JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Properties of Triangle - 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q. 17. ABC is a triangular park with AB = AC = 100 m. A television tower stands at the midpoint of BC. The angles of elevation of the top of the tower at A, B, C are 45°, 60°, 60°, respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Solution. Let ABC be the triangular region with AB = AC = 100 m
Let M be the mid pt of BC at which tower LM stands.
As DABC is isosceles and M is mid pt. of BC
∴ AM ⊥ BC .
Let LM = h be the ht. of tower.
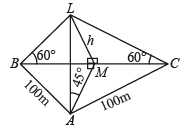
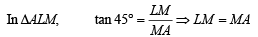
∴MA = h
Also in ΔBLM, 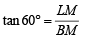
⇒ 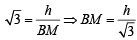
Now in rt ΔAMB, we have
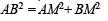
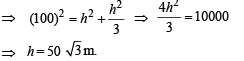
Q. 18. A vertical tower PQ stands at a point P. Points A and B are located to the South and East of P respectively. M is the mid point of AB. PAM is an equilateral triangle; and N is the foot of the perpendicular from P on AB. Let AN = 20 metres and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower at N is tan -1 (2) . Determine the height of the tower and the angles of elevation of the top of the tower at A and B.
Solution. Let PQ = h
As A and B are located to the south and east of P respectively,
∴ ∠APB = 90°. M is mid pt of AB. PAM is an equilateral Δ
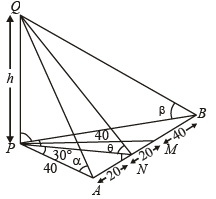
∴ ∠ APM = 60° :
Also PN ⊥ AB, therefore AN = NM = 20 m
⇒ AP = 40 m
Let angles of elevation of top of the tower from A, N and B be α, θ and β respectively. ATQ, tan θ = 2
In ΔPQN 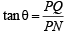
⇒ 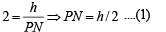
Also in ΔAPM, ∠APM = 60° (being equilateral Δ) and PN is altitude ∴ ∠APN = 30° (as in equilateral Δ altitude bisects the vertical angle.
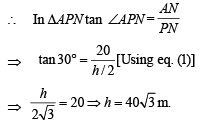
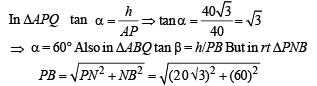
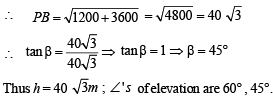
Q. 19. The sides of a triangle are three consecutive natural numbers and its largest angle is twice the smallest one. Determine the sides of the triangle.
Solution. Let the sides of Δ be n, n + 1, n + 2 where n ∈ N .
Let a = n, b = n + 1, c = n + 2
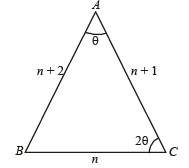
Let the smallest angle ∠A = θ then the greatest ∠C = 2θ
InΔABC by applying Sine Law we get,
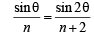
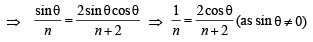
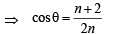
In ΔABC by Cosine Law, we get
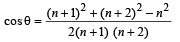 ....(2)
....(2)
Comparing the values of cos θ from (1) and (2), we get
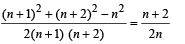
⇒ (n + 2)2 (n + 1) = n (n + 2)2 + n (n + 1)2 – n3
⇒ n (n + 2)2 + (n + 2)2 = n (n + 2)2 + n (n + 1)2 – n3
⇒ n2 + 4n + 4 = n3 + 2n2 + n – n3
⇒ n2 – 3n – 4 = 0 ⇒ (n + 1) (n – 4) = 0
⇒ n = 4 (as n ≠ – 1)
∴ Sides of Δ are 4, 4 + 1, 4 + 2, i.e. 4, 5, 6.
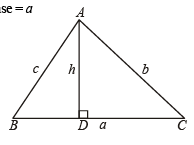
Q. 20. In a triangle of base a the ratio of the other two sides is r (< 1). Show that the altitude of the triangle is less than of equal to 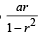
Solution. Given that, In ΔABC, base = a
and c/b = r
To find altitude, h.
We have, in ΔABD,
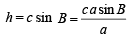
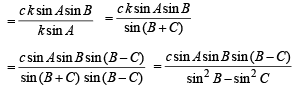
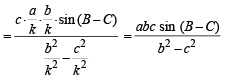
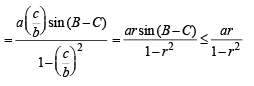
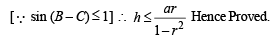
Q. 21. A man notices two objects in a straight line due west. After walking a distance c due north he orserves that the objects subtend an angle α at his eye; and, after walking a further distance 2c due north, an angle β . Show that the distance between the objects is 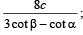 the height of the man is being ignored.
the height of the man is being ignored.
Solution. Let the man initially be standing at ‘A’ and ‘B’ be the position after walking a distance ‘c’, so total distance becomes 2c and the objects being observed are at ‘C’ and ‘D’.
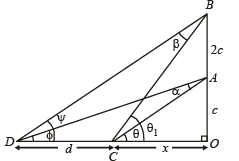
Now we have OA = c, AB = 2c
Let CO = x and CD = d
Let ∠CAD = α and ∠CBD = β
∠ACO = θ and ∠ADC = φ
∠BCD = ψ and ∠BCO = θ1
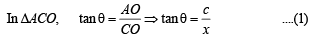
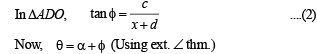
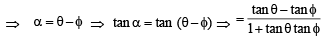
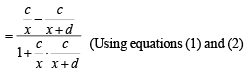
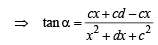
⇒ x2 + c2 + xd = cd cot α ....(3)
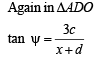 ....(4)
....(4)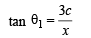 ....(5)
....(5)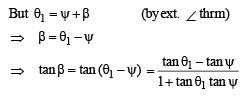
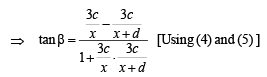
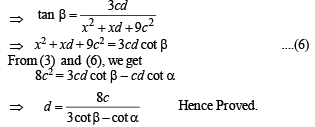
Q. 22. Three circles touch the one another externally. The tangent at their point of contact meet at a point whose distance from a point of contanct is 4. Find the ratio of the product of the radii to the sum of the radii of the circles.
Solution. Let us consider three circles with centres at A, B and C and with radii r1, r2 and r3 respectively which touch each other externally at P, Q and R. Let the common tangents at P, Q and R meet each other at O. Then OP = OQ = OR = 4 (given) (lengths of tangents from a pt to a circle are equal).
Also OP ⊥ AB, OQ ⊥ AC, OR ⊥ BC.
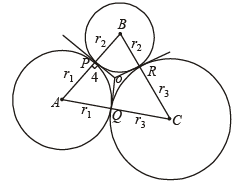
⇒ O is the incentre of the ΔABC
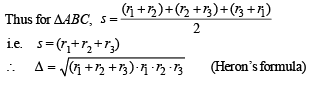
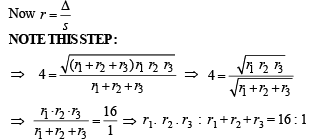
Q. 23. An observer at O notices that the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is 30°. The line joining O to the base of the tower makes an angle of tan–1 (1 /√2) with the North and is inclined Eastwards. The observer travels a distance of 300 meters towards the North to a point A and finds the tower to his East. The angle of elevation of the top of the tower at A is φ , Find φ and the height of the tower.
Solution. Let PQ be the tower of height h. A is in the north of O and P is towards east of A.
∴ ∠OAP = 90°; ∠QOP = 30°; ∠QAP = φ
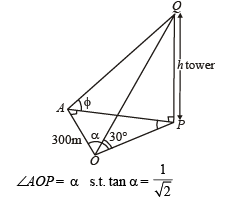
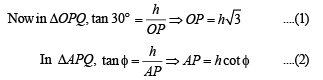
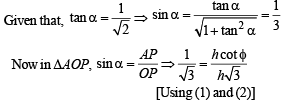
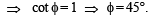
Again in ΔOAP, using Pythagoras thm, we get
OP2 = OA2 + AP2
⇒ 3h2 = 90000 + h2 cot2 45° ⇒ h = 150√2m
Q. 24. A tower AB leans towards west making an angle a with the vertical. The angular elevation of B, the topmost point of the tower is β as observed from a point C due west of A at a distance d from A. If the angular elevation of B from a point D due east of C at a distance 2d from C is γ, then prove that 2 tan α = – cot β + cot γ.
Solution. Let AB be the tower leaning towards west making an angle a with vertical
At C, ∠ of elevation of B is β and at D the
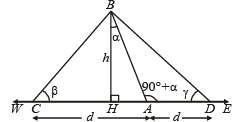
∠of elevation of B is γ
CA = AD = d
KEY CONCEPT :
m : n theorem: In DABC where point D divides BC in the ratio m : n. and ∠ADC = θ
(i)(m + n) cot θ = n cot θ – m cot C
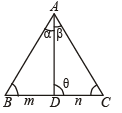
(ii)(m + n) cot θ = m cot α – n cot β
In ΔBCD, A divides CD in the ratio 1 : 1 where base ∠'s are β and γ and ∠BAD = 90° + α
∴ By applying m : n theorem we get
(1 + 1) cot (90° + α) = 1.cot β – 1. cot γ
⇒ – 2 tan α = cot β – cot γ
⇒ 2 tan α = cot γ – cot β
Hence Proved
Q. 25. Let A1, A2,.........., An be the vertices of an n-sided regular polygon such that 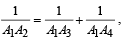 Find the value of n.
Find the value of n.
Solution. Let a be the side of n sided regular polygon A1A2A3A4.....An
∴ ∠Subtended by each side at centre 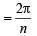
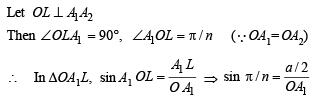
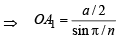 ....(1)
....(1)
Again by geometry it can be proved that OM ⊥ A1A3
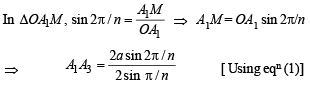
Also if ON ⊥ A1A4, then ON bisects angle
∠ A1OA4 = 3(2π/n)
∴ ∠ A1ON = 3 π/n
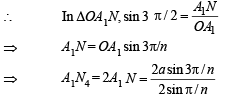
But given that
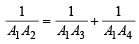
⇒ 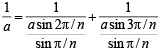
⇒ sin 3π/n sin 2π/n
= (sin 3π/n+sin 2π/n) sin π/n
⇒ 2 sin 3π/n sin 2π/n
= 2 sin 3π/n sin π/n + 2 sin 2π/n sin π/n
⇒ cos π/n – cos 5π/n
= cos 2π/n – cos 4π/n + cos π/n – cos 3π/n
⇒ cos 2π/n + cos 5π/n = cos 4π/n + cos 3π/n
⇒ 2 cos 7π/2n cos 3π/2n = 2 cos 7π/2n cos π/2n
⇒ cos 7π/2n (cos 3π/2n – cos π/2n) = 0
⇒ cos 7π/2n . 2 sin 2π/n sin π/n = 0
⇒ cos 7π/2n = 0
or sin 2π/n = 0 or sin π/n = 0
⇒ 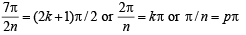
⇒ 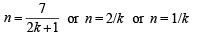
But n should be a +ve integer being no. of sides and n > 4 (four vertices being considered in the question)
∴ the only possibility is 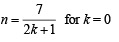
∴ n = 7
Q. 26. Consider the following statements concerning a triangle ABC
(i) The sides a, b, c and area D are rational.
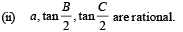
(iii) a, sin A, sin B, sin C are rational.
Prove that (i) ⇒ (ii) ⇒ (iii) ⇒ (i)
Solution. (I) a, b c and D are rational.
⇒ 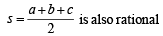
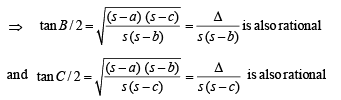
Hence (I) ⇒ (II).
(II) a, tan B/2, tan C/2 are rational.
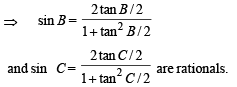
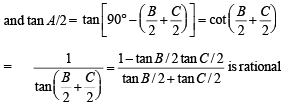
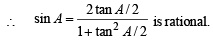
Hence (II) ⇒ (III)
(III) a, sin A, sin B, sin C are rational.
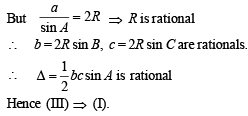
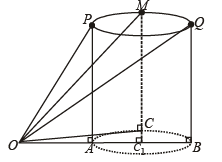
Q. 27. A bird flies in a circle on a horizontal plane. An observer stands at a point on the ground. Suppose 60° and 30° are the maximum and the minimum angles of elevation of the bird and that they occur when the bird is at the points P and Q respectively on its path. Let θ be the angle of elevation of the bird when it is a point on the arc of the circle exactly midway between P and Q. Find the numerical value of tan2θ. (Assume that the observer is not inside the vertical projection of the path of the bird.)
Solution. Let A, B and C be the projections of the pts.
P, Q and M on the ground.
ATQ, ∠POA = 60°, ∠QOB = 30°, ∠MOC = θ
Let h be the ht of circle from ground, then
AP = CM = BQ = h
Let OA = x and AB = d (diameter of the projection of the circle on ground with C1 as centre).
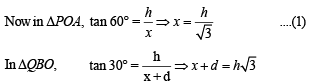
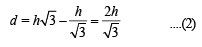
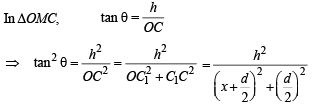
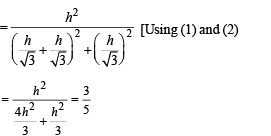
Q. 28. Prove that a triangle ABC is equilateral if and only if tan A + tan B + tan C = 3√3.
Solution. Let ABC is an equilateral D then
A = B = C = 60°
⇒ tan A + tan B + tan C = 3√3
Conversely, suppose
tan A + tan B + tan C = 3√3 ....(1)
Now using A.M. > G.M. (equality occurs when no’s are equal)
For tan A, tan B, tan C, we get
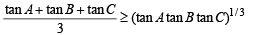
But in any ΔABC, we know that tan A+ tan B + tan C = tan A tan B tan C
∴ Last inequality becomes
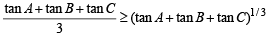
⇒ (tan A + tan B + tan C)2/3 > 3
⇒ tan A + tan B + tan C > 3√3
where equality occurs when tan A, tan B, tan C are equal, i.e., A = B = C
⇒ DABC is equilateral.
Q. 29. Let ABC be a triangle having O and I as its circumcenter and in centre respectively. If R and r are the circumradius and the inradius, respectively, then prove that (IO)2 = R2 – 2Rr. Further show that the triangle BIO is a right-angled triangle if and only if b is arithmetic mean of a and c.
Solution. In DABC, O and I are circumcen tre and incentre of Δ respectively and R and r are the respective radii of circum circle and incircle.
To prove (IO)2 = R2 – 2Rr
First of all we will find IO. Using cosine law in ΔAOI
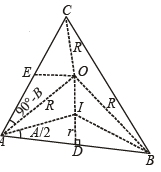
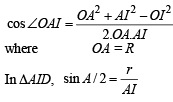
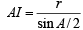
AI = 4R sin B/2 sin C/2 [Using r = 4R sin A/2 sin B/2 sin C/2]
Also, ∠OAI = ∠IAE – ∠OAE
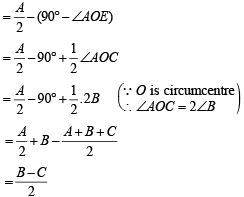
Substituting all these values in equation (1) we get
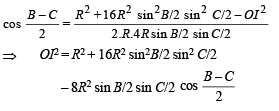
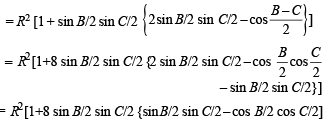
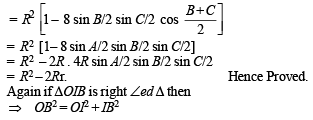
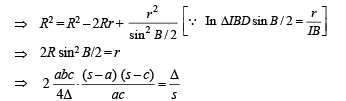
⇒ b (s – a) (s – c) = 2 (s – a) (s – b) (s – c)
⇒ b = 2s – 2b ⇒ b = a + c – b
⇒ a + c = 2b ⇔ a, b, c are in A.P..
⇒ b is A.M. between a and c. Hence Proved.
Q. 30. Let ABC be a triangle with incentre I and inradius r. Let D,E,F be the feet of the perpendiculars from I to the sides BC, CA and AB respectively. If r1, r2 and r3 are the radii of circles inscribed in the quadrilaterals AFIE, BDIF and CEID respecitvely, prove that
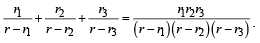
Solution. Let MN = r3 = MP = MQ , ID = r
⇒ IP = r – r3
Clearly IP and IQ are tangents to circle with centre M.
∴ IM must be the ∠ bisector of ∠ PIQ
⇒ ∠PIM = ∠QIM = θ1
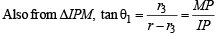
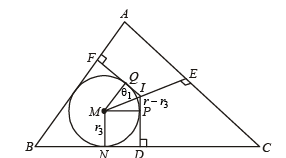
Here DI = r
Similarly, in other quadrilaterals, we get
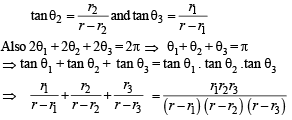
Q. 31. If D is the area of a trian gle with side lengths a, b, c, th en show that 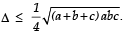 Also show that the equality occurs in the above inequality if and only if a = b = c.
Also show that the equality occurs in the above inequality if and only if a = b = c.
Solution. We know, 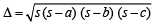
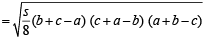
Since sum of two sides is always greater than third side;
∴ b + c – a, c + a – b, a + b – c > 0
⇒ (s – a) (s – b) (s – c) > 0
Let s – a = x, s – b = y, s – c = z
Now, x + y = 2 s – a – b = c
Similary, y + z = a and z + x = b
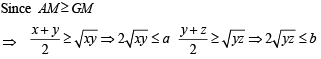
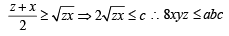
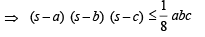
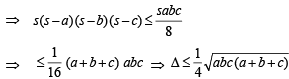
and equality holds when x = y = z ⇒ a = b = c
Q. 32. If In is the area of n sided regular polygon inscribed in a circle of unit radius and On be the area of the polygon circumscribing the given circle, prove that
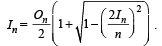
Solution. Let OAB be one triangle out of n of a n sided polygon inscribed in a circle of radius 1.
Then 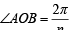
OA = OB = 1
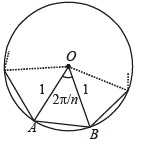
∴ Using Area of isosceles Δ with vertical ∠θ and equal sides as
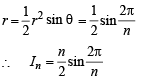 ...... (1)
...... (1)
Further consider the n sided polygon subscribing on the circle.
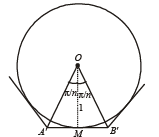
A'MB' is the tangent of the circle at M.
⇒ A'MB' ⊥ OM
⇒ A'MO is right angled triangle, right angle at M.
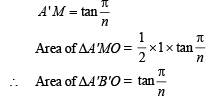
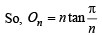 ............(2)
............(2)
Now, we have to prove
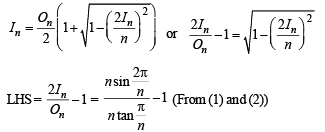
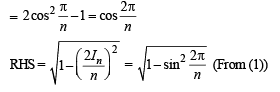
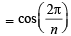 Hence Proved.
Hence Proved.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|
















