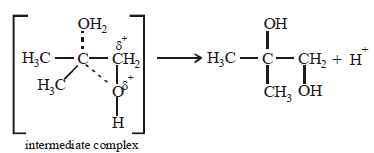
18. Which of the following is the correct method for synthesising methyl-t-butyl ether and why?
(i) (CH3)3CBr + NaOMe →
(ii) CH3Br + NaO-t-Bu → (1997 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
The method given in (ii) is the correct method for the formation of ether because method (i) leads alkene as the main product.
NOTE :
3° alkyl halides are easily dehydrohalogenated by base.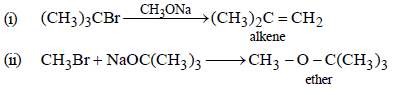
19. Write the intermediate steps for each of the following reaction.
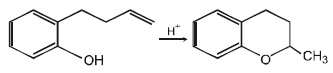
Solution :
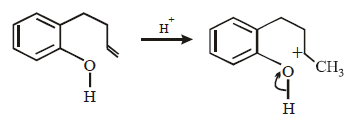
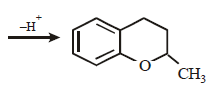
20. Explain briefly the formation of the products giving the structures of the intermediates. (1999 - 3 Marks)
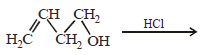
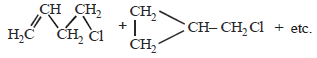
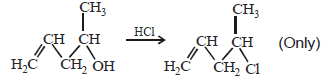
Solution :
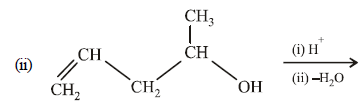
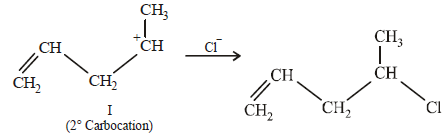
(i) NOTE :
Since the large propenyl group is attached to the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group, so the reaction is likely to occur via SN1 mechanism.
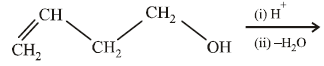
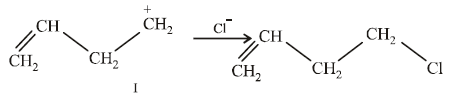
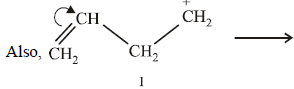
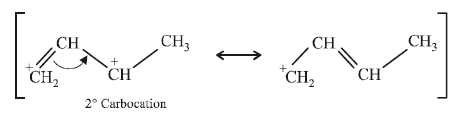
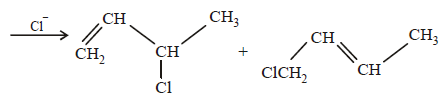
NOTE :
In the intermediate carbocation, Ia carbon bearing positive charge has CH3 group which decreases the positive charge and hence prevents cyclisation of the
compound.
21. A biologically active compound, bombykol (C16H30O) is obtained from a natural source. The structure of the compound is determined by the following reactions.
(2002 - 5 Marks)
(a) On hydrogenation, bombykol gives a compound A, C16H34O, which reacts with acetic anhydride to give an ester;
(b) Bombykol also reacts with acetic anhydride to give another ester, which on oxidative ozonolysis (O3/H2O2) gives a mixture of butanoic acid, oxalic acid and 10-
acetoxydecanoic acid.
Determine the number of double bonds in bombykol. Write the structures of compound A and bombykol. How many geometrical isomers are possible for bombykol?
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
Let us summarise the given facts.
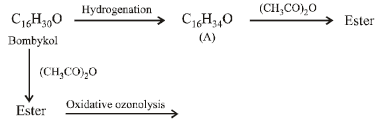
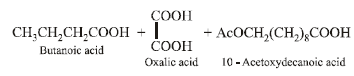
(i) Hydrogenation of bombykol (C16H30O) to C16H34O (A) indicates the presence of two double bonds in bombykol.
(ii) Reaction of A with acetic anhydride to form ester indicates the presence of an alcoholic group in A and hence also in bombykol.
(iii) Products of oxidative ozonolysis of bombykol ester suggests the structure of bombykol.
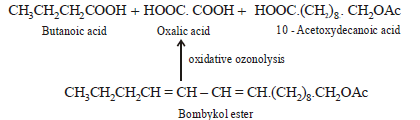
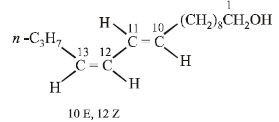
The structure of the bombykol ester suggests that bombykol has the following structure :
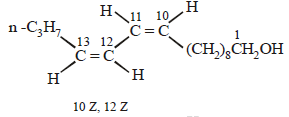
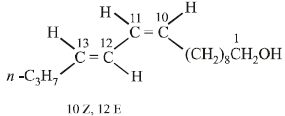
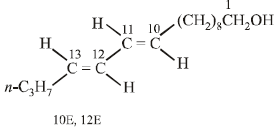
CH3CH2CH2CH = CH – CH = CH.(CH2)8.CH2OH (Bombykol) and the structure of A is
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2(CH2)8.CH2OH or C16H33OH.
Four geometrical isomers are possible for the above bombykol structure (as it has two double bonds).
22. An organic compound (P) of molecular formula C5H10O is treated with dil. H2SO4 to give two compounds (Q) and (R) both of which respond iodoform test. The rate of reaction of (P) with dil. H2SO4 is 1010 faster than the reaction of ethylene with dil. H2SO4. Identify the organic compounds, (P), (Q) and (R) and explain the extra reactivity of (P). (2004 - 4 Marks)
Solution :
(i) Molecular formula of P, C5H10O indicates 1º of unsaturation. So it should have double bond.
(ii) Acidic hydrolysis of P to Q and R, both of which responds iodoform test, indicates that Q and R should have following structure.
CH3CH2OH, (CH3)2CHOH, CH3CHO or CH3COR
The only possible linkage that can explain such hydrolysis is ether. Hence P should have following type of structure.
C2 – Component – O – C3 – Component
Further either the C2 – or the C3 – component should have double bond, thus the possible structure for P should be either of the following two structures which explains all the
given reactions.
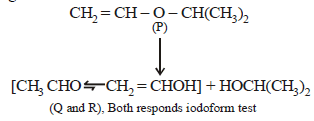
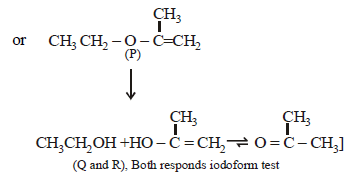
Extra reactivity of P toward dil. H2SO4 than ethylene is due to formation of highly stable carbocation
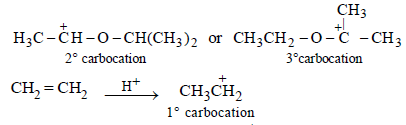
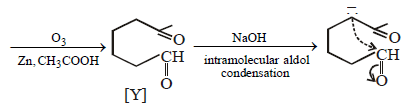
23. Identify (X) and (Y) in the following reaction sequence. (2005 - 2 Marks)
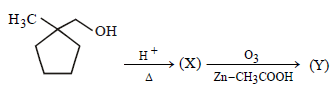
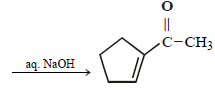
Solution :
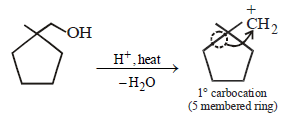
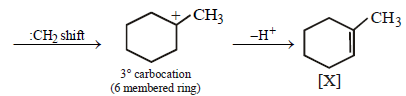
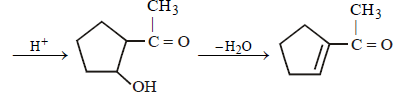
|
446 docs|929 tests
|





















