JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): The d & f-Block Elements & Coordination Compounds- 1 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
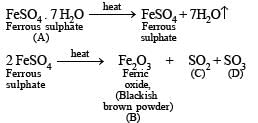
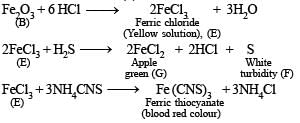
Q.1. A certain inorganic compound (A) on heating loses its water of crystallisation. On further heating, a blackish brown powder (B) and two oxides of sulphur (C and D) are obtained. The powder (B) on boiling with hydrochloric acid gives a yellow solution (E). When H2S is passed in (E) a white turbidity (F) and an apple green solution (G) are obtained. The solution (E) on treatment with thiocyanate ions gives a blood red coloured compound (H). Identify compounds from (A) to (H). (1978)
Solution. (i) Since the compound (A) on strong heating gives two oxides of sulphur (C and D) which might be SO2 and SO3, it must be a sulphate.
(ii) The reaction of compound (E) with thiocyanate to give blood red coloured compound (H) indicates that (E) must have Fe3+ ion.
Thus the compound (A) must be ferrous sulphate, FeSO4.7H2O, which explains all given reactions as below (Fe2+ ion of FeSO4 is changed to Fe3+ during heating).
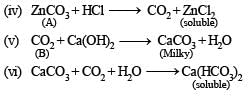
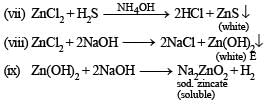
Q.2. A white amorph ous powder (A) on heatin g yields a colourless, non-combustible gas (B) and a solid (C). The latter compound assumes a yellow colour on heating and changes to white on cooling. ‘C’ dissolves in dilute acid and the resulting solution gives a white precipitate on adding K4Fe(CN)6 solution.
‘A’ dissolves in dilute HCl with the evolution of gas, which is identical in all respects with ‘B’. The gas ‘B’ turns lime water milky, but the milkiness disappears with the continuous passage of gas. The solution of ‘A’, as obtained above, gives a white precipitate (D) on the addition of excess of NH4OH and passing H2S. Another portion of the solution gives initially a white precipitate (E) on the addition of sodium hydroxide solution, which dissolves on futher addition of the base. Identify the compounds A, B, D, and E. (1979)
Ans. T
Solution.
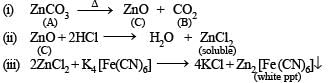
Q.3. State with balanced equations, what happens when
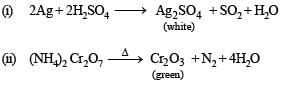
(i) Silver is treated with hot concentrated sulphuric acid.
(ii) Ammonium dichromate is heated.
(iii) Hydrogen sulphide is passed through a solution of potassium peramagnate acidified with dilute sulphuric acid. (1979)
Solution.
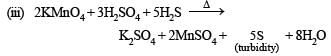
Q.4. A solution of FeCl3 in water gives a brown precipitate on standing. (1980)
Solution. On standing FeCl3 is hydrolysed and produces colloidal solution of Fe(OH)3 which is in form of brown precipitate.

Q.5. Complete the following equation (no balancing is needed) :
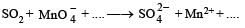
Solution. 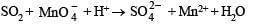
Q.6. State with balanced equations what happens when :
(i) sulphur dioxide gas is bubbled through an aqueous solution of copper sulphate in presence of potassium thiocyanate. (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) aqueous solution of ferric sulphate and potassium iodide are mixed. (1984 - 2 Marks)
(iii) aqueous solution of potassium manganate and acid are mixed. (1984 - 2 Marks)
(iv) aqueous solution of potassium chromate and acid are mixed. (1984 - 2 Marks)
(v) potassium permanganate interacts with manganese dioxide in presence of potassium hydroxide; (1985 - 1 Mark)
(vi) potassium ferrocyanide is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid; (1985 - 1 Mark)
(vii) Gold is dissolved in aqua regia. (1987 - 1 Mark)
(viii) Write balanced equations for the extraction of silver from silver glance by cyanide process. (1988 - 1 Mark)
(ix) Silver chloride is treated with aqueous sodium cyanide and the product thus formed is allowed to react with zinc in alkaline medium. (1989 - 1 Mark)
(x) Cobalt(II) solution reacts with KNO2 in acetic acid medium. (1989 - 1 Mark)
(xi) Write balanced equations for the extraction of copper from copper pyrites by self-reduction. (1990 - 2 Marks)
(xii) A mixture of potassium dichr omate and sodium chloride is heated with concentrated H2SO4. (1990 - 1 Mark)
(xiii) Iron reacts with cold dilute nitric acid. (1990 - 1 Mark)
(xiv) Potassium permanganate is added to a hot solution of manganous sulphate. (1990 - 1 Mark)
(xv) Copper reacts with HNO3 to give NO and NO2 in molar ratio of 2 : 1. (1992 - 1 Marks)
Cu + HNO3 → ........... + NO + NO2 + ........... .
(xvi) Na2CO3 is added to a solution of copper sulphate. (1992 - 1 Marks)
CuSO4 + Na2CO3 + H2O → ........... + Na2SO4 + ...........
(xvii) Potassium dichromate and concentrated hydrochloric acid are heated together. (1992 - 1 Mark)
(xviii) AgBr + Na2S2O3 → .... + ...... (1993 - 1 Mark)
(xix) (NH4)2 S2O8 + H2O + MnSO4 → .... + ...... +........ (1993 - 1 Mark)
(xx) [MnO4]2- + H+ →......... + [MnO4]- + H2O (1994 - 1 Mark)
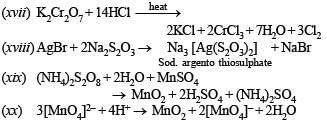
(xxi) 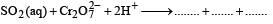 (1994 - 1 Mark)
(1994 - 1 Mark)
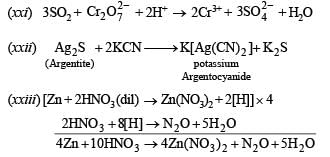
(xxii) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of argentite with KCN and name the products in solution. (1996 - 1 Mark)
(xxiii) Write balanced equations for the reaction of zinc with dilute nitric acid. (1997 - 1 Mark)
Solution.
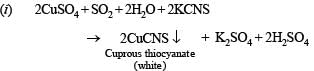
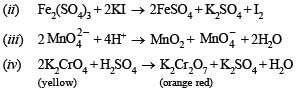
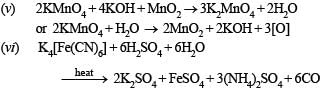
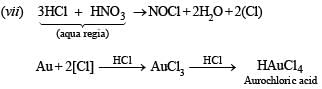
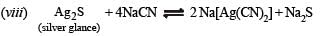
4Na2S + SO2 + 2H2O → 2 Na2SO4 + 4 NaOH + 2S
[NOTE : Na2S is converted into Na2SO4 to avoid reversibility of first reaction]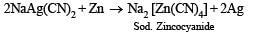
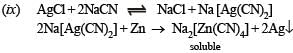
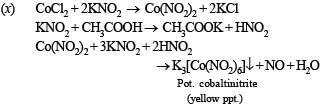
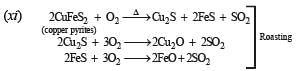
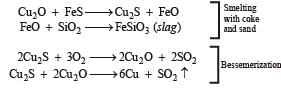
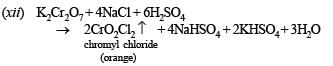
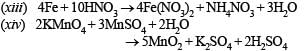
This is known as Volhard method for estimation of manganese.
(xv) The individual reactions are
3Cu + 8HNO3 (dil.) → 2NO + 3Cu(NO3)2 + 4H2O
Cu + 4HNO3 (dil.) → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
For the molar ratio of 2 : 1 of NO and NO2, we will have
7Cu + 20HNO3 → 7Cu(NO3)2 + 4NO + 2NO2 + 10H2O
(xvi) 2CuSO4 + 2Na2CO3 + H2O → CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 + 2Na2SO4 + CO2
Q.7. Give balanced equations for extraction of silver from its sulphide ore (1982 - 2 Marks)
Solution. Equations for extraction of silver from its sulphide ore.
Cyanide Process :
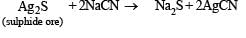
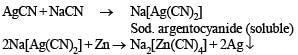
[NOTE : Zn is more electropositive than Ag.]
Q.8. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Silver bromide is used in photography. (1983 - 1 Mark)
(ii) Most transition metal compounds are coloured. (1986 - 1 Mark)
(iii) Zinc and not copper is used for the recovery of metallic silver from complex [Ag(CN)2]–. Explain. (1987 - 1 Mark)
(iv) The colour of mercurous chloride, Hg2Cl2, changes from white to black when treated with ammonia. (1988 - 1 Mark)
(v) The species [CuCl4]2– exists while [CuI4]2– does not. (1992 - 1 Mark)
(vi) CrO3 is an acid anhydride. (1999 - 2 Marks)
Solution. (i) It is because silver bromide, being sensitive to light, reduces into metallic silver grains when light fall on it.
(ii) The transition metals form coloured compounds and coloured complexes. They have vacant d-orbitals.
Electrons take up energy from the visible region and move to higher energy levels. The visible colour of the substance is the complementary colour of the absorbed light. [NOTE : The colour is due to d-d transitions]
(iii) Zinc is cheaper and stronger reducing agent than copper and zinc is volatile
(iv) Mercurous chloride changes from white to black when treated with ammonia due to the formation of finely divided mercury.
(v) Cu2+ is reduced to Cu+ by I–, hence cupric iodide is converted into cuprous iodide so [CuI4]2– does not exist, Cl– cannot effect this change and thus [CuCl4]2– exists.
(vi) CrO3 is acid anhydride of H2CrO4 (Chromic acid) [Anhydride are formed by loss of water from acid]
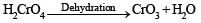
In H2Cr2O4, Cr is present in + 6 oxidation state.
Q.9. State the conditions under which the following preparation is carried out.
Potassium permanganate from manganese hydroxide.
Give the necessary equations which need not be balanced. (1983 - 1 Mark)
Solution. 2Mn(OH)2 + 5NaBiO3 + 18H+ → 2MnO4– + 5Bi3+ + 5Na+ + 11H2O
Q.10. What happens when :
(i) aqueous ammonia is added dropwise to a solution of copper sulphate till it is in excess. (1985 - 1 Mark)
(ii) CrCl3 solution is treated with sodium hydroxide and then with hydrogen peroxide. (1985 - 1 Mark)
Solution.
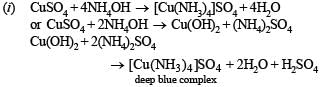
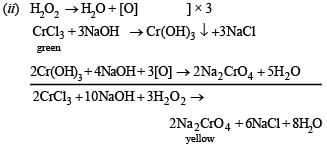
Q.11. Mention the products formed when zinc oxide is treated with excess of sodium hydroxide solution. (1986 - 1 Mark)
Ans. sodium zincate, water
Solution. 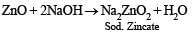
Q.12. What is the actual reducing agent of haematite in blast furnace? (1987 - 1 Mark)
Ans. CO
Solution. Carbon monoxide is the actual reducing agent of haematite in blast furnace.
Q.13. The acidic, aqueous solution of ferrous ion forms a brown complex in the presence of NO3- ,by the following two steps.
Complete and balance the equations : (1993 - 2 Marks)
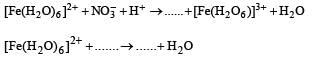
Solution. 3[Fe(H2O)6]2+ + NO3- + 4H+ → NO + 3[Fe(H2O)6]3+ + 2H2O
[Fe(H2O)6]2+ + NO → [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ + H2O
Q.14. Identify the complexes which are expected to be coloured.
Explain
(i) [Ti(NO3)4]
(ii) [Cu(NCCH3)4]+ BF4–
(iii) [Cr(NH3)6]3+3Cl–
(iv) K3 [VF6]
Ans. (iii), (iv)
Solution. For the explanation of colouration of complexes, first of all find out the number of unpaired electrons present in outer available d-orbitals
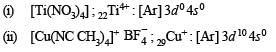
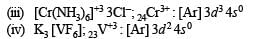
Due to the presence of unpaired electrons in d-orbitals, two complexes i.e., [Cr(NH3)6]3+ 3Cl– and K3 [VF6] are coloured.
Others having all paired electrons are colourless
Q.15. Write down the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(i) [Co(NH3)5 ONO]Cl2 (1995 - 1 Mark)
(ii) K3[Cr (CN)6] (1995 - 1 Mark)
(iii) [Cr(NH3)5CO3]Cl (1996 - 1 Mark)
Ans. (i) pentamminenitritocobalt (III) chloride,
(ii) potassium hexacyanochromate (III)
(iii) pentamminecarbonatochromium (III) chloride
Solution. (i) Pentamminenitritocobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium hexacyanochromate (III)
(iii) Pentamminecarbonatochromium (III) chloride.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|





















