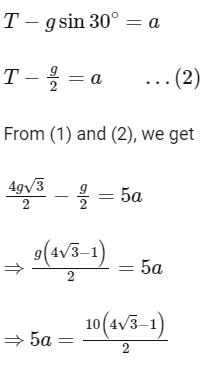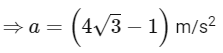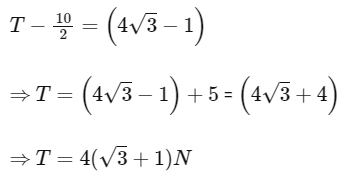Q1: The position vector of a particle related to time t is given by 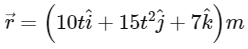
The direction of net force experienced by the particle is :
(a) Positive x - axis
(b) Positive y - axis
(c) Positive z - axis
(d) In x - y plane
Ans: (b)
To find the direction of the net force experienced by the particle, we need to find the acceleration vector of the particle and then use Newton's second law, which states that the net force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration vector.
The position vector of the particle is given by:
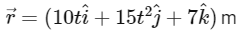
Differentiating 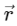 twice with respect to time t, we get the acceleration vector:
twice with respect to time t, we get the acceleration vector:
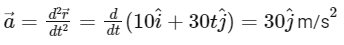
Therefore, the acceleration vector is 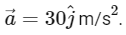
Using Newton's second law, the net force on the particle is given by:
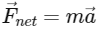
where m is the mass of the particle. Since we are only interested in the direction of the net force, we can ignore the magnitude of the acceleration and focus on its direction, which is along the positive y -axis.
Q2: Three forces F1 = 10 N, F2 = 8 N, F3 = 6 N are acting on a particle of mass 5 kg. The forces F2 and F3 are applied perpendicularly so that particle remains at rest. If the force F1 is removed, then the acceleration of the particle is:
(a) 4.8 ms−2
(b) 7 ms−2
(c) 2 ms−2
(d) 0.5 ms−2
Ans: (c)
Since the particle is initially at rest, the net force acting on it is zero. This means that the forces F1 , F2, and F3 are balanced. Given that F2 and F3 are acting perpendicularly, we can represent the balance of forces as follows:
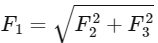
We can now calculate the equivalent force resulting from F2 and F3:
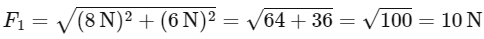
Since the particle is initially at rest, when the force F1 is removed, only F2 and F3 remain. The net force acting on the particle is the equivalent force resulting from F2 and F3, which we have calculated to be 10 N.
Now, we can use Newton's second law to find the acceleration of the particle:
F = ma
Where:
F is the net force acting on the particle
m is the mass of the particle
a is the acceleration of the particle
Rearranging the equation to solve for a : a = F/m
Plugging in the values for F and m :
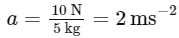
The acceleration of the particle when the force F1 is removed is 2 ms−2, which corresponds to Option C.
Q3: A body of mass 500 g moves along x -axis such that it's velocity varies with displacement x according to the relation v = 10√x m / s the force acting on the body is:-
(a) 166 N
(b) 5 N
(c) 25 N
(d) 125 N
Ans: (c)
Given that the velocity of the body varies with displacement x according to the relation:
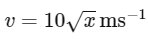
To find the force acting on the body, we first need to find its acceleration, which can be obtained by differentiating the velocity with respect to time. However, we don't have the velocity expressed as a function of time, but rather as a function of displacement. To work around this, we will use the chain rule:
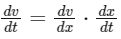
Now, differentiate the velocity with respect to displacement:
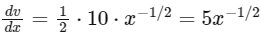
Recall that dx/dt is the velocity, so we have:
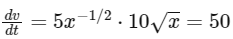
Thus, the acceleration is constant and equal to 50 m/s². Now we can find the force acting on the body using Newton's second law:
F = ma
First, convert the mass from grams to kilograms:
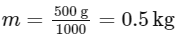
Now, calculate the force:
F = (0.5 kg) (50 ms −2) = 25 N
The force acting on the body is 25 N.
Q4: At any instant the velocity of a particle of mass 500 g is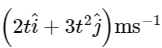 . If the force acting on the particle at
. If the force acting on the particle at 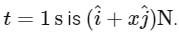 Then the value of x will be:
Then the value of x will be:
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 3
Ans: (d)
Given the velocity vector of a particle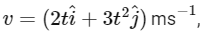 the acceleration a is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time. So, we have:
the acceleration a is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time. So, we have:
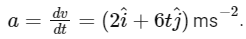
At s t = 1 s , the acceleration a is ms 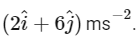
According to Newton's second law, the force F is equal to the mass m times acceleration a. The mass m is given as g 500 g , or equivalently, kg 0.5 kg.
Therefore, the force F on the particle at s t = 1 s is:
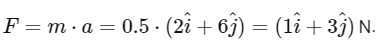
So, the force acting on the particle at 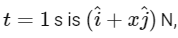 where x = 3.
where x = 3.
Therefore, the answer is x = 3.
Q5: As shown in the figure a block of mass 10 kg lying on a horizontal surface is pulled by a force F acting at an angle 30∘, with horizontal. For μs = 0.25 , the block will just start to move for the value of F : [Given g = 10 ms−2]
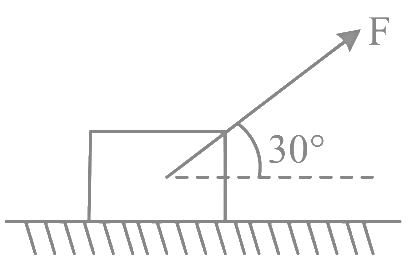 (a) 25.2 N
(a) 25.2 N
(b) 35.7 N
(c) 20 N
(d) 33.3 N
Ans: (a)
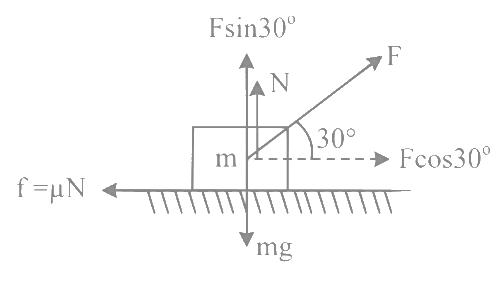
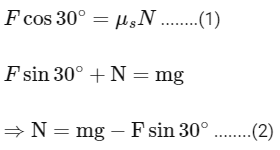
From equation 1,
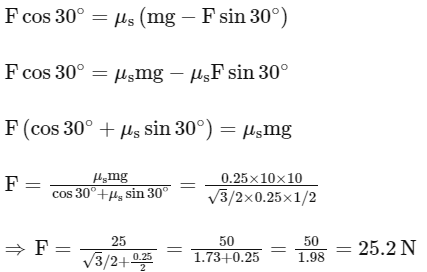
Q6: Figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) show variation of force with time.
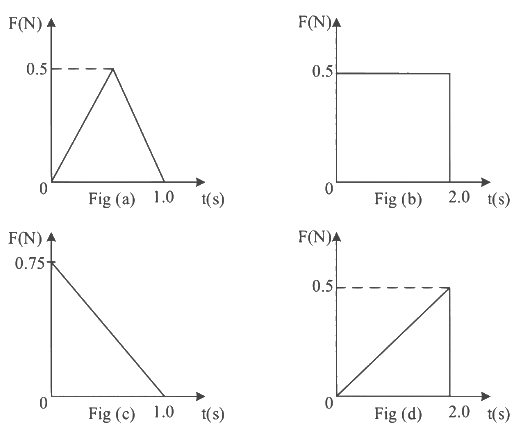 The impulse is highest in figure.
The impulse is highest in figure.
(a) Fig (c)
(b) Fig (d)
(c) Fig (a)
(d) Fig (b)
Ans: (d)
As we know that impulse is given by
I = Δ P = F × Δ t
or I = Area of f − t graph For fig (a)
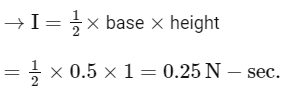
For fig (b),
I = length × width
= 2 × 0.5 = 1 N -sec
For fig (c),
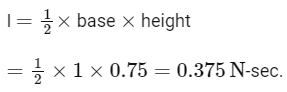
For fig (d),
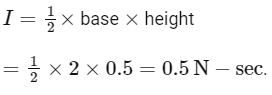
Impulse is highest for that figure, whose area under F-t is maximum and i.e. figure(b)
Option (D) is correct.
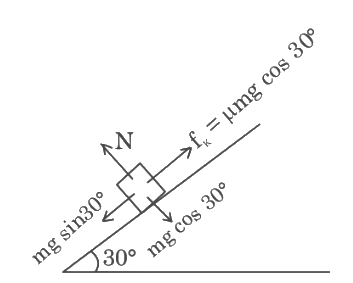
Q7: A block of mass 5 kg is placed at rest on a table of rough surface. Now, if a force of 30 N is applied in the direction parallel to surface of the table, the block slides through a distance of 50 m in an interval of time 10 s . Coefficient of kinetic friction is (given, g = 10 ms−2):
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.75
(c) 0.60
(d) 0.50
Ans: (d)
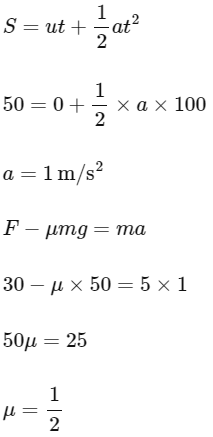
Q8: A body of mass 10 kg is moving with an initial speed of 20 m/s. The body stops after 5 s due to friction between body and the floor. The value of the coefficient of friction is:
(Take acceleration due to gravity g = 10 ms−2)
(a) 0.3
(b) 0.2
(c) 0.5
(d) 0.4
Ans: (d)
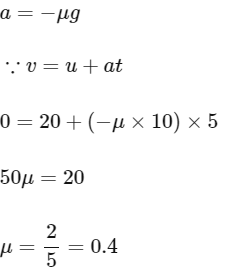
Q9: As shown in figure, a 70 kg garden roller is pushed with a force of  = 200 N at an angle of 30∘ with horizontal. The normal reaction on the roller is (Given g = 10 ms−2)
= 200 N at an angle of 30∘ with horizontal. The normal reaction on the roller is (Given g = 10 ms−2)
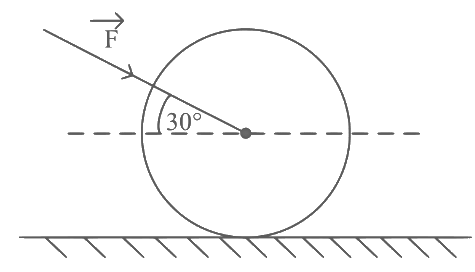 (a) 800 N
(a) 800 N
(b) 600 N
(c) 200 √3 N
(d) 800 √2 N
Ans: (a)
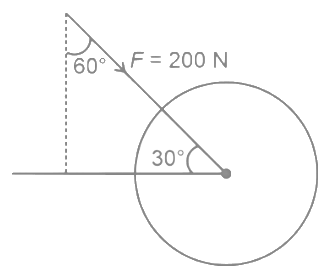 Normal reaction = 70 g + F cos 60
Normal reaction = 70 g + F cos 60
= 700 + 100
= 800 N
Q10: A block of √3 kg is attached to a string whose other end is attached to the wall. An unknown force F is applied so that the string makes an angle of 30∘ with the wall. The tension T is: (Given g = 10 ms−2)
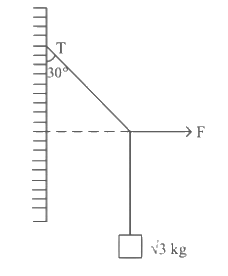 (a)15 N
(a)15 N
(b) 10 N
(c) 25 N
(d) 20 N
Ans: (d)
Drawing the FBD of the point where F is applied
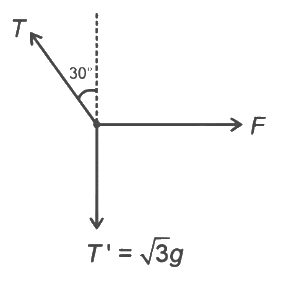 T′ = √3g
T′ = √3g
⇒ T cos30∘ = √3g
⇒ T = 2g = 20N
Q11: A force acts for 20 s on a body of mass 20 kg, starting from rest, after which the force ceases and then body describes 50 m in the next 10 s. The value of force will be:
(a) 40 N
(b) 20 N
(c) 5 N
(d) 10 N
Ans: (c)
m = 20kg
t = 20sec.
Acceleration = F/20m/s2
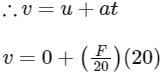
= F ms−1
Now for next 10 sec.
S = ut
50 = F(10)
F = 5
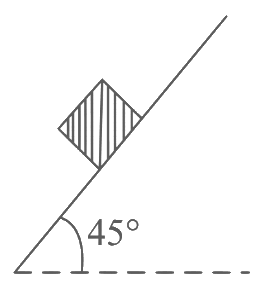
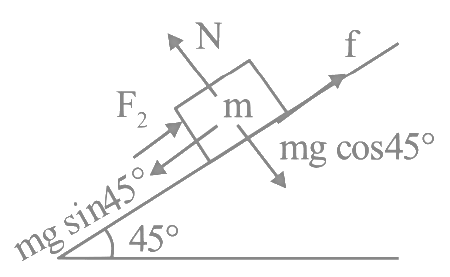
Q12: The time taken by an object to slide down 45∘ rough inclined plane is n times as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth 45∘ incline plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the incline plane is:
(a) 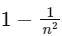
(b) 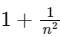
(c) 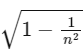
(d) 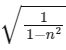
Ans: (a)
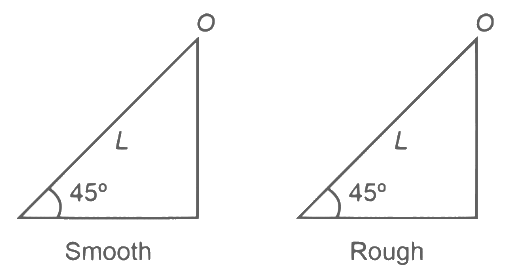 Smooth case:
Smooth case:
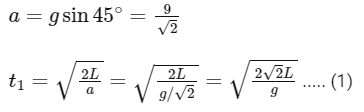
Rough case:
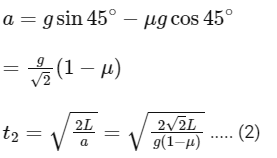
From (1) to (2) and t1 = t2/n we have
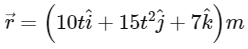
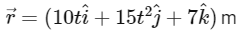
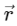 twice with respect to time t, we get the acceleration vector:
twice with respect to time t, we get the acceleration vector: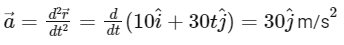
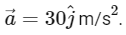
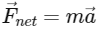
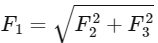
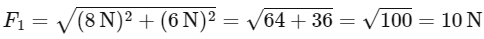
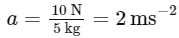
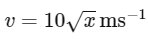
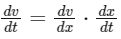
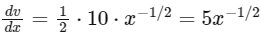
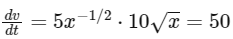
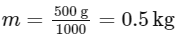
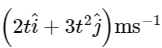 . If the force acting on the particle at
. If the force acting on the particle at 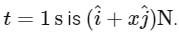 Then the value of x will be:
Then the value of x will be: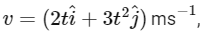 the acceleration a is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time. So, we have:
the acceleration a is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time. So, we have: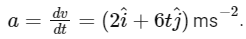
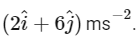
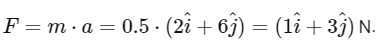
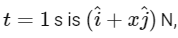 where x = 3.
where x = 3. (a) 25.2 N
(a) 25.2 N
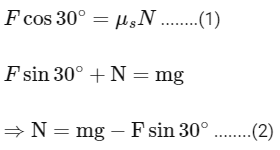
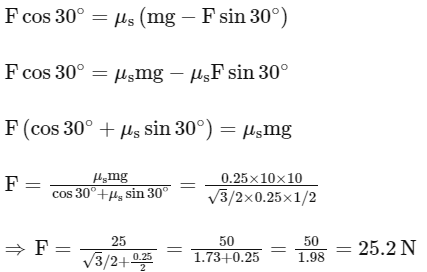
 The impulse is highest in figure.
The impulse is highest in figure.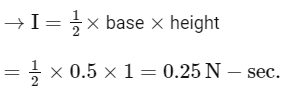
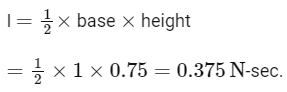
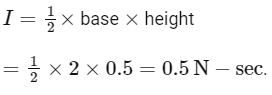
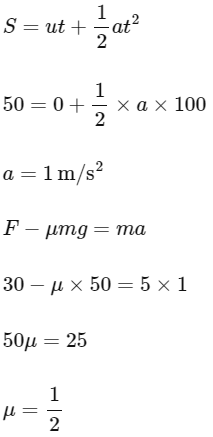
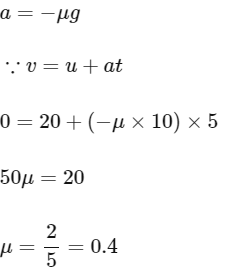
 = 200 N at an angle of 30∘ with horizontal. The normal reaction on the roller is (Given g = 10 ms−2)
= 200 N at an angle of 30∘ with horizontal. The normal reaction on the roller is (Given g = 10 ms−2) (a) 800 N
(a) 800 N Normal reaction = 70 g + F cos 60
Normal reaction = 70 g + F cos 60 (a)15 N
(a)15 N T′ = √3g
T′ = √3g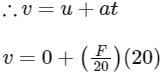
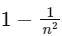
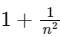
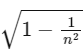
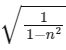
 Smooth case:
Smooth case: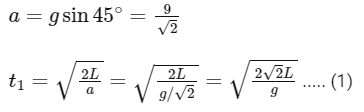
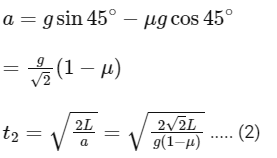
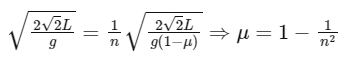
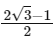
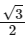
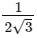
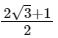
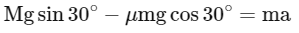
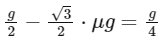
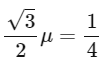
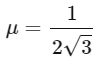
 (a) 0.60
(a) 0.60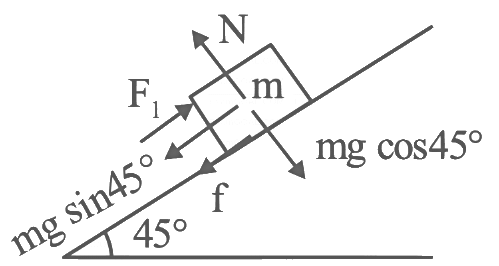
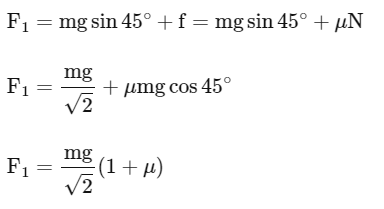
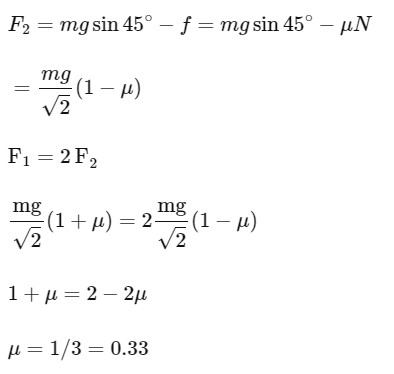
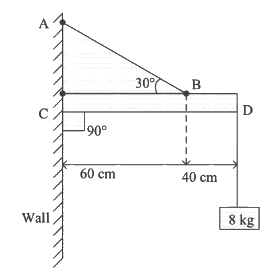 (a) 90 N
(a) 90 N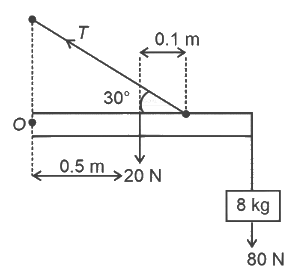 Torque balance about ' O '
Torque balance about ' O '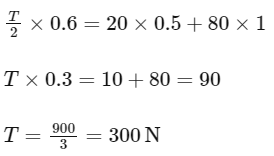
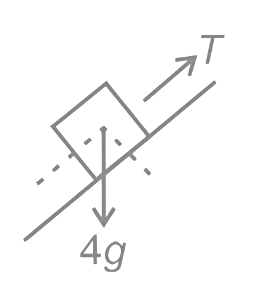
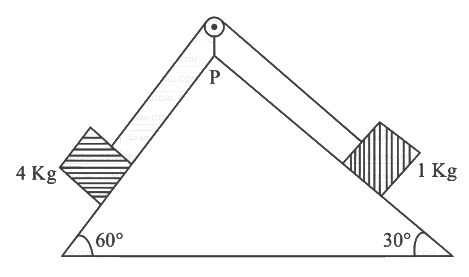 (a) (4√3 − 1)N
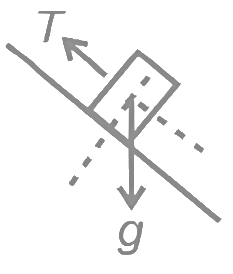
(a) (4√3 − 1)N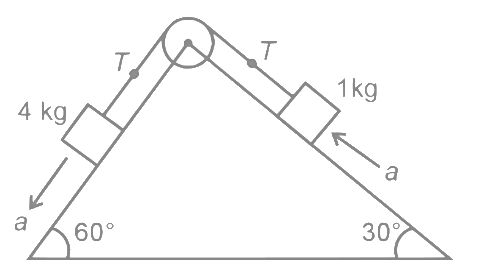 Let's consider T tension in string and a acceleration of blocks. FBD of 4kg
Let's consider T tension in string and a acceleration of blocks. FBD of 4kg