Key Concepts: Democracy & Diversity - Class 10 PDF Download
A Story from Mexico Olympics
Read this real event, which happened in 1968 during the Olympics held in Mexico City:
Two African-American athletes, Tommie Smith and John Carlos, won the gold and bronze medal respectively in the 200 mt. race. For the medal ceremony, both of them wore no shoes and stood in their black socks. They were representing Black poverty and racial discrimination against them in the USA. They also raised black-gloved clenched fists to symbolise Black Power. The athlete from Australia, Peter Norman, who won the silver medal, wore a human rights badge to declare his support to the two Americans.
 Social Diversities
Social Diversities
- Do you know what was the result of their actions? The Olympic Committee took back their medals for making a political statement and thus violating the Olympic spirit.
- When they returned to the USA, they had to face public criticism.
- Peter Norman was also penalised for not being included in the next Olympics.
- Martin Luther King started a movement called Civil Rights Movement in the USA (1954-1968) to abolish legal racial discrimination against the African Americans. They used a non-violent approach and used civil disobedience as a method against discrimination.
- Another movement, which started in 1966 and lasted till 1975, was called The Black Power movement. It was a militant movement and even advocated violence to end racism in the USA.
Differences, Similarities, Divisions
Origin of Social Differences
This incident shows how people respond to social divisions and inequalities
Social divisions can have many forms.
- Social divisions can be based on regional differences (as in Belgium and Sri Lanka — different languages spoken in different regions).
- They can be based on different religions (Sri Lanka)
- They can be based on racial discrimination (USA, South Africa)
- Social divisions can lead to social inequalities.
- Two kinds of social divisions : (i) Based on accident of birth, (ii) Based on people's choices.
- All social differences do not result in social divisions. Some can unite people also.
Overlapping and Cross-Cutting Differences
Now think-
- Most of the social differences are not of our own making, they are based on an accident of birth. Our race, our colour, our religion, our gender or country of birth, are not chosen by us.
- But some social differences are made by us only by choice. For example –
1) Non-belief in God, or to follow a different religion,
2) where and what to study,
3) which profession to follow
4) also choose the games or cultural activities we want to follow, etc.
Our choices lead to the formation of social groups. - It is not necessary that all social differences should lead to social divisions. People belonging to different social groups share differences and similarities, which cut across all political boundaries.
Important: If religion creates similarities, it can divide people over the issue of caste or sect (Catholic or Protestant, Brahmin or Scheduled Caste).
- Rich and poor persons in the same family differ from each other and lack closeness to each other, for they feel they are different.
| Overlapping | Anti-Cross-Cutting Differences |
Why was there a social division between the Whites and Blacks in USA? | There was a division because the Blacks were homeless and discriminated against. They were not given justice and this created social differences and divisions. |
The same problem is faced by Dalits in India. | The Dalits face injustice and discrimination in India at the hands of the upper castes. |
- The above is an example of one difference overlapping other differences, people of the same religion feel they belong to different communities.
- Take another example: In Ireland, a Christian country, the division is because of religion between the Protestants and Catholics.
- In Northern Ireland, if you are a Catholic you are bound to be poor and you may have been discriminated against. There have been conflicts between the two.
Cross-Cutting Differences
- In the Netherlands, Catholics and Protestants both can be either rich or poor, with the result they have never had any trouble. Unlike Ireland, there has never been any trouble in the Netherlands. There reason class and religion cut across each other.
- Which kind of division is more dangerous?
Overlapping social differences. They can create deep social divisions. Examples :
(i) Led to ethnic war in Sri Lanka which has not yet ended.
(ii) Led to the Partition of India in 1947. - Cross-cutting social differences are easier to handle and accommodate.
- It is important to note here that social divisions of one kind or another exist in every country. No country, big or small, has a homogeneous society, i.e., a society with similar kinds of people and hardly any ethnic differences.
- There is another reason — People from one region or country shift to another region or country (both within a country and another country) to seek better economic opportunities. These migrants create social differences and divisions.
Politics of Social Divisions
Range of Outcomes
- (a) Violent Conflict
Example: Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
(b) Reason: Ethno-religious with the political fallout.
Example: Republic predominantly Catholic. Northern Ireland 53% Protestant, 44% Catholics. The Republic wanted them to unite.
(c) Parties: The Nationalists represented the Republic, the Unionists represented Northern Ireland and wanted to remain within the U.K.
Example: Violent war where hundreds were killed. The Republic of Ireland fought with Northern Ireland as well as with the U.K.
Final Outcome: A peace treaty signed in 1998 ended the armed struggle. - Yugoslavia also faced ethno-religious differences. They led to political competition. Civil war followed and Yugoslavia have been broken up now into seven independent nations, namely; Bosnia, Macedonia Croatia, Herzegovina, Kosovo, Serbia and Montenegro. Conclusion: Social divisions should not be allowed to influence the politics of a country. We have seen the result in our own country— Partition into India and Pakistan. In a democracy, how do social divisions affect the people?
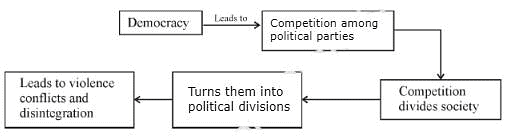
(i) Social divisions will be reflected in politics (Example: India)
(ii) Political parties will refer to these divisions.
(iii) Political parties would try to redress the grievances of minorities.
(iv) Voting is affected in most countries. People from one community prefer some parties more than others.
(v) In some countries, there are parties that focus on one community only.
Three Determinants
- How do people see their identities? If people think they are Indians first, and then they are Bengali, Punjabi etc. or a religious or language group, then there will be no conflict. Trouble in Ireland was because they thought that first, they were Catholics or Protestants and then Irish.
In Belgium, it was the opposite.
First Belgians, then Dutch or French-speaking. - It depends on how political leaders raise the demands of any community. It is easier to accommodate demands that are within the constitutional framework and are not at the cost of another community. Peace remains if one community does not try to dominate the others. For example, in Sri Lanka, the demands of "only Sinhala ’ was at the cost of the Tamil-speaking community'. In Yutos via, each of the groups made demands from itself only, with the result that the country was divided into six nations.
- Depends on how the government reacts to the demands. If the riders are willing to share power (as in Belgium) there is no threat to the unity' of the country. But if suppressed in the name of national unity (as in Sri Lanka), it leads to violence.
FAQs on Key Concepts: Democracy & Diversity - Class 10
| 1. What social divisions were present during the Mexico Olympics? |  |
| 2. How did politics impact the Mexico Olympics? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of democracy and diversity in the Mexico Olympics story? |  |
| 4. What were the range of outcomes that arose from the Mexico Olympics? |  |
| 5. How did the Mexico Olympics story reflect the concept of differences and similarities? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|