JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Simple Harmonic Motion | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
Q1: Two particles, 1 and 2, each of mass m, are connected by a massless spring, and are on a horizontal frictionless plane, as shown in the figure. Initially, the two particles, with their center of mass at x₀, are oscillating with amplitude a and angular frequency ω. Thus, their positions at time t are given by x₁(t) = (x₀ + d) + a sin ωt and x₂(t) = (x₀ - d) - a sin ωt, respectively, where d > 2a.Particle 3 of mass m moves towards this system with speed u₀ = aω/2, and undergoes instantaneous elastic collision with particle 2, at time t₀. Finally, particles 1 and 2 acquire a center of mass speed v_cm and oscillate with amplitude b and the same angular frequency ω.
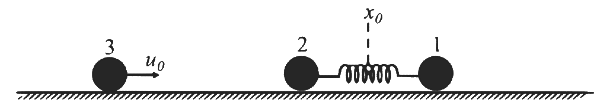
If the collision occurs at time t₀ = 0, the value of vcm / (aω) will be _____. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: 0.75
At T t
Before collision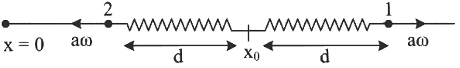 After collision
After collision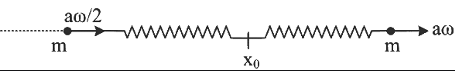 vCM = m ⋅ aω2 + m ⋅ aωm + m
vCM = m ⋅ aω2 + m ⋅ aωm + m
vCM = 3aω4
VCMaω = 34
VCMaω = 0.75
Q2: Two particles, 1 and 2, each of mass m, are connected by a massless spring, and are on a horizontal frictionless plane, as shown in the figure. Initially, the two particles, with their center of mass at x₀, are oscillating with amplitude a and angular frequency ω. Thus, their positions at time t are given by x₁(t) = (x₀ + d) + a sin ωt and x₂(t) = (x₀ - d) - a sin ωt, respectively, where d > 2a.
Particle 3 of mass m moves towards this system with speed u₀ = aω/2, and undergoes instantaneous elastic collision with particle 2, at time t₀. Finally, particles 1 and 2 acquire a center of mass speed v_cm and oscillate with amplitude b and the same angular frequency ω.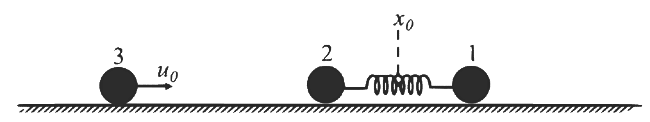
If the collision occurs at time t₀ = π/(2ω), then the value of 4b²/a² will be _____. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: 4.25
t0 = π2ω = T4
Particles are at extreme position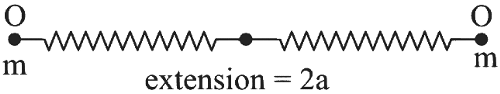 After collision
After collision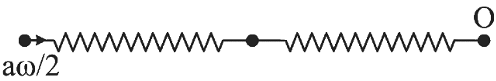 in C-frame
in C-frame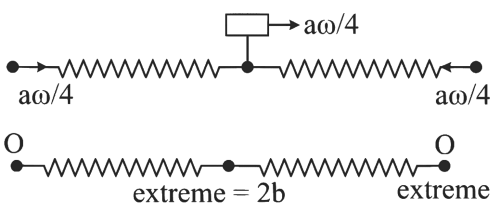 using WET,
using WET,
Wspring = ΔK
12 k (2b)2 - 12 k (2a)2 = 2 × 12 m × (a4) 2 (k = spring constant)
4kb2 - 4ka2 = 2 × m × a216 × 2km
4b2 = 174 a2
4b2a2 = 4.25
2023
Q1: In an experiment for determination of the focal length of a thin convex lens, the distance of the object from the lens is 10 ± 0.1 cm and the distance of its real image from the lens is 20 ± 0.2 cm. The error in the determination of focal length of the lens is n%. The value of n is ______. [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
Ans: 1
Given :
- Object distance cm u = 10.0 ± 0.1cm
- Image distance cm v = 20.0 ± 0.2cm
According to the lens formula for a thin lens :
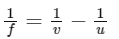
So, we can calculate the focal length :
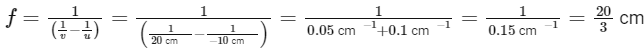
Next, we need to calculate the error in the determination of the focal length. For that, we find the differential of the lens formula :
Then, the derivative of the equation gives us the change in the focal length (df) in terms of the changes in the object distance (du) and the image distance (dv):
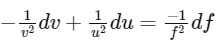
For maximum error, we get :
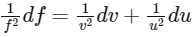
This equation tells us how errors in (u) and v propagate to an error in f. Now, when you compute the relative error in the focal length, you get :
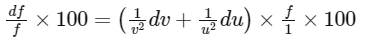
Plugging in your values of u = 10 cm, du =0.1 cm, v = 20 cm, dv = 0.2 cm, and f = 20/3 cm, you indeed get:
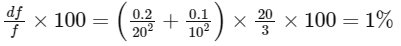
So, the error in the focal length of the lens is indeed 1% (i.e., n = 1).
2022
Q1: In a particular system of units, a physical quantity can be expressed in terms of the electric charge e, electron mass me, Planck's constant ℎ, and Coulomb's constant
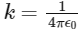 , where ε0 is the permittivity of vacuum. In terms of these physical constants, the dimension of the magnetic field is
, where ε0 is the permittivity of vacuum. In terms of these physical constants, the dimension of the magnetic field is 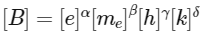 . The value of α + β + γ + δ is______. [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2]
. The value of α + β + γ + δ is______. [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2]Ans: 4
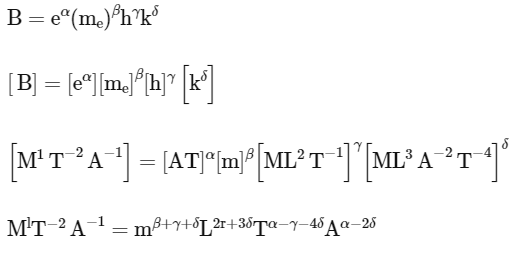
Compare : 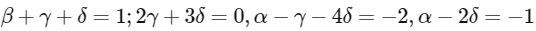
On Solving: 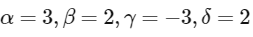
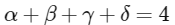
2019
Q1: An optical bench has 1.5 m long scale having four equal divisions in each cm. While measuring the focal length of a convex lens, the lens is kept at 75 cm mark of the scale and the object pin is kept at 45 cm mark. The image of the object pin on the other side of the lens overlaps with image pin that is kept at 135 cm mark. In this experiment, the percentage error in the measurement of the focal length of the lens is _______. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2]
Ans: 1.38
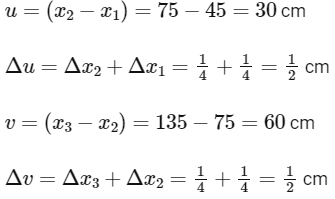
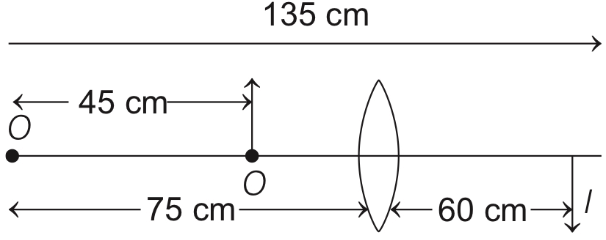
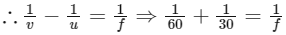
∴ f = 20 cm Also, 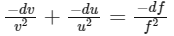
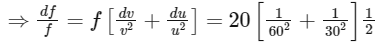
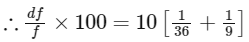
= 50/36
= 1.38 and 1.39 (both)
2018
Q1: A steel wire of diameter 0.5 mm and Young's modulus 2 × 1011Nm−2 carries a load of mass M. The length of the wire with the load is 1.0 m. A vernier scale with 10 divisions is attached to the end of this wire. Next to the steel wire is a reference wire to which a main scale, of least count 1.0 mm , is attached. The 10 divisions of the vernier scale correspond to 9 divisions of the main scale. Initially, the zero of vernier scale coincides with the zero of main scale. If the load on the steel wire is increased by 1.2 kg, the vernier scale division which coincides with a main scale division is _____________. Take g = 10ms−2, and π = 3.2 [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
Ans: 3
We know that 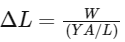
where W is weight or load = mg = 1.2 × 10 = 12 kg m s−2, Y is Young's modulus = 2 × 1011 N m−2, L is length of wire with load = 1.0 m, A is area of steel wire
= 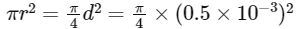
Therefore,
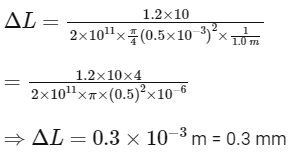
Now, least count of vernier scale = 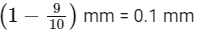
Therefore, Vernier reading = 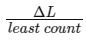
Vernier reading = 0.3 mm / 0.1 mm = 3
Therefore, 3rd vernier scale division coincides with the main scale division.
|
291 videos|648 docs|183 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Simple Harmonic Motion - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) and how is it characterized? |  |
| 2. What are the key formulas used in Simple Harmonic Motion? |  |
| 3. How do energy transformations occur in Simple Harmonic Motion? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the phase constant in SHM? |  |
| 5. How can one determine the frequency and period of a simple harmonic oscillator? |  |






















