JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Electrochemistry- 1 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
1. The density of copper is 8.94 g/ml. Find out the number of coulombs needed to plate an area 10 cm × 10 cm to a thickness 10–2 cm using CuSO4 solution as electrolyte. (1979)
Ans: 27171.96 coulombs
Solution: 
2. (a) 19 gm of molten SnCl2 is electrolysed for some time. Inert electrodes are used. 0.119 gm of Sn is deposited at the cathode. No substance is lost during the electrolysis. Find the ratio of the weights of SnCl2: SnCl4 after electrolysis.
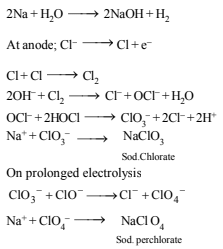
(b) A hot solution of NaCl in water is electrolysed. Iron electrodes are used. Diaphragm cell is not used. Give equations for all the chemical reactions that take place during electrolysis.
(c) Find the charge in coulombs of 1 gram ion of N3– (1980)
Ans: (a) 71.34 : 1, (c) 2.06 × 104 coulombs
Solution: 
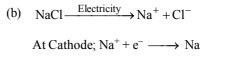
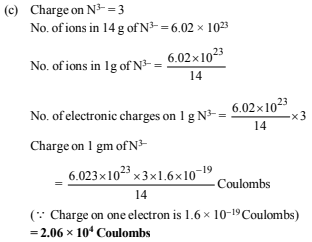
3. Complete and balance the following equations (1980)
(i) KNO3 + FeSO4 + H2SO4(conc) 
(ii) H2S + K2CrO4 + H2SO4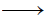
(iii) KI + H2SO4(conc) 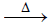
(iv) Mg3N2 + H2O 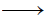
(v) Al + KMnO4 + H2SO4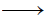
Solution: 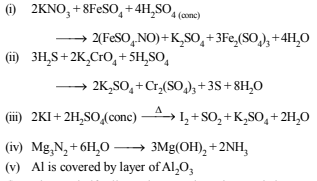
4. Consider the cell (1982 - 2 Marks)
Zn | Zn2+ (aq) (1.0 M) || Cu2+ (aq) (1.0 M) | Cu.
The standard reduction potentials are :
+0.350 volts for 2e– + Cu2+ (aq) → Cu and –0.763 volts for 2e– + Zn2+ (aq) → Zn
(i) Write down the cell reaction.
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell.
(iii) Is the cell reaction spontaneous or not?
Ans: (ii) 1.113 volts, (iii) spontaneous
Solution:
(i) The two half cell reactions can be written as below :
(iii) Since emf of the cell is Positive, the reaction as written is Spontaneous.
5. In an electrolysis experiment current was passed for 5 hours through two cells connected in series. The first cell contains a solution of gold and the second contains copper sulphate solution. 9.85 g of gold was deposited in the first cell. If the oxidation number of gold is +3, find the amount of copper deposited on the cathode of the second cell. Also calculate the magnitude of the current in amperes.(1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs) (1983 - 3 Marks)
Ans: 4.7625 g, 0.8042 A
Solution:
Gold deposited in the first cell = 9.85 g
At. wt. of Gold = 197, Oxidation number of gold = +3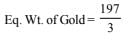
W = Zit
(where W stands for the weight of ions deposited, i for
current and t for time and Z for electro-chemical equivalent
of the electrolyte.)
∵ Charge required to deposit 1 g eq. of gold = 1F = 96,500 C
∴ Charge required to deposit 9.85 g of gold or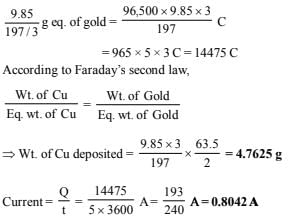
6. How long a current of 3 ampere has to be passed through a solution of silver nitrate to coat a metal surface of 80 cm2 with a 0.005 mm thick layer? Density of silver is 10.5 g/cm3. (1985 - 3 Marks)
Ans: 125.09 sec
Solution:
Volume of the surface = area × thickness|
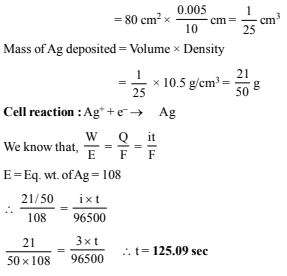
7. The EMF of a cell corresponding to the reaction :
Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn2+ + (0.1 M) + H2 (g) (1 atm.) is 0.28 volt at 25ºC.
Write the half-cell reactions and calculate the pH of the solution at the hydrogen electrode.
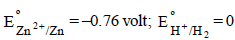 (1986 - 4 Marks)
(1986 - 4 Marks)
Ans: 8.62
Solution:
Half cell reactions will be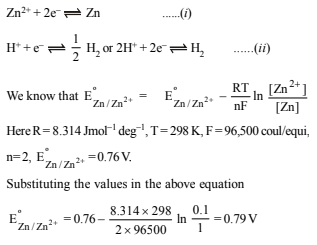
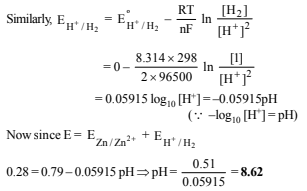
8. During the discharge of a lead storage battery, the density of sulphuric acid fell from 1.294 to 1.139 g/ml. Sulphuric acid of density 1.294 g/ml is 39% by weight and that of 1.139 g/ml is 20% H2SO4 by weight. The battery holds 3.5 litres of the acid and the volume remained practically constant during the discharge.
Calculate the number of ampere-hours for which the battery must have been used. The charging and discharging reactions are : (1986 - 5 Marks)
Anode :
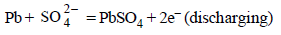
Cathode :
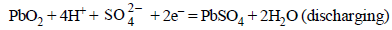
Note : Both the reactions take place at the anode and cathode respectively during discharge. Both reaction get reverse during charging.
Ans: 265.02 Ah
Solution:
In lead storage battery the anodic and cathodic reactions
during discharge (or operation or working) are as :
(i) Anode Reaction :
In both the half cell reactions H2SO4 is consumed and hence conc. of H2SO4 decreases during the working (discharging of the battery. For the withdrawl of 2F = 2 × 96500 C of electric charge, 2 mol of H2SO4 are consumed. Density of H2SO4 solution (used as electrolyte) falls during working of the cell.
Both reactions get reversed on charging the battery leading to regeneration of H2SO4
as : Formerly anode but now cathode (recharging)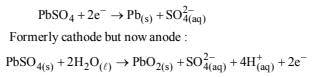
[NOTE: In 1986 IIT-JEE paper there was a mistake in the question paper itself. Reaction (ii) was shown to take place during recharging of the battery which is infact the reaction
occuring at cathodic half cell during operation (discharging) of the battery.]
9. A 100 watt, 110 volt incandescent lamp is connected in series with an electrolyte cell containing cadmium sulphate solution. What weight of cadmium will be deposited by the current flowing for 10 hours? (1987 - 5 Marks)
Ans: 19.06 g
Solution: 
10. A cell contains two hydrogen electrodes. The negative electrode is in contact with a solution of 10–6 M hydrogen ions. The EMF of the cell is 0.118 V at 25ºC. Calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions at the positive electrode. (1988 - 2 Marks)
Ans: 10–4 M
Solution: 
NOTE It is a concentration cell as both the electrodes are made of same element. Negative electrode acts as anode in a galvanic cell.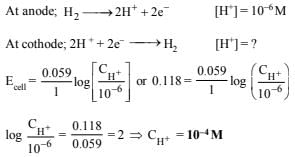
11. In a fuel cell hydrogen and oxygen react to produce electricity. In the process hydrogen gas is oxidised at the anode and oxygen at the cathode. If 67.2 litre of H2 at STP react in 15 minutes, what is the average current produced? If the entire current is used for electro deposition of copper from copper (II) solution, how many grams of copper will be deposited? (1988 - 4 Marks)
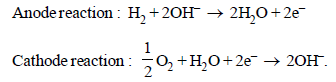
Ans: 643.3 A, 190.50 g
Solution:
For the given reactions, it is obvious that 22.4 litres of H2 gas require 2 Faraday electricity.
∴ 67.2 litres of H2 will produce = 6 Faraday electricity
Q = C × t; 6 × 96500 = C × 15 × 60
12. An acidic solution of Cu2+ salt containing 0.4 g of Cu2+ is electrolysed until all the copper is deposited. The electrolysis is continued for seven more minutes with the volume of solution kept at 100 ml. and the current at 1.2 amp. Calculate the volume of gases evolved at NTP during the entire electrolysis. (1989 - 5 Marks)
Ans: 99.79 ml, 58.48 ml
Solution:
The chemical reactions taking place at the two electrodes are
Thus in first case, Cu2+ ion will be discharged at the cathode and O2 gas at the anode. Let us calculate the volume of gas(O2) discharged during electrolysis.
According to Faraday’s second law 31.75 g Cu ≡ 8 g of oxygen ≡ 5.6 litres of O2 at NTP

13. The standard reduction potential at 25ºC of the reaction, 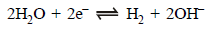 is –0.8277V. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction
is –0.8277V. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction 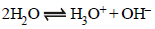 at 25ºC. (1989 - 3 Marks)
at 25ºC. (1989 - 3 Marks)
Ans: 9.88 × 10–15
Solution: 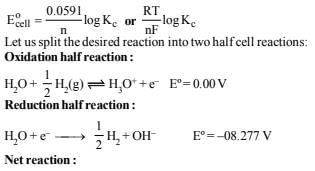

14. The standard reduction potential of Cu++/Cu and Ag+/Ag electrodes are 0.337 and 0.799 volt respectively. Construct a galvanic cell using these electrodes so that its standard e.m.f. is positive. For what concentration of Ag+ will the e.m.f. of the cell, at 25ºC, be zero if the concentration of Cu++ is 0.01 M? (1990 - 3 Marks)
Ans: 1.48 × 10–9 M
Solution:

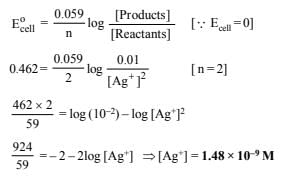
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















