JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles & Technique | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Arrange the following in :
(i) Increasing reactivity towards HCN
CH3CHO, CH3COCH3, HCHO, C2H5COCH,
(ii) n-butane, n-butanol, n-butyl chlor ide, isobutane in increasing order of boiling point.
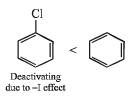
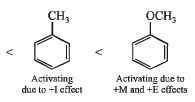
(iii) benzene, toluene, methoxybenzene, chlorobenzene in increasing order of reactivity towards sulphonation with fuming sulphuric acid.
(iv) Increasing order of acid strength
ClCH2COOH (I), CH3CH2COOH (II), ClCH2CH2COOH (III), (CH3)2CHCOOH (IV), CH3COOH (V)
(v) Increasing reactivity in nucleophilic substitution reactions
CH3F, CH3I, CH3Br, CH3Cl
Ans. (i) C2H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO
(ii) isobutane < n-butane < n-butyl chloride < n-butanol
(iii) chlorobenzene < benzene < toluene < methoxybenzene
(iv) IV < II < III < V < I
(v) CH3F < CH3Cl < CH3Br < CH3I
Solution.
(i) TIPS/Formulae : It is a case of nucleophilic addition reaction. More the electron deficiency of the carbonyl carbon, greater will be its reactivity towards nucleophilic addition.
C2H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO

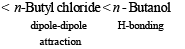
Straight chain alkane isomer has higher boiling point than the isomeric branched chain isomer because the former isomer has larger surface area which leads to large vander Waals attractive forces.
(iii) NOTE : –OCH3 and –CH3 groups are activating group while –Cl is a deactivating group for electrophilic substitution.
(iv) Presence of electron withdrawing group increases the acidic character of the –COOH due to –I effect, while presence of electron-donating group (alkyl groups) decreases the acidic character due to +I effect. Thus
IV < II < V < III < I
(v) NOTE : A weaker base is a better leaving group. Rate of reaction will be R – I > R – Br >R – Cl > R – F. because I– is the best, while F– is the poorest leaving groups among halide ions.
Q.2. (i) Write the IUPAC name of :
CH3CH2CH = CHCOOH
(ii) Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
(iii) Write the IUPAC name for the following :
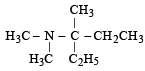
Ans. (i) Pent-2-en-1-oic acid or 2-Pentenoic acid
(ii) 5, 6-diethyl-3-methyl-4-decene
(iii) 3–(N, N dimethylamino)-3–methylpentane
Solution.
(i) 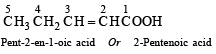
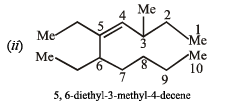
(iii) IUPAC name is
3–(N, N-dimethylamino)–3–methylpentane.
Q.3. For nitromethane molecule, write structure(s).
(i) showing significant resonance stabilisation.
(ii) indicating tautomerism.
Solution.
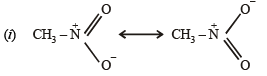
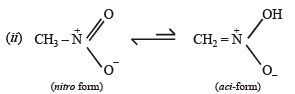
Q.4. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Carbon oxygen bond lengths in formic acid are 1.23Å and 1.36Å and both the carbon oxygen bonds in sodium formate have the same value i.e. 1.27Å.
(ii) Phenyl group is known to exert negative inductive effect. But each phenyl ring in biphenyl (C6H5 – C6H5) is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution .
(iii) Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic reagents
(iv) CH2=CH– is more basic than HC ≡ C– .
(v) Normally, ben zene gives electroph ilic substitution reaction rather than electrophilic addition reaction although it has double bonds.
Solution.
(i) In formic acid, resonance is not possible with the result there are two types of C – O bonds. In sodium formate, resonance is possible, so both of the C – O bonds have same bond length.

(ii) In biphenyl, one of the phenyl groups acts as electron donor and the other electron acceptor due to mesomeric effect. This makes it more reactive than benzene.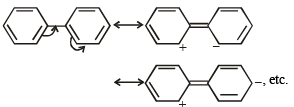
(iii) The low reactivity of halogen atom in aryl and vinyl halides towards nucleophiles is due to resonance.
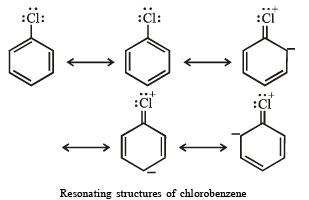
NOTE : Due to resonance, carbon-chlorine bond acquires partial double bond character, hence it becomes shorter and stronger and thus cannot be easily replaced by nucleophiles.
(iv) CH ≡ C–, C– is sp hybridised and more electronegative then the 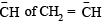 which is sp2 hybridised.
which is sp2 hybridised.
Thus the former can better accomodate electron pair hence less basic.
(v) Benzene gives electrophilic substitution reaction rather than electrophilic addition reactions because it will have a stable benzene ring in the product, whereas electrophilic addition on benzene destroys the benzenoid ring.
Q.5. Write the structural formula of 4-chloro-2-pentene.
Ans. 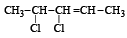
Solution. 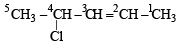
Q.6. Write tautomeric forms for phenol.
Solution.
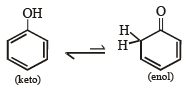
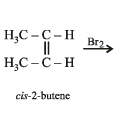
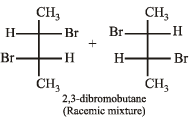
Q.7. Write down the structures of the stereoisomers formed when cis-2-butene is reacted with bromine.
Solution. cis-Alkenes add bromine to form racemic mixture.
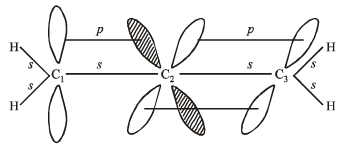
Q.8. Discuss the hybridisation of carbon atoms in allene (C3H4) and show the π-orbital overlaps.
Solution.
Q.9. Identify the pairs of enantiomers and diastereomers from the following compounds I, II and III
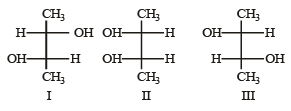
Ans. enantionmers – I & III; diastereomers – I & II and II & III.
Solution. In order to convert a molecule with two stereogenic centres to its enantiomer, the confuguration at both centres must be reversed. Reversing the configuration at only one stereogenic centre converts it to a distereomeric structure.
Thus structures I and III are enantiomers; while structures I and II as well as II and III are diastereomers.
Q.10. Which one is more soluble in diethyl ether - anhydrous AlCl3 or hydrous AlCl3? Explain in terms of bonding.
Ans. Anyhydrous AlCl3
Solution.
TIPS/Formulae :
Diethyl ether acts as a lewis base and anhydrous AlCl3 as a lewis acid.
Anyhydrous AlCl3 is more soluble in diethyl ether because the oxygen atom of ether donates its pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of electron deficient aluminium of AlCl3 through the formation of coordinate bond. In case of hydrated AlCl3 aluminium is not electron deficient as oxygen atom of water molecule has already donated its pair of electrons to meet the electron deficiency of aluminium.
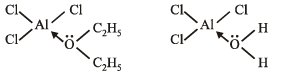
Q.11. Match the Ka values
Ka
(a) Benzoic acid 6.4 × 10–5
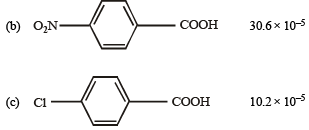
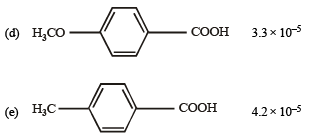
Solution. NOTE : Higher the Ka value, more stronger is the acid. Correct order of acidic strength of the given acids is
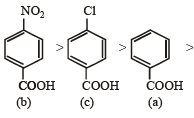
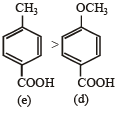
Hence the Ka values of the five acids will be in the order.
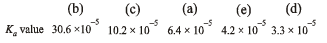
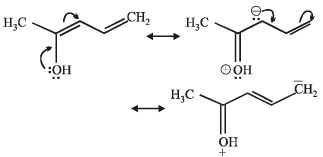
Q.12.
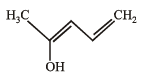
Write resonance structure of the given compound.
Solution.
Q.13. Which of the following is more acidic and why ?
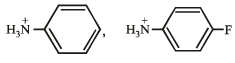
Solution. Presence of an electron-attracting group increases acidity of the compound. Thus
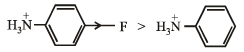
Q.14. (i) 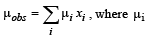 is the dipole moment of a stable conformer of the molecule, Z – CH2 – CH2 – Z and xi is the mole fraction of the stable conformer..
is the dipole moment of a stable conformer of the molecule, Z – CH2 – CH2 – Z and xi is the mole fraction of the stable conformer..
Given : μobs = 1.0 D and x(Anti) = 0.82
Draw all the stable conformers of Z – CH2 – CH2 – Z and calculate the value of μ(Gauche).
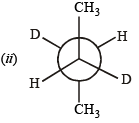
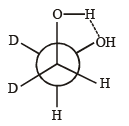
(ii) Draw the stable conformer of Y – CHD – CHD – Y (meso form), when Y = CH3 (rotation about C2 – C3) and Y = OH (rotation about C1 – C2) in Newmann projection.
Ans. (i) µ(gauche) = 5.55 D
Solution.
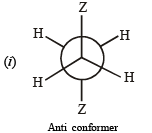
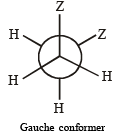
Given, mole fraction of anti conformer = 0.82
∴ mole fraction of gauche conformer = 0.18

|
446 docs|929 tests
|





















