JEE Main Previous Year Questions (2025): Indefinite Integral | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
[JEE Main MCQs]
Q1: Let a ∈ (0,π/2) be fixed. If the integral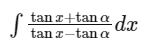 = A(x) cos 2α + B(x) sin 2α + C, where C is a constant of integration, then the functions A(x) and B(x) are respectively :
= A(x) cos 2α + B(x) sin 2α + C, where C is a constant of integration, then the functions A(x) and B(x) are respectively :
(a) x – α and loge|cos(x – α)|
(b) x + α and loge|sin(x – α)|
(c) x + α and loge|sin(x + α)|
(d) x – α and loge|sin(x – α)|
Ans: (d)
To solve the given integral, first we simplify the expression in the integral as follows :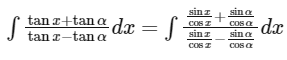
Simplifying further, this becomes :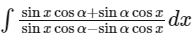
By using the formula for sin(a + b) = sin a cos b + cos a sin b and sin(a - b) = sin a cos b - cos a sin b, we get: 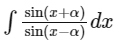
Now, let's use the substitution method. Let t = x - α, therefore x = y + α and dx = dt. Substituting these values into the integral, we get :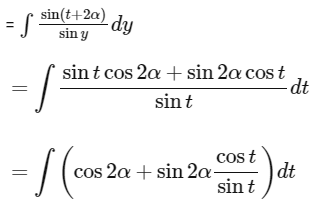
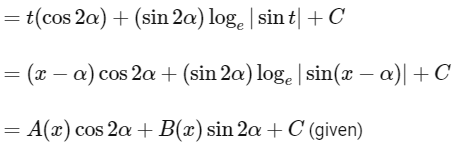
Now on comparing, we get
A(x) = x−α and B(x) = loge|sin(x−α)
Q2: The integral 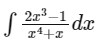 is equal to: (Here C is a constant of integration)
is equal to: (Here C is a constant of integration)
(a) 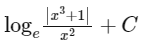
(b) 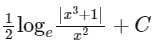
(c) 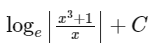
(d) 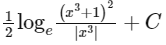
Ans: (c)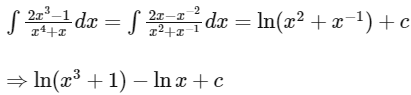
Q3: If ∫x5e-x2 dx = g(x)e-x2 + C where c is a constant of integration, then g(–1) is equal to :
(a) 1
(b) −1
(c) -(5/2)
(d) -(1/2)
Ans: (c)
Let x2 = t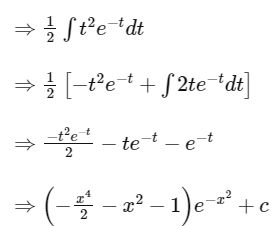
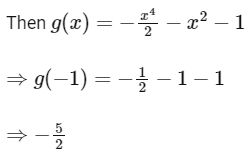
Q4: If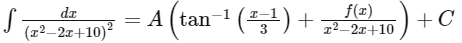 where C is a constant of integration then:
where C is a constant of integration then:
where C is a constant of integration then :
(a) A = 1/54 and f(x) = 9(x–1)2
(b) A = 1/54 and f(x) = 3(x–1)
(c) A = 1/81 and f(x) = 3(x–1)
(d) A = 1/27 and f(x) = 9(x–1)2
Ans: (b)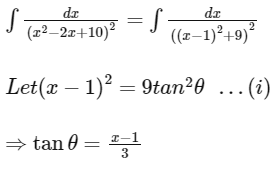
On Differentiating ...(i)
2(x – 1)dx = 18tanθ sec2θ dθ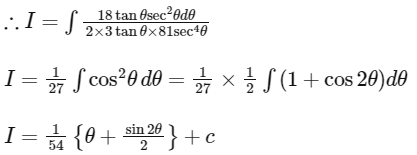
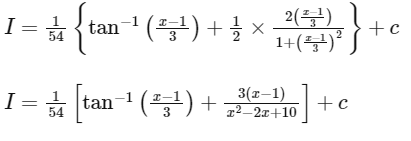
then A = 1/54
f(x) = 3(x – 1)
Q5: If ∫esec x (sec x tan x f(x) + sec x tan x + sex2x)dx = esecx f(x) + c. Then f(x) is
(a) x sec x + tan x + 1/2
(b) sec x + xtan x - 1/2
(c) sec x - tan x - 1/2
(d) sec x + tan x + 1/2
Ans: (d)
Given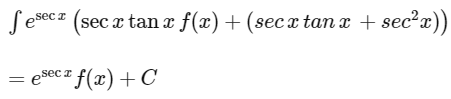
Differentiating both sides with respect to x,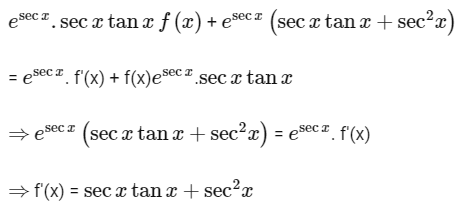
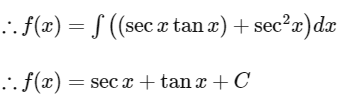
From question we can not find the value of C. So we have to choose any random value of C where (sec x + tan x) present.
Only in option D, (sec x + tan x) term present. So only possible option is D.
Q6: The integral ∫sec2/3 x cosec4/3 x dx is equal to (Hence C is a constant of integration)
(a) -3/4 tan-4/3 x + C
(b) 3tan–1/3x + C
(c) –3cot–1/3x+ C
(d) - 3tan–1/3x + C
Ans: (d)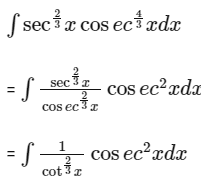
Let cot x = t3
⇒ - cosec2x dx = 3t2dt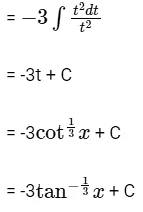
Q7: If 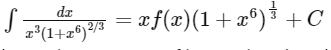 where C is a constant of integration, then the function ƒ(x) is equal to
where C is a constant of integration, then the function ƒ(x) is equal to
(a) 3/x2
(b) 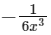
(c) 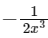
(d) 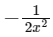
Ans: (c)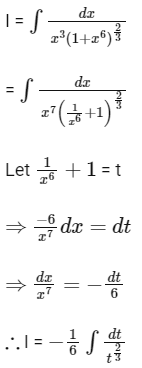
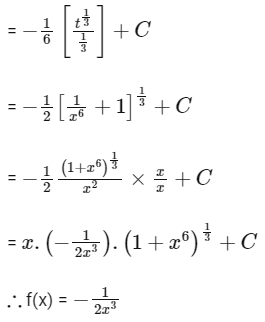
Q8: 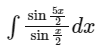 is equal to
is equal to
(where c is a constant of integration)
(a) 2x + sinx + 2sin2x + c
(b) x + 2sinx + sin2x + c
(c) x + 2sinx + 2sin2x + c
(d) 2x + sinx + sin2x + c
Ans: (b)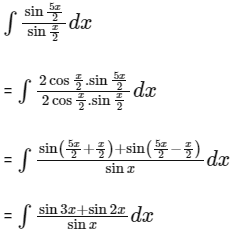
Use sin2x = 2sinxcosx and sin3x = 3sinx – 4sin3x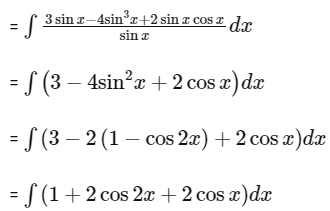
= x + sin2x + 2sinx + C
Q9: The integral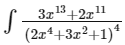 dx is equal to : (where C is a constant of integration)
dx is equal to : (where C is a constant of integration)
(a) 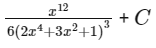
(b) 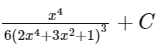
(c) 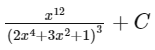
(d) 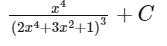
Ans: (a)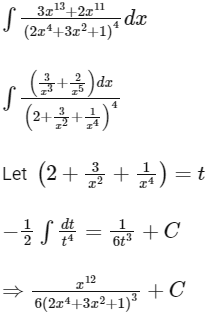
Q10: The integral ∫ cos(loge x) dx is equal to : (where C is a constant of integration)
(a) x/2 [sin(loge x) − cos(loge x)] + C
(b) x[cos(loge x) + sin(loge x)] + C
(c) x/2 [cos(loge x) + sin(loge x)] + C
(d) x[cos(loge x) − sin(loge x)] + C
Ans: (c)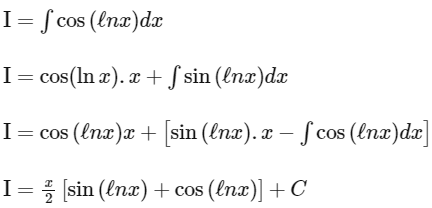
Q11: If 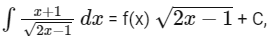 where C is a constant of integration, then f(x) is equal to :
where C is a constant of integration, then f(x) is equal to :
(a) 2/3 (x − 4)
(b) 1/3 (x + 4)
(c) 1/3 (x + 1)
(d) 2/3 (x + 2)
Ans: (b)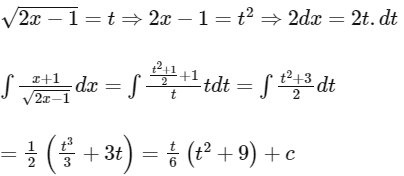
Q12: If 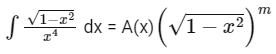 + C for a suitable chosen integer m and a function A(x), where C is a constant of integration, then (A(x))m equals :
+ C for a suitable chosen integer m and a function A(x), where C is a constant of integration, then (A(x))m equals :
(a) 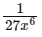
(b) 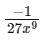
(c) 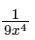
(d) 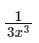
Ans: (b)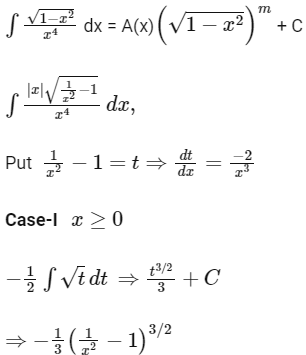
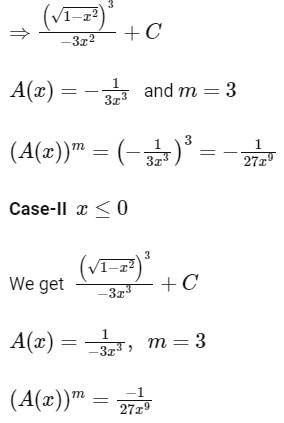
Q13: If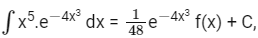 where C is a constant of inegration, then f(x) is equal to -
where C is a constant of inegration, then f(x) is equal to -
(a) − 2x3 − 1
(b) − 2x3 + 1
(c) 4x3 + 1
(d) − 4x3 − 1
Ans: (d)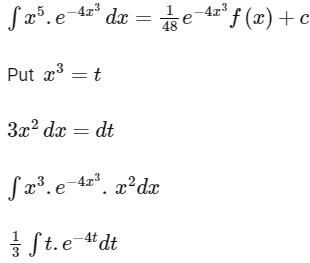
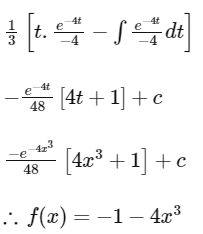
Q14: Let n ≥ 2 be a natural number and 0 < θ < π/2. Then 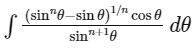 is equal to (where C is a constant of integration)
is equal to (where C is a constant of integration)
(a) 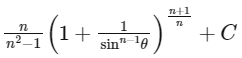
(b) 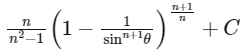
(c) 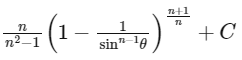
(d) 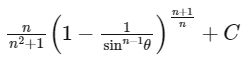
Ans: (c)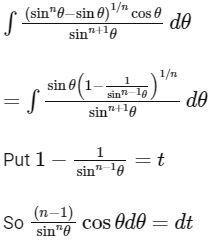
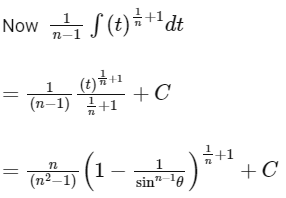
Q15: 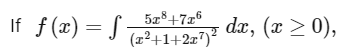
f(0) = 0 , then the value of f(1) is :
(a) -(1/2)
(b) -(1/4)
(c) 1/2
(d) 1/4
Ans: (d)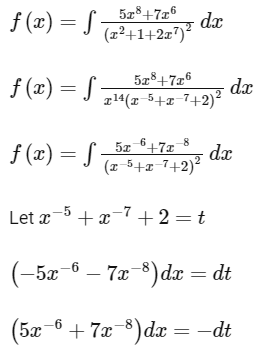
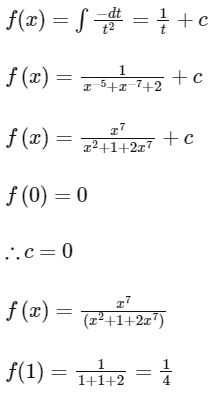
Q16: For x2 ≠ nπ + 1, n ∈ N (the set of natural numbers), the integral
is equal to (where c is a constant of integration)
(a)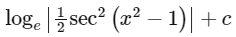
(b) 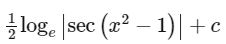
(c) 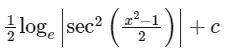
(d) 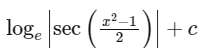
Ans: (d)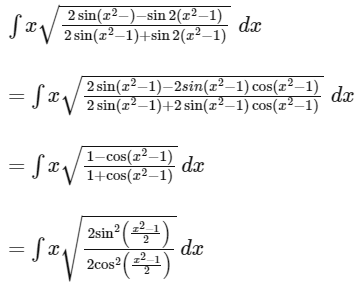
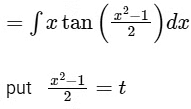
⇒ x2 - 1 = 2t
⇒ 2xdx = 2dt
⇒ xdx = dt
∴ ∫ tan t dt
= In |sec t| + C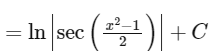
|
481 docs|964 tests
|




















