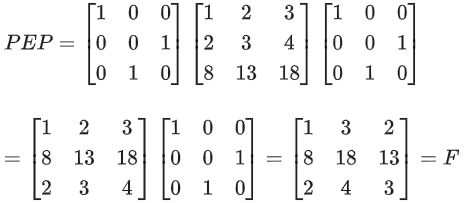
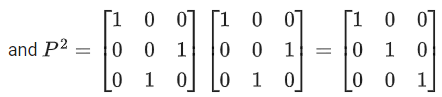
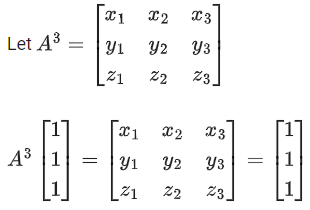
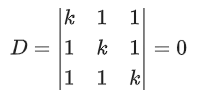
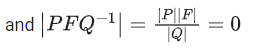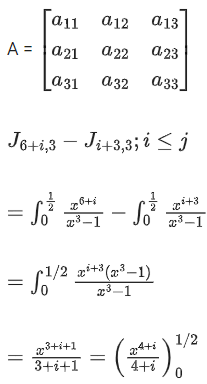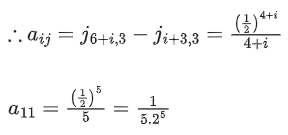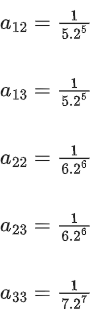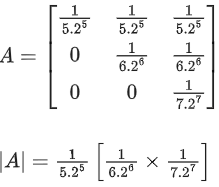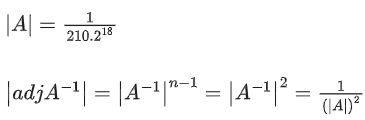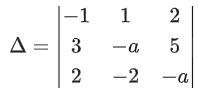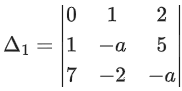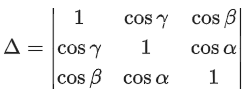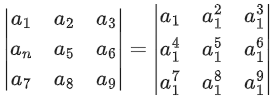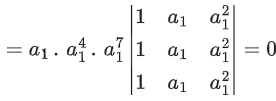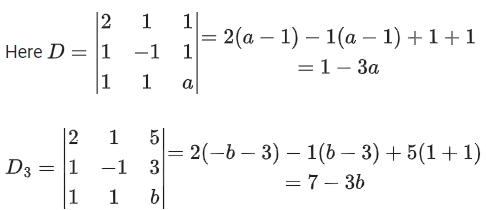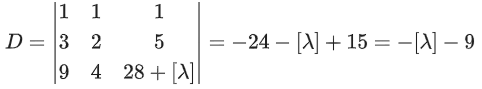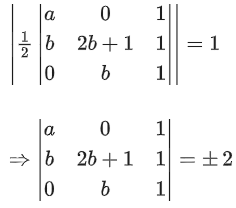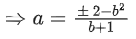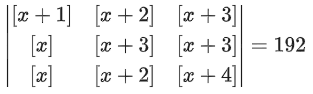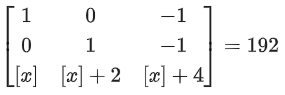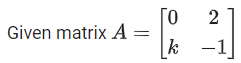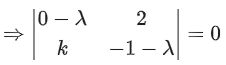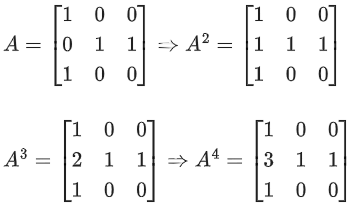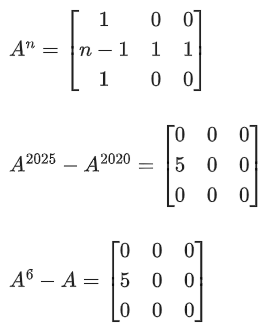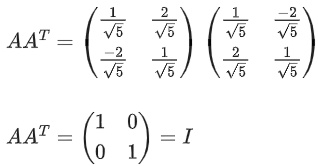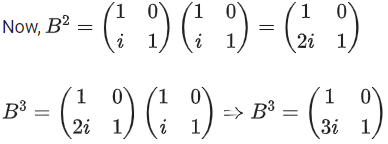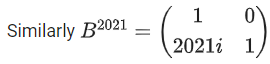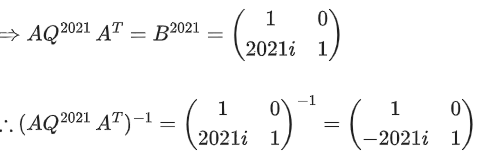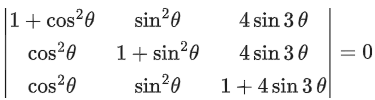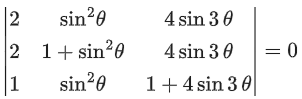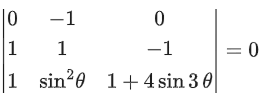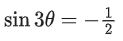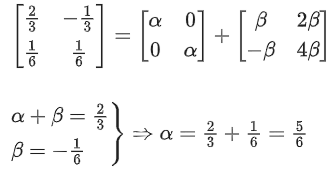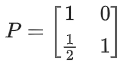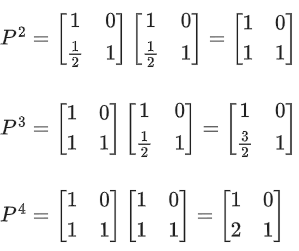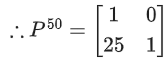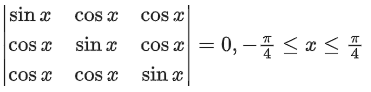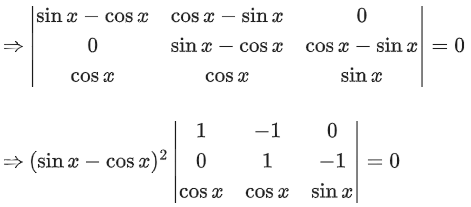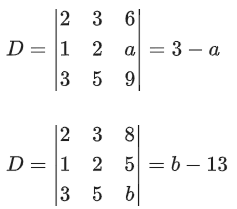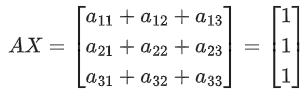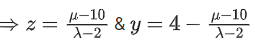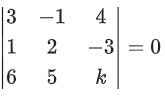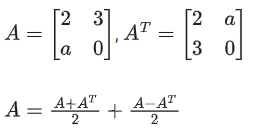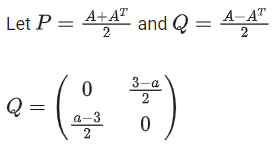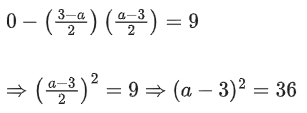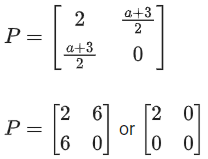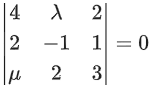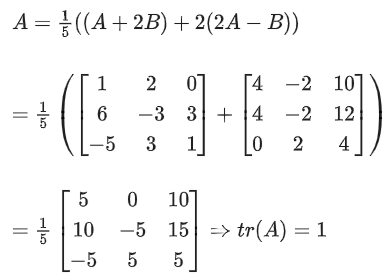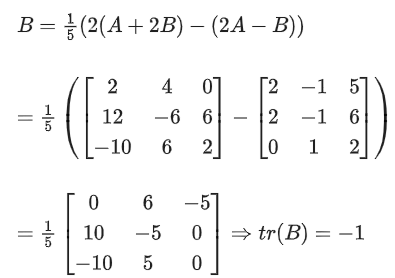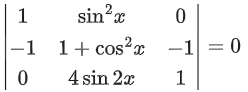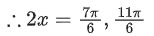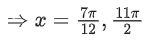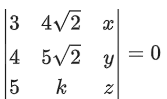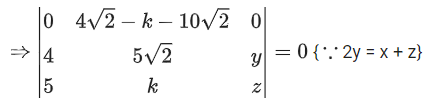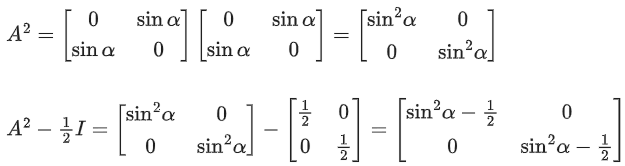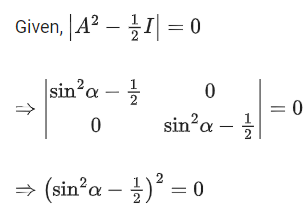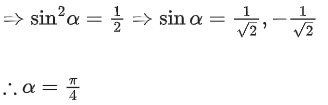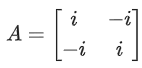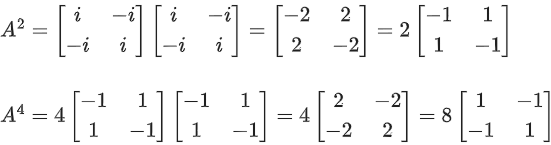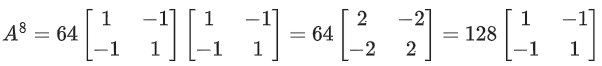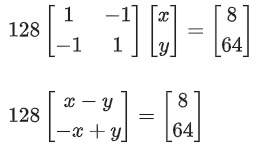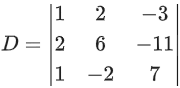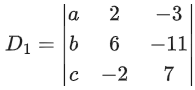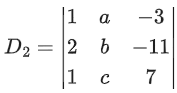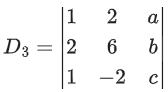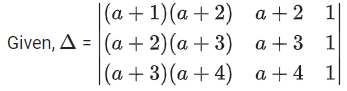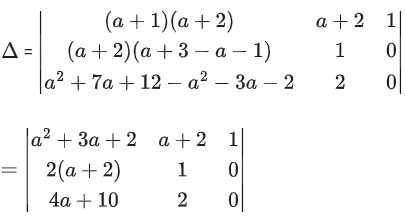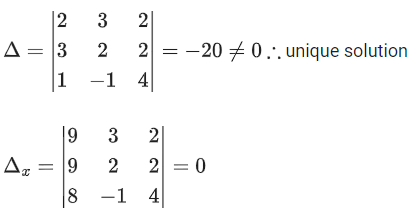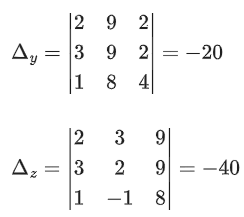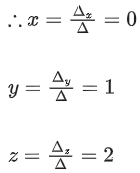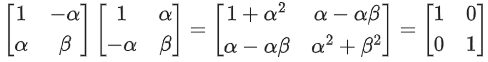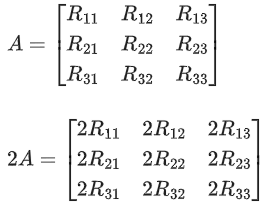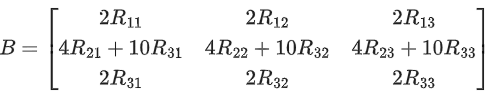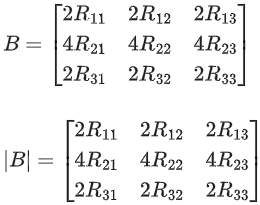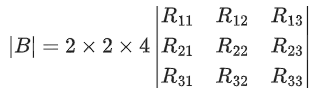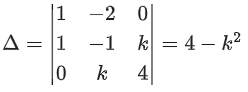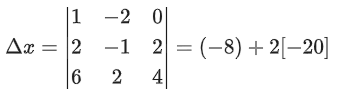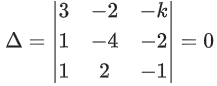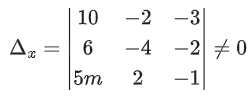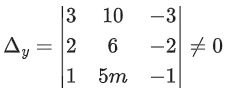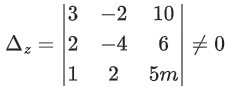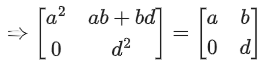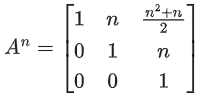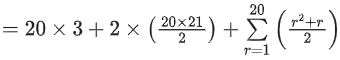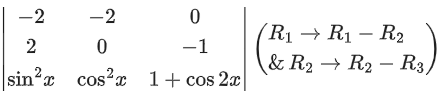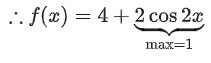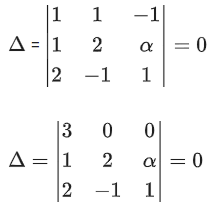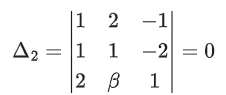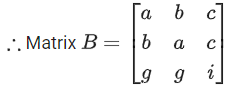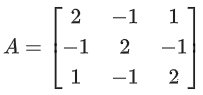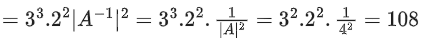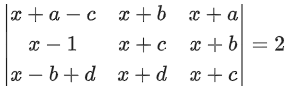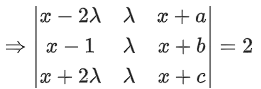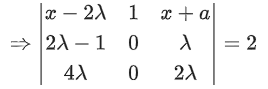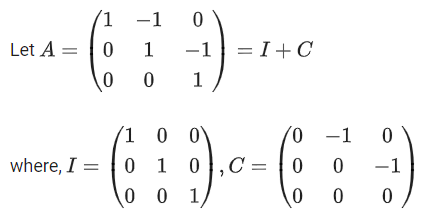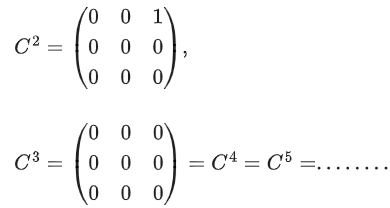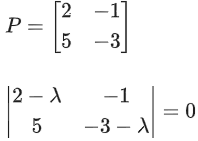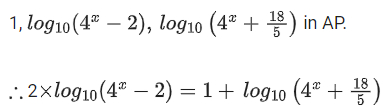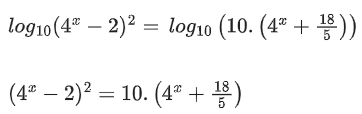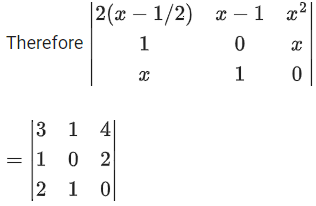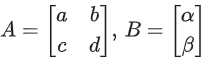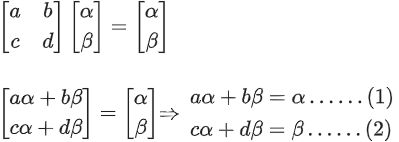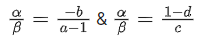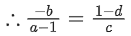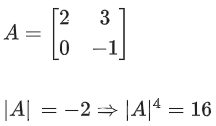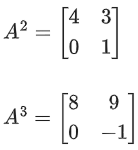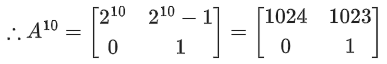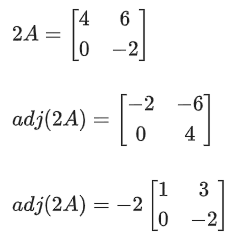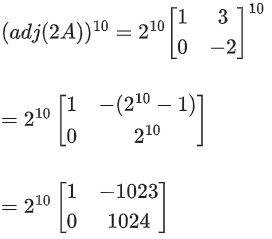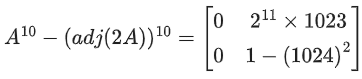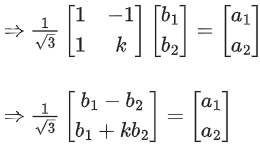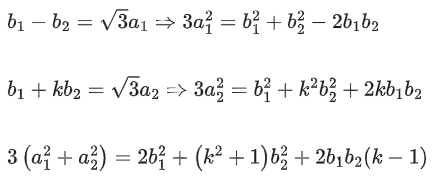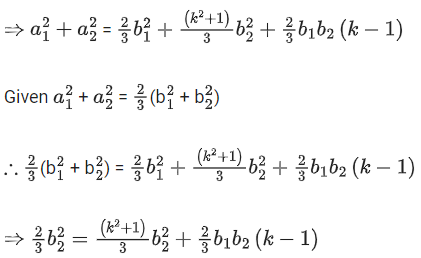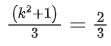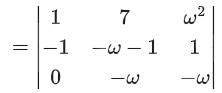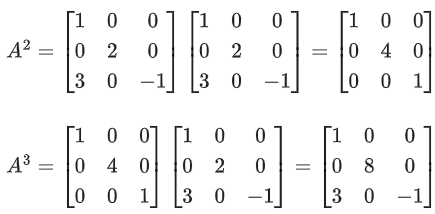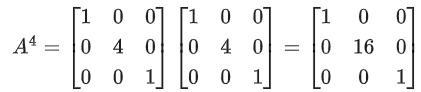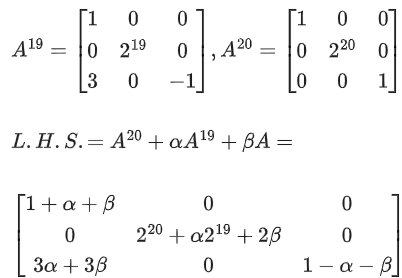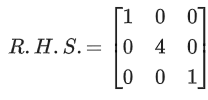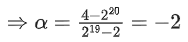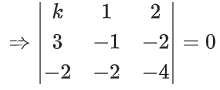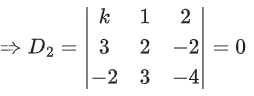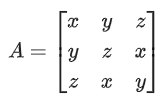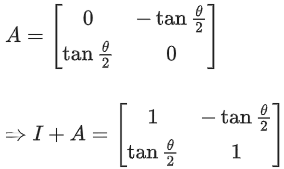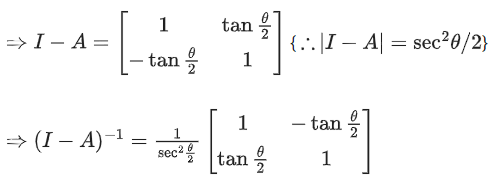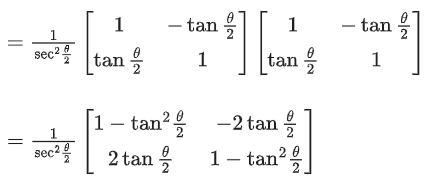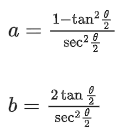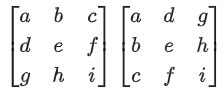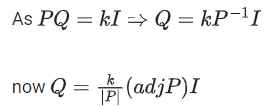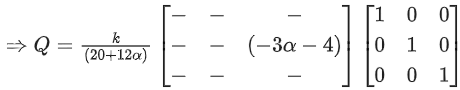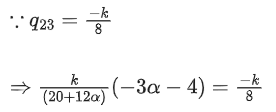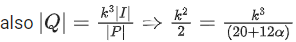Q.58. For any 3 × 3 matrix M, let |M| denote the determinant of M. Let I be the 3 × 3 identity matrix. Let E and F be two 3 × 3 matrices such that (I − EF) is invertible. If G = (I − EF)−1, then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE? (JEE Advanced 2021)
(a) | FE | = | I − FE| | FGE |
(b) (I − FE)(I + FGE) = I
(c) EFG = GEF
(d) (I − FE)(I − FGE) = I
Ans. a, b, c
∵ I − EF = G−1 ⇒ G − GEF = I ..... (i)
and G − EFG = I ..... (ii)
Clearly, GEF = EFG → option (c) is correct.
Also, (I − FE) (I + FGE)
= I − FE + FGE − FEFGE
= I − FE + FGE − F(G − I) E
= I − FE + FGE − FGE + FE
= I → option (b) is correct but option (d) is incorrect.
∵ (I − FE) (I − FGE) = I − FE − FGE + F(G − I) E
= I − 2FE
Now, (I − FE) (− FGE) = − FE
⇒ | I − FE | | FGE | = | FE |
→ option (a) is correct.
Q.59. For any 3 × 3 matrix M, let | M | denote the determinant of M. Let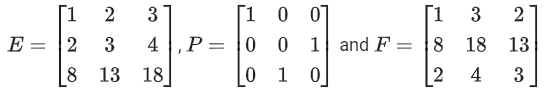
If Q is a nonsingular matrix of order 3 × 3, then which of the following statements is(are) TRUE? (JEE Advanced 2021)
(a) F = PEP and P2 =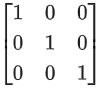
(b) | EQ + PFQ−1 | = | EQ | + | PFQ−1 |
(c) | (EF)3 | > | EF |2
(d) Sum of the diagonal entries of P−1EP + F is equal to the sum of diagonal entries of E + P−1FP
Ans. a, b, d
For option (a)
Hence, option (a) is correct.
For option (b)
|EQ + PFQ−1| = |EQ| + |PFQ−1| .... (i)
∵ | E | = 0 and | F | = 0 and | Q | ≠ 0
∴ |EQ| = |E||Q| = 0
Let R = EQ + PFQ−1 .... (ii)
⇒ RQ = EQ2 + PF = EQ2 + P2EP = EQ2 + EP [∵ P2 = I]
= E(Q2 + P)
⇒ |RQ| = |E(Q2 + P)|
⇒ |R||Q| = |E||Q2 + P| = 0 [∵ | E | = O]
⇒ |R| = 0 (as |Q| ≠ 0) ..... (iii)
From Eqs. (ii) and (iii), we get Eq. (i) is true.
Hence, option (b) is correct.
For option (c)
|(EF)3| > |EF|2
i.e. 0 > 0 which is false.
For option (d)
∵ P2 = I ⇒ P−1 = P
∴ P−1FP = PFP = PPEPP = E
So, E + P−1FP = E + E = 2E
⇒ Tr(E + P−1FP) = Tr(2E) = 2Tr(E) ..... (iv)
and P−1EP + F
⇒ PEP + F = 2PEP [∵ F = PEP]
∴ Tr(2PEP)=2Tr(PEP)=2Tr(F)=2Tr(E) ..... (v)
From Eqs. (iv) and (v) option (d) is also correct.
Q.60. Let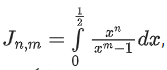 ∀ n > m and n, m ∈ N. Consider a matrix A = [aij]3 × 3 where
∀ n > m and n, m ∈ N. Consider a matrix A = [aij]3 × 3 where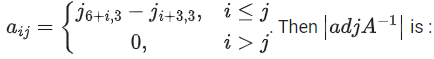 (JEE Main 2021)
(JEE Main 2021)
(a) (15)2 × 242
(b) (15)2 × 234
(c) (105)2 × 238
(d) (105)2 × 236
Ans. c
= (210.218)2
= (105)2 × 238
Q.61. Consider the system of linear equations
−x + y + 2z = 0
3x − ay + 5z = 1
2x − 2y − az = 7
Let S1 be the set of all a ∈ R for which the system is inconsistent and S2 be the set of all a∈R for which the system has infinitely many solutions. If n(S1) and n(S2) denote the number of elements in S1 and S2 respectively, then (JEE Main 2021)
(a) n(S1) = 2, n(S2) = 2
(b) n(S1) = 1, n(S2) = 0
(c) n(S1) = 2, n(S2) = 0
(d) n(S1) = 0, n(S2) = 2
Ans. c
= −1(a2 + 10) − 1(−3a − 10) + 2(−6 + 2a)
= −a2 − 10 + 3a + 10 − 12 + 4a
Δ = −a2 + 7a − 12
Δ = −[a2 − 7a + 12]
Δ = −[(a − 3)(a − 4)]
= a + 35 − 4 + 14a
= 15a + 31
Now, Δ1 = 15a + 31
For inconsistent Δ = 0 ∴ a = 3, a = 4 and for a = 3 and 4, Δ1 ≠ 0
n(S1) = 2
For infinite solution: Δ = 0 and Δ1 = Δ2 = Δ3 = 0
Not possible
∴ n(S2) = 0
Q.62. If α + β + γ = 2π, then the system of equations
x + (cos γ)y + (cos β)z = 0
(cos γ)x + y + (cos α)z = 0
(cos β)x + (cos α)y + z = 0 has: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) no solution
(b) infinitely many solution
(c) exactly two solutions
(d) a unique solution
Ans. b
Given α + β + γ = 2π
= 1 − cos2α − cosγ(cosγ − cosα cosβ) + cosβ(cosα cosγ − cosβ)
= 1 − cos2α − cos2β − cos2γ + 2cosα cosβ cosγ
= sin2α − cos2β − cosγ(cosγ − 2cosα cosβ)
= −cos(α + β)cos(α − β) − cosγ(cos(2π − (α − β)) − 2cosα cosβ)
= −cos(2π − γ)cos(α − β) − cosγ(cos(α + β) − 2cosα cosβ)
= −cosγ cos(α − β) + cosγ(cosα cosβ + sinα sinβ)
= −cosγ cos(α − β) + cosγ cos(α − β)
= 0
So, the system of equation has infinitely many solutions.
Q.63. If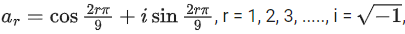 then the determinant
then the determinant  is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) a2a6 − a4a8
(b) a9
(c) a1a9 − a3a7
(d) a5
Ans. c
r = 1, 2, 3, ......, a1, a2, a3, ..... are in G.P.
Now, a1a9 − a3a7 = a110 − a110 = 0
Q.64. If the following system of linear equations
2x + y + z = 5
x − y + z = 3
x + y + az = b
has no solution, then: (JEE Main 2021)
(a)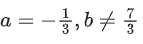
(b)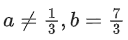
(c)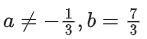
(d)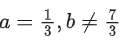
Ans. d
forsystem has no solutions.
Q.65. Let [λ] be the greatest integer less than or equal to λ. The set of all values of λ for which the system of linear equations
x + y + z = 4,
3x + 2y + 5z = 3,
9x + 4y + (28 + [λ])z = [λ] has a solution is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) R
(b) (−∞, −9) ∪ (−9, ∞)
(c) [−9, −8)
(d) (−∞, −9) ∪ [−8, ∞)
Ans. a
if [λ] + 9 ≠ 0 then unique solution
if [λ] + 9 = 0 then D1 = D2 = D3 = 0
so infinite solutions
Hence, λ can be any red number.
Q.66. Let A(a, 0), B(b, 2b + 1) and C(0, b), b ≠ 0, |b| ≠ 1, be points such that the area of triangle ABC is 1 sq. unit, then the sum of all possible values of a is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a)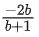
(b)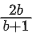
(c)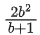
(d)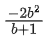
Ans. d
⇒ a(2b + 1 − b) − 0 + 1(b2 − 0) = ±2
Sum of possible values of 'a' is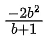
Q.67. Let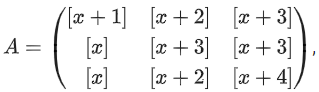 where [t] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to t. If det(A) = 192, then the set of values of x is the interval: (JEE Main 2021)
where [t] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to t. If det(A) = 192, then the set of values of x is the interval: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) [68, 69)
(b) [62, 63)
(c) [65, 66)
(d) [60, 61)
Ans. b
R1 → R1 − R3 & R2 → R2 − R3
2[x] + 6 + [x] = 192 ⇒ [x] = 62
Q.68. If the matrix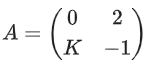 satisfies A(A3 + 3I) = 2I, then the value of K is: (JEE Main 2021)
satisfies A(A3 + 3I) = 2I, then the value of K is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 1/2
(b)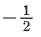
(c) -1
(d) 1
Ans. a
A4 + 3IA = 2I
⇒ A4 = 2I − 3A
Also characteristic equation of A is |A−λI|=0
⇒ λ + λ2 − 2k = 0
⇒ A + A2 = 2K . I
⇒ A2 = 2KI − A
⇒ A4 = 4K2I + A2 − 4AK
Put A2 = 2KI − A
and A4 = 2I − 3A
2I − 3A = 4K2I + 2KI − A − 4AK
⇒ I(2 − 2K − 4K2) = A(2 − 4K)
⇒ −2I(2K2 + K − 1) = 2A(1 − 2K)
⇒ −2I(2K − 1)(K + 1) = 2A(1 − 2K)
⇒ (2K − 1)(2A) − 2I(2K − 1)(K + 1) = 0
⇒ (2K − 1)[2A − 2I(K + 1)] = 0
⇒ K = 1/2
Q.69. Let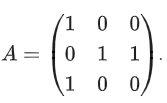 Then A2025 − A2020 is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
Then A2025 − A2020 is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) A6 − A
(b) A5
(c) A5 − A
(d) A6
Ans. a
Q.70. If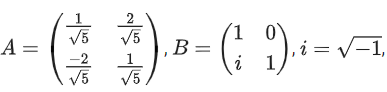 and Q = ATBA, then the inverse of the matrix A Q2021 AT is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
and Q = ATBA, then the inverse of the matrix A Q2021 AT is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a)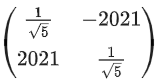
(b)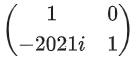
(c)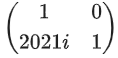
(d)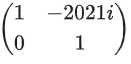
Ans. b
Q2 = ATBAATBA = ATBIBA
⇒ Q2 = ATB2A
Q3 = ATB2AATBA ⇒ Q3 = ATB3A
Similarly: Q2021 = ATB2021A
∴ AQ2021 = AT = AATB2021AAT = IB2021I
Q.71. Let θ ∈ (0, π/2). If the system of linear equations
(1 + cos2θ)x + sin2θy + 4sin3θz = 0
cos2θx + (1 + sin2θ)y + 4sin3θz = 0
cos2θx + sin2θy + (1 + 4sin3θ)z = 0
has a non-trivial solution, then the value of θ is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 4π/9
(b) 7π/18
(c) π/18
(d) 5π/18
Ans. b
C1 → C1 + C2
R1 → R1 − R2, R2 → R2 − R3
or 4sin3θ = −2
θ = 7π/18
Q.72. Let A and B be two 3 × 3 real matrices such that (A2 − B2) is invertible matrix. If A5 = B5 and A3B2 = A2B3, then the value of the determinant of the matrix A3 + B3 is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 0
Ans. d
C = A2 − B2; | C | ≠ 0
A2 = B5 and A3B2 = A2B2
Now, A5 − A3B2 = B5 − A2B3
⇒ A3 (A2 − B2) + B3 (A2 − B2) = 0
⇒ (A3 + B3(A2 − B2) = 0
⇒ A3 + B3 = 0 (∵|A2 − B2 ≠ 0|)
Q.73. Let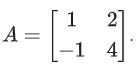 If A−1 = αI + βA, α, β ∈ R, I is a 2 × 2 identity matrix then 4(α − β) is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
If A−1 = αI + βA, α, β ∈ R, I is a 2 × 2 identity matrix then 4(α − β) is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 5
(b) 8/3
(c) 2
(d) 4
Ans. d
∴ 4(α − β) = 4(1) = 4
Q.74. If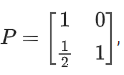 then P50 is: (JEE Main 2021)
then P50 is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a)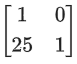
(b)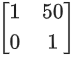
(c)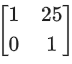
(d)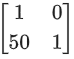
Ans. a
Q.75. The number of distinct real roots of 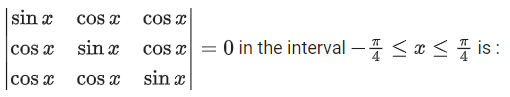 (JEE Main 2021)
(JEE Main 2021)
(a) 4
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans. b
Apply: R1 → R1 − R2 & R2 → R2 − R3
⇒ (sinx − cosx)2(sinx + 2cosx) = 0
∴ x = π/4
Q.76. The values of a and b, for which the system of equations
2x + 3y + 6z = 8
x + 2y + az = 5
3x + 5y + 9z = b
has no solution, are: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) a = 3, b ≠ 3
(b) a ≠ 3, b ≠ 13
(c) a ≠ 3, b = 3
(d) a = 3, b = 13
Ans. a
If a = 3, b ≠ 13, no solution.
Q.77. Let A = [aij] be a real matrix of order 3 × 3, such that ai1 + ai2 + ai3 = 1, for i = 1, 2, 3. Then, the sum of all the entries of the matrix A3 is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 9
Ans. c
⇒ AX = X
Replace X by AX
A2X = AX = X
Replace X by AX
A3X = AX = X
Sum of all the element = 3
Q.78. The values of λ and μ such that the system of equations x + y + z = 6, 3x + 5y + 5z = 26, x + 2y + λz = μ has no solution, are: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) λ = 3, μ = 5
(b) λ = 3, μ ≠ 10
(c) λ ≠ 2, μ = 10
(d) λ = 2, μ ≠ 10
Ans. d
x + y + z = 6 ..... (i)
3x + 5y + 5z = 26 .... (ii)
x + 2y + λz = μ ..... (iii)
5 × (i) − (ii) ⇒ 2x = 4 ⇒ x = 2
∴ from (i) and (iii)
y + z = 4 ..... (iv)
2y + λz = μ − 2 .....(v)
(v) − 2 × (iv)
⇒ (λ − 2)z = μ − 10
∴ For no solution λ = 2 and μ ≠ 10.
Q.79. The value of k ∈ R, for which the following system of linear equations
3x − y + 4z = 3,
x + 2y − 3z = −2
6x + 5y + kz = −3,
has infinitely many solutions, is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 3
(b) −5
(c) 5
(d) −3
Ans. b
⇒ 3(2k + 15) + K + 18 − 28 = 0
⇒ 7k + 35 = 0
⇒ k = − 5
Q.80. Let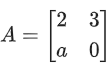 , a ∈ R be written as P + Q where P is a symmetric matrix and Q is skew symmetric matrix. If det(Q) = 9, then the modulus of the sum of all possible values of determinant of P is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
, a ∈ R be written as P + Q where P is a symmetric matrix and Q is skew symmetric matrix. If det(Q) = 9, then the modulus of the sum of all possible values of determinant of P is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 36
(b) 24
(c) 45
(d) 18
Ans. a
Det (Q) = 9
a − 3 = ±6 ⇒ a = 9, −3
| P | = - 36 or 0
∴ | −36 + 0 | = 36
Q.81. Define a relation R over a class of n × n real matrices A and B as
"ARB iff there exists a non-singular matrix P such that PAP−1 = B".
Then which of the following is true? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) R is reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
(b) R is symmetric, transitive but not reflexive
(c) R is reflexive, symmetric but not transitive
(d) R is an equivalence relation
Ans. d
For reflexive relation,
∀(A, A) ∈ R for matrix P.
⇒ A = PAP−1 is true for P = 1
So, R is reflexive relation.
For symmetric relation,
Let (A, B) ∈ R for matrix P.
⇒ A = PBP−1
After pre-multiply by P−1 and post-multiply by P, we get
P−1AP = B
So, (B, A) ∈ R for matrix P−1.
So, R is a symmetric relation.
For transitive relation,
Let ARB and BRC
So, A = PBP−1 and B = PCP−1
Now, A = P(PCP−1)P−1
⇒ A = (P)2C(P−1)2 ⇒ A = (P)2 ⋅ C ⋅ (P2)−1
∴(A, C) ∈ R for matrix P2.
∴ R is transitive relation.
Hence, R is an equivalence relation.
Q.82. Let the system of linear equations
4x + λy + 2z = 0
2x − y + z = 0
μx + 2y + 3z = 0, λ, μ ∈ R.
has a non-trivial solution. Then which of the following is true? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) μ = 6, λ ∈ R
(b) λ = 3, μ ∈ R
(c) μ = −6, λ ∈ R
(d) λ = 2, μ ∈ R
Ans. a
Given, system of linear equations
4x + λy + 2z = 0
2x − y + z = 0
μx + 2y + 3z = 0
For non-trivial solution, Δ = 0
⇒ 4(−3 − 2) − λ(6 − μ) + 2(4 + μ) = 0
⇒ −λ(6 − μ) − 2(6 − μ) = 0
⇒ (6 − μ)(λ + 2) = 0
⇒ λ = −2 and μ ∈ R or μ = 6 and λ ∈ R.
Q.83. Let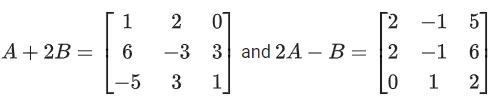 If Tr(A) denotes the sum of all diagonal elements of the matrix A, then Tr(A) − Tr(B) has value equal to (JEE Main 2021)
If Tr(A) denotes the sum of all diagonal elements of the matrix A, then Tr(A) − Tr(B) has value equal to (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 0
(d) 3
Ans. b
Similarly,
Tr(A) − Tr(B) = 1 − (−1) = 2
Q.84. The solutions of the equation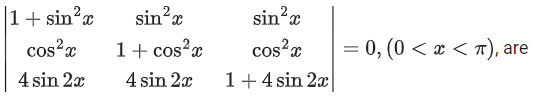 (JEE Main 2021)
(JEE Main 2021)
(a)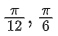
(b)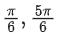
(c)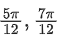
(d)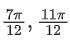
Ans. d
By using C1 → C1 − C2 and C3 → C3 − C2 we get
Expanding by R1 we get
1(1 + cos2x + 4sin2x) − sin2x(−1) = 0
⇒ 2 + 4sin2x = 0
⇒ sin2x = −1/2
⇒ 2x = nπ + (−1)n(−π/6), n ∈ Z
Q.85. If x, y, z are in arithmetic progression with common difference d, x ≠ 3d, and the determinant of the matrix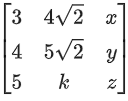 is zero, then the value of k2 is: (JEE Main 2021)
is zero, then the value of k2 is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 72
(b) 12
(c) 36
(d) 6
Ans. a
R1 → R1 + R3 − 2R2
⇒ (k − 6√2)(4z − 5y) = 0
⇒ k = 6√2 or 4z = 5y (Not possible ∵ x, y, z in A.P.)
So, k2 = 72
∴ Option (A)
Q.86. If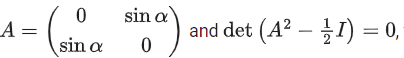 then a possible value of α is: (JEE Main 2021)
then a possible value of α is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) π/4
(b) π/6
(c) π/2
(d) π/3
Ans. a
Q.87. The system of equations kx + y + z = 1, x + ky + z = k and x + y + zk = k2 has no solution if k is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 0
(b) −1
(c) −2
(d) 1
Ans. c
⇒ k(k2 − 1) − (k − 1) + (1 − k) = 0
⇒ (k − 1)(k2 + k − 1 − 1) = 0
⇒ (k − 1)(k2 + k − 2) = 0
⇒ (k − 1)(k − 1)(k + 2) = 0
⇒ k = 1, k = −2
for k = 1 equation identical so k = −2 for no solution.
Q.88. Let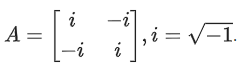 Then, the system of linear equations
Then, the system of linear equations
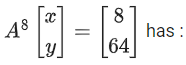 (JEE Main 2021)
(JEE Main 2021)
(a) Exactly two solutions
(b) Infinitely many solutions
(c) A unique solution
(d) No solution
Ans. d
⇒ 128(x − y) = 8
⇒ x − y = 1/16 .... (1)
and 128(−x + y) = 64 ⇒ x − y = −1/2 .... (2)
⇒ No solution (from eq. (1) & (2))
Q.89. Consider the following system of equations:
x + 2y − 3z = a
2x + 6y − 11z = b
x − 2y + 7z = c,
where a, b and c are real constants. Then the system of equations: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) has no solution for all a, b and c
(b) has a unique solution when 5a = 2b + c
(c) has infinite number of solutions when 5a = 2b + c
(d) has a unique solution for all a, b and c
Ans. c
= 20 − 2(25) −3(−10)
= 20 − 50 + 30 = 0
= 20a − 2(7b + 11c) −3(−2b − 6c)
= 20a − 14b − 22c + 6b +18c
= 20a − 8b − 4c
= 4(5a − 2b − c)
= 7b + 11c − a(25) −3(2c − b)
= 7b + 11c − 25a − 6c + 3b
= −25a + 10b + 5c
= −5(5a − 2b − c)
= 6c + 2b − 2(2c − b) − 10a
= −10a + 4b + 2c
= −2(5a − 2b − c)
for infinite solution
D = D1 = D2 = D3 = 0
⇒ 5a = 2b + c
Q.90. The value of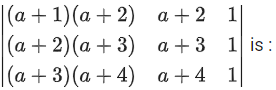 (JEE Main 2021)
(JEE Main 2021)
(a) −2
(b) 0
(d) (a + 2)(a + 3)(a + 4)
(d) (a + 1)(a + 2)(a + 3)
Ans. a
R2 → R2 − R1 and R3 → R3 − R1
= 4(a + 2) − 4a − 10
= 4a + 8 − 4a − 10 = −2
Q.91. Let A be a symmetric matrix of order 2 with integer entries. If the sum of the diagonal elements of A2 is 1, then the possible number of such matrices is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 12
Ans. b
= a2 + 2b2 + c2 = 1
a = 1, b = 0, c = 0
a = 0, b = 0, c = 1
a = −1, b = 0, c = 0
c = −1, b = 0, a = 0
Q.92. The following system of linear equations
2x + 3y + 2z = 9
3x + 2y + 2z = 9
x − y + 4z = 8 (JEE Main 2021)
(a) does not have any solution
(b) has a solution (α, β, γ) satisfying α + β2 + γ3 = 12
(c) has a unique solution
(d) has infinitely many solutions
Ans. c
Unique solution: (0, 1, 2)
Q.93. If for the matrix,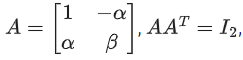 then the value of α4 + β4 is: (JEE Main 2021)
then the value of α4 + β4 is: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 4
Ans. c
1 + α2 = 1
α2 = 0
α2 + β2 = 1
β2 = 1
α4 = 0
β4 = 1
α4 + β4 = 1
Q.94. Let A be a 3 × 3 matrix with det(A) = 4. Let Ri denote the ith row of A. If a matrix B is obtained by performing the operation R2 → 2R2 + 5R3 on 2A, then det(B) is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 64
(b) 16
(c) 128
(d) 80
Ans. a
R2 → 2R2 + 5R3
R2 → R2 − 5R3
= 16 × 4
= 64
Q.95. For the system of linear equations:
x − 2y = 1, x − y + kz = −2, ky + 4z = 6, k ∈ R,
consider the following statements:
(A) The system has unique solution if k ≠ 2, k ≠ −2.
(B) The system has unique solution if k = −2
(C) The system has unique solution if k = 2
(D) The system has no solution if k = 2
(E) The system has infinite number of solutions if k ≠ −2.
Which of the following statements are correct? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (B) and (E) only
(b) (C) and (D) only
(c) (A) and (E) only
(d) (A) and (D) only
Ans. d
x − 2y + 0.z = 1
x − y + kz = −2
0.x + ky + 4z = 6
For unique solution 4 − k2 ≠ 0
⇒ k ≠ ± 2
For k = 2:
x − 2y + 0.z = 1
x − y + 2z = −2
0.x + 2y + 4z = 6
Δx = −48 ≠ 0
For k = 2, Δx ≠ 0
∴ For K = 2; The system has no solution.
Q.96. Let A and B be 3 × 3 real matrices such that A is symmetric matrix and B is skew-symmetric matrix. Then the system of linear equations (A2B2 − B2A2) X = O, where X is a 3 × 1 column matrix of unknown variables and O is a 3 × 1 null matrix, has: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) no solution
(b) exactly two solutions
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) a unique solution
Ans. c
AT = A, BT = −B
Let A2B2 − B2A2 = P
PT = (A2B2 − B2A2)T = (A2B2)T − (B2A2)T
= (B2)T (A2)T − (A2)T (B2)T
= B2A2 − A2B2
⇒ P is skew-symmetric matrix
∴ ay + bz = 0 ..... (1)
−ax + cz = 0 .... (2)
−bx −cy = 0 ..... (3)
From equation 1, 2, 3
Δ = 0 & Δ1 = Δ2 = Δ3 = 0
∴ equation have infinite number of solution
Q.97. The system of linear equations
3x - 2y - kz = 10
2x - 4y - 2z = 6
x + 2y - z = 5m
is inconsistent if: (JEE Main 2021)
(a) k ≠ 3, m ∈ R
(b) k = 3, m ≠ 4/5
(c) k = 3, m = 4/5
(d) k ≠ 3, m ≠ 4/5
Ans. b
3(4 + 4) + 2(−2 + 2) − k(4 + 4) = 0
⇒ k = 3
10(4 + 4) + 2(−6 + 10m) − 3(12 + 20m) ≠ 0
80 − 12 + 20m − 36 − 60m ≠ 0
40m ≠ 32 ⇒ m ≠ 4/5
3(−6 + 10m) − 10(−2 + 2) − 3(10m − 6) ≠ 0
−18 + 30m − 30m + 18 ≠ 0 ⇒ 0
3(−20m − 12) + 2(10m − 6) + 10(4 + 4) − 40m + 32 ≠ 0 ⇒ m ≠ 4/5
Q.98. The number of elements in the set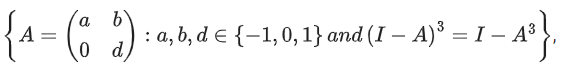 where I is 2 × 2 identity matrix, is: (JEE Main 2021)
where I is 2 × 2 identity matrix, is: (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 8
(I − A)3 = I3 − A3 − 3A(I − A) = I − A3
⇒ 3A(I − A) = 0 or A2 = A
⇒ a2 = a, b(a + d − 1) = 0, d2 = d
If b ≠ 0, a + d = 1 ⇒ 4 ways
If b = 0, a = 0, 1 & d = 0, 1 ⇒ 4 ways
⇒ Total 8 matrices
Q.99. If the system of linear equations
2x + y − z = 3
x − y − z = α
3x + 3y + βz = 3
has infinitely many solution, then α + β − αβ is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 5
2 × (i) − (ii) − (iii) gives :
− (1 + β)z = 3 − α
For infinitely many solution
β + 1 = 0 = 3 − α ⇒ (α, β) = (3, −1)
Hence, α + β − αβ = 5
Q.100. Let A be a 3 × 3 real matrix. If det(2Adj(2 Adj(Adj(2A)))) = 241, then the value of det(A2) equal __________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 4
adj (2A) = 22 adjA
⇒ adj(adj (2A)) = adj(4 adjA) = 16 adj (adj A)
= 16 | A | A
⇒ adj (32 | A | A) = (32 | A |)2 adj A
12(32| A |)2 |adj A | = 23 (32 | A |)6 | adj A |
23 . 230 | A |6 . | A |2 = 241
| A |8 = 28 ⇒ | A | = ±2
| A |2 = | A |2 = 4
Q.101. If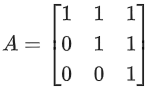 and M = A + A2 + A3 + ....... + A20, then the sum of all the elements of the matrix M is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
and M = A + A2 + A3 + ....... + A20, then the sum of all the elements of the matrix M is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 2020
So, required sum
= 60 + 420 + 105 + 35 × 41 = 2020
Q.102. Let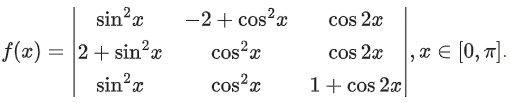 Then the maximum value of f(x) is equal to ______________. (JEE Main 2021)
Then the maximum value of f(x) is equal to ______________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 6
= −2(cos2x) + 2(2 + 2cos2x + sin2x)
= 4 + 4cos2x − 2(cos2x − sin2x)
⇒ f(x)max = 4 + 2 = 6
Q.103. For real numbers α and β, consider the following system of linear equations:
x + y − z = 2, x + 2y + αz = 1, 2x − y + z = β. If the system has infinite solutions, then α + β is equal to ______________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 5
For infinite solutions
Δ = Δ1 = Δ2 = Δ3 = 0
Δ = 3(2 + α) = 0
⇒ α = −2
1(1 + 2β) −2(1 + 4) − (β − 2) = 0
β − 7 = 0
β = 7
∴ α + β = 5
Q.104. Let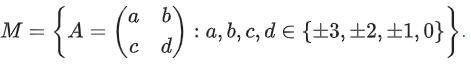 Define f : M → Z, as f(A) = det(A), for all A ∈ M, where z is set of all integers. Then the number of A∈M such that f(A) = 15 is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Define f : M → Z, as f(A) = det(A), for all A ∈ M, where z is set of all integers. Then the number of A∈M such that f(A) = 15 is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 16
| A | = ad − bc = 15
where a, b, c, d ∈ {±3, ±2, ±1, 0}
Case I ad = 9 & bc = −6
For ad possible pairs are (3, 3), (−3, −3)
For bc possible pairs are (3, −2), (−3, 2), (−2, 3), (2, −3)
So total matrix = 2 × 4 = 8
Case II ad = 6 & bc = −9
Similarly total matrix = 2 × 4 = 8
⇒ Total such matrices are = 16
Q.105. Let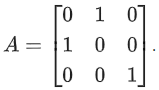 Then the number of 3 × 3 matrices B with entries from the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and satisfying AB = BA is ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Then the number of 3 × 3 matrices B with entries from the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and satisfying AB = BA is ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 3125
∵ AB = BA
⇒ d = b, e = a, f = c, g = h
No. of ways of selecting a, b, c, g, i
= 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
= 55 = 3125
∴ No. of matrices B = 3125
Q.106. Let A = {aij} be a 3 × 3 matrix,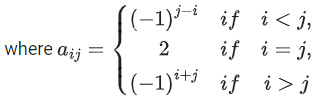
then det(3Adj(2A−1)) is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 108
|A| = 4
det(3adj(2A−1))
= 33|adj(2a−1)|
Q.107. Let a, b, c, d in arithmetic progression with common difference λ. If 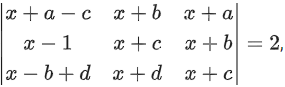 then value of λ2 is equal to ________________. (JEE Main 2021)
then value of λ2 is equal to ________________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 1
C2 → C2 − C3
R2 → R2 − R1, R3 → R3 − R1
⇒ 1(4λ2 − 4λ2 + 2λ) = 2
⇒ λ2 = 1
Q.108. Let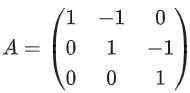 and B = 7A20 − 20A7 + 2I, where I is an identity matrix of order 3 × 3. If B = [bij], then b13 is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
and B = 7A20 − 20A7 + 2I, where I is an identity matrix of order 3 × 3. If B = [bij], then b13 is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 910
B = 7A20 − 20A7 + 2I
= 7(I + C)20 + 20(I + C)7 + 2I
= 7(I + 20C + 20C2C2) − 20(I + 7C + 7C2C2) + 2I
So b13 = 7 × 20C2C2 − 20 × 7C2 = 910
Q.109. Let I be an identity matrix of order 2 × 2 and P =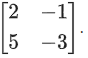 Then the value of n ∈ N for which Pn = 5I − 8P is equal to ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Then the value of n ∈ N for which Pn = 5I − 8P is equal to ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 6
⇒ λ2 + λ − 1 = 0
⇒ P2 + P − I = 0
⇒ P2 = I − P
⇒ P4 = I + P2 − 2P
⇒ P4 = 2I − 3P
Now, P4 . P2 = (2I − 3P)(I − P) = 2I − 5P + 3P2
⇒ P6 = 5I − 8P
So n = 6
Q.110. If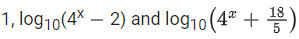 (4x+185) are in arithmetic progression for a real number x, then the value of the determinant
(4x+185) are in arithmetic progression for a real number x, then the value of the determinant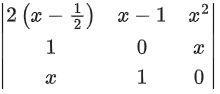 is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
is equal to: (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 2
(4x)2 + 4 − 4.4x = 10.4x + 36
(4x)2 − 14.4x − 32 = 0
(4x)2 + 2.4x − 16.4x − 32 = 0
4x(4x + 2) − 16.(4x + 2) = 0
(4x + 2)(4x − 16) = 0
4x = -2 (Not Possible)
Or 4x = 16
⇒ x = 2
= 3(−2) − 1(0 − 4) + 4(1 − 0)
= −6 + 4 + 4 = 2
Q.111. Let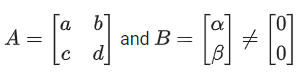 such that AB = B and a + d = 2021, then the value of ad − bc is equal to ___________. (JEE Main 2021)
such that AB = B and a + d = 2021, then the value of ad − bc is equal to ___________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 2020
AB = B
α(a − 1) = −bβ and cα = β(1 − d)
−bc = (a − 1)(1 − d)
−bc = a − ad − 1 + d
ad − bc = a + d − 1
= 2021 - 1 = 2020
Q.112. If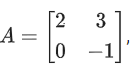 then the value of det(A4) + det(A10 − (Adj(2A))10) is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
then the value of det(A4) + det(A10 − (Adj(2A))10) is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 16
|A10 − adj(2A)10| = 0
∴ det(A4) + det(A10 − (Adj(2A))10)
= 16 + 0 = 16
Q.113. Let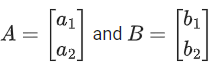 be two 2 × 1 matrices with real entries such that A = XB, where
be two 2 × 1 matrices with real entries such that A = XB, where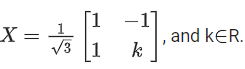 If
If 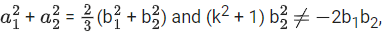 then the value of k is __________. (JEE Main 2021)
then the value of k is __________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 1
XB = A
Comparing both sides, We get
⇒ k2 = 1
⇒ k = ± 1 ......(1)
and 2/3(k − 1)=0 ⇒ k = 1 ....(2)
From (1) and (2),
k = 1
Q.114. The total number of 3 × 3 matrices A having entries from the set {0, 1, 2, 3} such that the sum of all the diagonal entries of AAT is 9, is equal to _____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 766
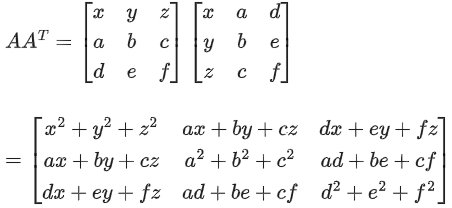
Tr(AAT) = x2 + y2 + z2 + a2 + b2 + c2 + d2 + e2 + f2 = 9
Case-I: Nine ones = 1 case
Case-II: 8 zeroes and one entry is 3 = 9!/8!=9 cases
Case-III: Two 2’s, one 1’s and 6 zeroes == 63 × 4 = 252
Case IV: one 2, five 1, rest 0= 63 × 8 = 504
∴ Total cases = 9 + 252 + 504 + 1 = 766
Q.115. 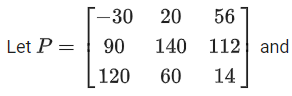
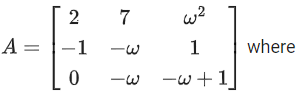
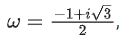 and I3 be the identity matrix of order 3. If the
and I3 be the identity matrix of order 3. If the
determinant of the matrix (P−1AP−I3)2 is αω2, then the value of α is equal to ______________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 36
|P−1AP−I|2
= |(P−1AP − I)(P−1AP−1)2|
= |P−1APP−1AP − 2P−1AP + I|
= |P−1A2P − 2P−1AP + P−1IP|
= |P−1(A2 − 2A + I)P|
= |P−1(A − I)2P|
= |P−1||A − I|2|P|
= |A − I|2
= (1(ω(ω + 1) + ω) − 7ω + ω2.ω)2
= (ω2 + 2ω − 7ω + 1)2
= (ω2 − 5ω + 1)2
= (−6ω)2
= 36ω2
∴ αω2 = 36ω2
⇒ α = 36
Q.116. If the matrix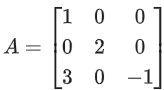 satisfies the equation
satisfies the equation
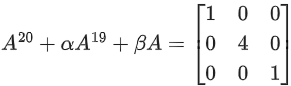 for some real numbers α and β, then β − α is equal to ___________. (JEE Main 2021)
for some real numbers α and β, then β − α is equal to ___________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 4
⇒ α + β = 0 and 220 + α219 + 2β = 4
⇒ 220 + α(219 − 2) = 4
⇒ β = 2
∴ β − α = 4
Q.117. If the system of equations
kx + y + 2z = 1
3x − y − 2z = 2
−2x −2y −4z = 3
has infinitely many solutions, then k is equal to __________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 21
D = 0
⇒ k (4 − 4) − 1 (− 12 − 4) + 2 (− 6 − 2)
⇒ 16 − 16 = 0
Also, D1 = D2 = D3 = 0
⇒ k(−8 + 6) − 1(− 12 − 4) + 2(9 + 4) = 0
⇒ − 2k + 16 + 26 = 0
⇒ 2k = 42
⇒ k = 21
Q.118. Let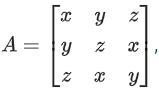 where x, y and z are real numbers such that x + y + z > 0 and xyz = 2. If A2 = I3, then the value of x3 + y3 + z3 is ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
where x, y and z are real numbers such that x + y + z > 0 and xyz = 2. If A2 = I3, then the value of x3 + y3 + z3 is ____________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 7
∴ |A| = (x3 + y3 + z3 − 3xyz)
Given A2 = I3
|A2| = 1
∴ (x3 + y3 + z3 − 3xyz)2 = 1
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 − 3xyz = 1 only as (x + y + z > 0)
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 = 6 + 1 = 7
Q.119. If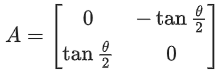 and
and
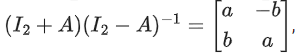 then 13(a2 + b2) is equal to (JEE Main 2021)
then 13(a2 + b2) is equal to (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 13
⇒ (1 + A)(I − A)−1
∴ a2 + b2 = 1
⇒ 13(a2 + b2) = 13
Q.120. Let M be any 3 × 3 matrix with entries from the set {0, 1, 2}. The maximum number of such matrices, for which the sum of diagonal elements of MTM is seven, is ________. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 540
a2 + b2 + c2 + d2 + e2 + f2 + g2 + h2 + i2 = 7
Case I: Seven (1's) and two (0's)
Number of such matrices = 9C2 = 36
Case II: One (2) and three (1's) and five (0's)
Number of such matrices ==504
∴ Total = 540
Q.121. Let where α ∈ R. Suppose Q = [ qij] is a matrix satisfying PQ = kl3 for some non-zero k ∈ R.
where α ∈ R. Suppose Q = [ qij] is a matrix satisfying PQ = kl3 for some non-zero k ∈ R.
If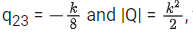 then a2 + k2 is equal to ______. (JEE Main 2021)
then a2 + k2 is equal to ______. (JEE Main 2021)
Ans. 17
⇒ 2(3α + 4) = 5 + 3α
3α = −3 ⇒ α = −1
⇒ (20 + 12α) = 2k ⇒ 8 = 2k ⇒ k = 4