Class 10 Social Science Key Concepts - Chapter 6 Political Parties
Overview
- Political parties are vehicles of federal sharing of political power and are mediators of social divisions in the field of democratic politics.
- The introduction of the national and regional political parties in India has been provided in the chapter.
 Symbols of Different Political Parties in India
Symbols of Different Political Parties in India
Why do we need political parties?
Political parties are needed because they perform a variety of functions. Modern democracies cannot exist without political parties. Without the existence of parties, the following situations may occur :
- Every candidate in the elections will be independent. No one will be able to make any promises to the people about any major policy changes.
- The government may be formed, but its utility will remain ever uncertain. Elected representatives will be responsible to their voters for what they do in the locality. But no one will be responsible for how the country will be run.
- The non-party based elections to the Panchayat occur in many states of India. Here the parties do not contest formally. It is generally noticed that the village gets split into more than one group, each of which puts up a ‘panel’ of its candidates. This creates the need for the political party.
Meaning
- A Political Party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
- They agree on some policies and programmes for the society with a view promoting the collective good.
- Parties reflect fundamental political divisions in society. Thus, a party is known by which part it stands for, which policies it supports and whose interests it upholds.
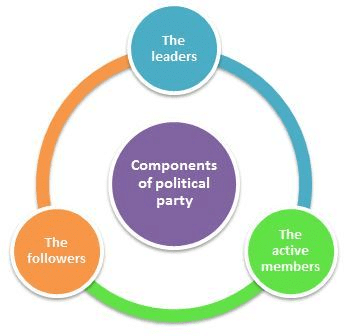
A political party has three components:
- The leaders
- The active members
- The followers
Functions
Political parties fill political offices and exercise political power. Parties do so by performing a series of functions mentioned below:
- Parties contest elections.
- Parties put forward different policies and programmes and the voters choose from them.
- Parties play a clear role in making laws for a country.
- Parties form and run governments.
- Those parties that lose in the elections play the role of opposition to the parties in power, by voicing different views and judging the government for its failures or wrong policies.
- Parties shape public opinion.
- Parties provide people access to government machinery and welfare schemes implemented by governments.
Necessity
- We need political parties because they perform all the functions which are mentioned above.
- Apart from this, political parties help in representing different views on various issues to the government.
- They bring various representatives together so that a responsible government could be formed.
- They work as a mechanism to support or restrain the government, make policies, justify or oppose them.
- Political parties fulfil the needs that every representative government has.
How many parties should we have?
- In a democracy, any group of citizens is free to form a political party. More than 750 parties are registered with the Election Commission of India.
- But not all these parties are serious competitors in the elections.
- So the question, then is: how many major or effective parties are good for democracy?
- In some countries, only one party is allowed to control and run the government.
Popular Participation in Political Parties
- Level of participation in the activities of the parties — very high in India.
- Advanced countries like Canada, Japan, Spain and South Korea much less.
- People in India who feel close to a political party — membership of political parties has also gone up.
- Various Different party Systems of Different Countries are below:
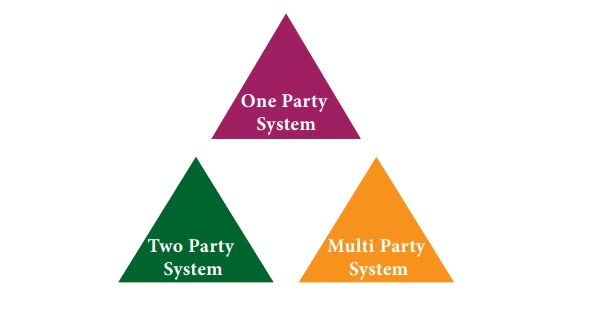
Party System
There are three types of party systems:(i) One-Party System
(ii) Two-Party System and
(iii) Multi-Party System.
One-Party System
- There is no competition in this system.
- The lone party nominates the candidates and the voters have only two choices —
(i) Not to vote at all or
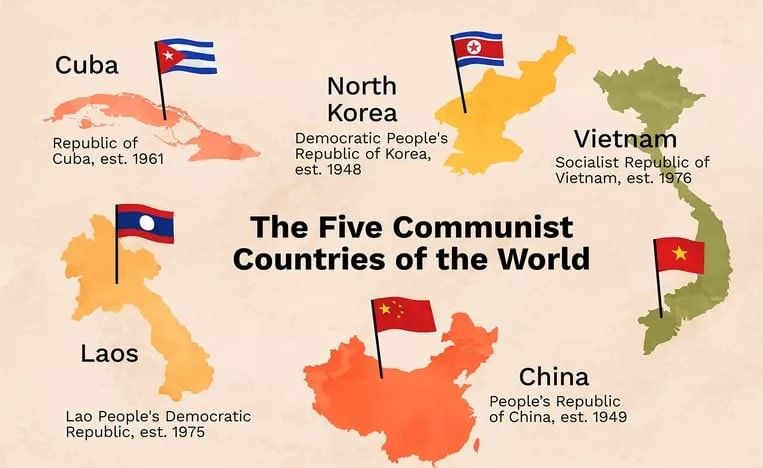
(ii) write ‘yes’ or ‘no’ against the name of the candidates nominated by the party. - This system has been popular in communist countries and other strict governments e.g., China, North Korea and Cuba.
- This system was also prevalent in USSR till Communism broke down.
Two-Party System
- The power shifts between two major, dominant parties. In this system, to win elections, the winner has to get a maximum number of votes, but not necessarily a majority of votes.
- The smaller parties usually merge with the bigger parties or they drop out of elections.
- This parliamentary system prevails in Great Britain and Canada, in which only two parties hold significant numbers of seats.
- Supporters of this system believe that this prevents the dangers of fragmentation (too many parties winning seats from different constituencies) and the government can run smoothly.
Multi-Party System
- It is the most common type of party system.
- In this system, three or more parties have the capacity to gain control of the government separately or in the coalition.
- When no party gains a majority of the legislative seats in a multi-party parliamentary system, then several parties join forces and form a coalition government.
- Supporters of this system point out that it allows more points of views to be represented in the government.
- Critics of this system point out that a multi-party system sometimes leads to political instability.
Alliance
When several parties in a multi-party system join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power, it is called an alliance or a front. India, in 2004 and 2009, had three such Alliances for parliamentary elections :
(i) National Democratic Alliance
(ii) The United Progressive Alliance and
(iii) Left Front.
National Parties

The proportion of votes for a party to be classified as national is:
- The party wins 2 per cent of the seats in the Lok Sabha (as of 2014, 11 seats) from at least 3 different States; or
- At a General Election to Lok Sabha or Legislative Assembly, the party polls 6% of votes in four States and in addition, it wins 4 Lok Sabha seats from any state or states; or
- A party gets recognition as State Party in four or more States.
Difference between a National Party and a Regional Party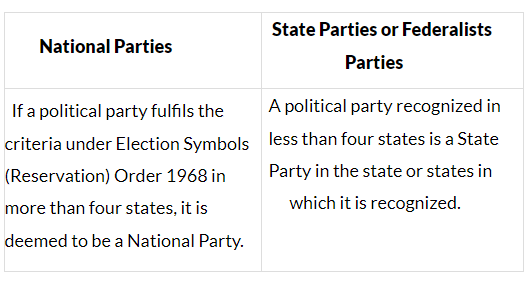
- A national party has influence all over the country or in many states of India. The influence of a state party is in a state or a few regions.
- National parties care for national interests, whereas regional parties promote mainly regional interests. For example, the DMK or AIDMK.
- Regional parties stand for greater autonomy for the states. The national parties, on the other hand, have to harmonise various conflicting regional interests.
- An exclusive symbol such as (lotus or hand) is reserved for a national party throughout India. But in the case of a regional party, a symbol for it is reserved for it in the state in which it is recognised.
Election Commission
Every party in India has to register with the Election Commission. The Commission treats every party as equal to the others, but it offers special facilities to large and established parties. They are given a unique symbol and are called, “recognised political parties.”
 Logo of Election Commission of India
Logo of Election Commission of India
Introduction to Major Political Parties in India
Indian National Congress (INC)
 Symbol of INC
Symbol of INC
- Founded in 1885, it led the movement for independence. After independence, it became free India’s premier political party.
- In the first five General Elections held, Congress virtually controlled the politics of the country. It lost the elections in 1977 following the Emergency rule.
- It made a comeback in 1980 under Indira Gandhi with a massive victory and reached its peak in the election of 1984.
- After 1991, Congress was on the decline and BJP rose in power. In the elections held in May 2004, Congress emerged as the winner with the help of its allies.
- It formed a coalition government called the United Progressive Alliance (UPA). In its manifestos, it projected a vision of a politically united, economically prosperous, socially just and culturally harmonious India.
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
 Symbol of Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
Symbol of Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
- Created in 1980, it champions the socio-religious values of the Hindu majority of India, conservative social policies, and strong national defence. Since its formation, the BJP has been a strong rival of the Indian National Congress.
- It has allied itself with regional parties to challenge the Congress Party, which dominated Indian politics for 40 years. The BJP’s rallying cry is “Hindutva”.
- It wants full territorial integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India and a uniform civil code.
- The BJP, in alliance with several other parties, led the Government of India between 1998 and 2004.
- It is now the recognised Opposition, and the leading party within the National Democratic Alliance (NDA).
Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
 Symbol of BSP
Symbol of BSP
- The Bahujan Samaj Party is a party formed to represent the OBC, SC, ST and religious minorities, those at the bottom of India’s caste system.
- The BSP was formed in 1984 by two leaders, Kanshiram and Mayawati.
- The main base of the party is in Uttar Pradesh. It also has a substantial following in Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Delhi and Punjab.
- It draws inspiration from the teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar Ramaswami Naicker. The BSP also draws inspiration from the teachings of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
Communist Party of India (Marxist) (CPI–M)
 Symbol of CPI and CPI-M
Symbol of CPI and CPI-M
- The Communist Party of India (Marxist), usually known as CPI (M), split from the Communist Party of India in 1964. It is strongest in the states of Kerala, West Bengal and Tripura as of 2006, and led the government in all these states till 2011 when it lost power in the first two.
- It believes in Marxism-Leninism and supports socialism, secularism and democracy. It opposes imperialism and communalism.
- Its supporters are farmers, agricultural labourers and scholars. In West Bengal CPI(M) has enjoyed power without a break, for 30 years.
Communist Party of India (CPI)
- It was formed in 1925, with beliefs in Marxism-Leninism, secularism and democracy. It is opposed to the forces of Group loyalty and Breakaway
- It believes that parliamentary democracy helps the interests of farmers, the working class, and the poor.
- The split in the party in 1964, and the formation of CPI (M) made its position weak. It has the following in the states of Kerala, West Bengal, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- It aims and promotes unity and coming together of all left parties to form a United Left Front.
Nationalist Congress Party (NCP)
 Symbol of NCP
Symbol of NCP
- It was formed on May 25, 1999, by Sharad Pawar, P.A. Sangama, and Tariq Anwar after they were thrown out of the Congress Party.
- They had objected to a person of foreign origin becoming the Prime Minister of India. NCP have major support in Maharashtra state. The NCP claims that it supports democracy, Gandhian secularism, equity, social justice and federalism.
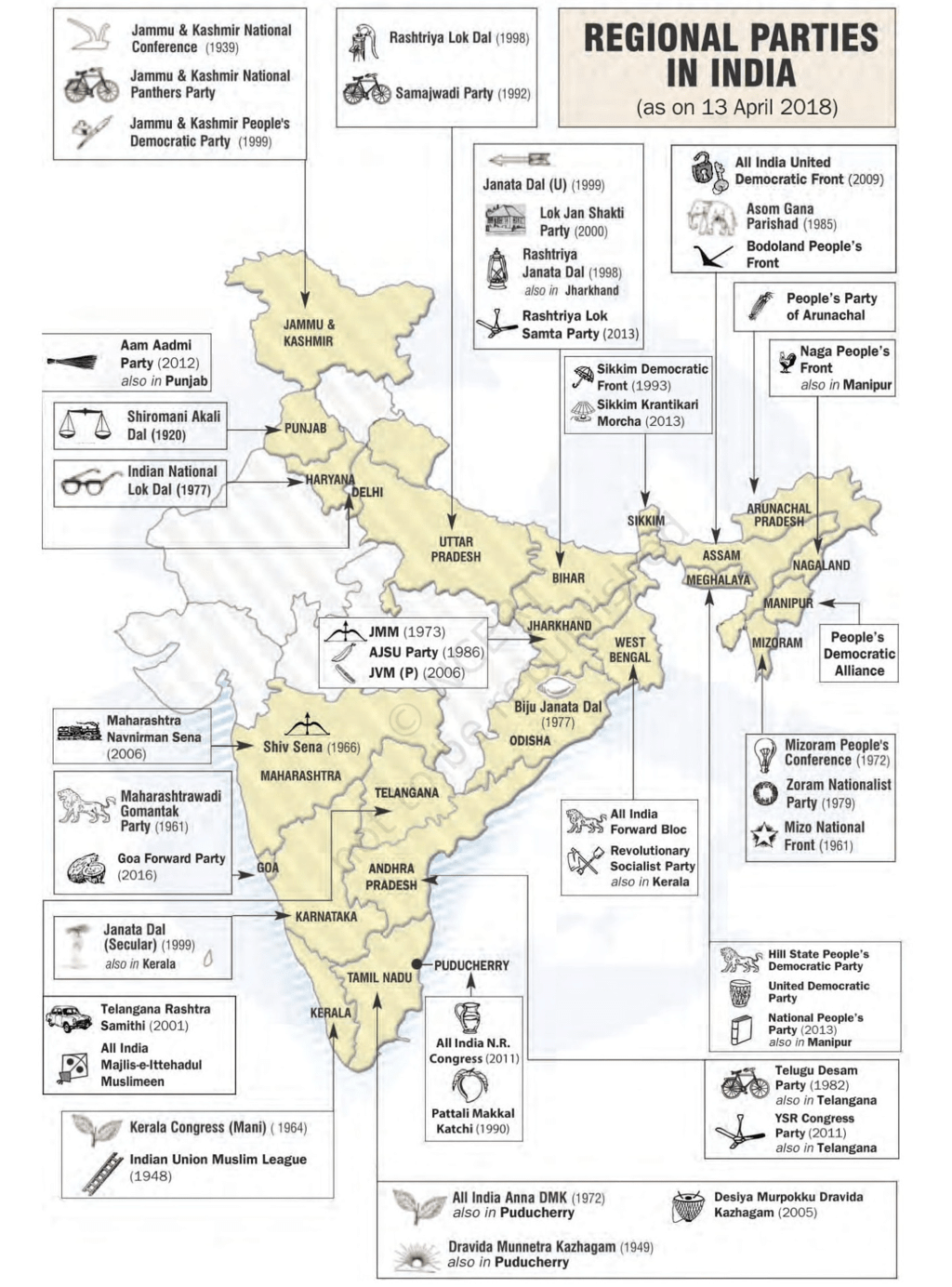
State Parties
- All parties, other than the six national parties, are classified as state parties by the Election Commission of India. They are also called regional parties.
- They can be all-India parties but have been successful only in some states. Examples; Samajwadi Party, Samata Party, Rashtriya Janata Dal. They have national-level political organisations.
- Some like the Biju Janata Dal, Sikkim Democratic Front, Mizo National Front have state identities. In the last years, no national party has been able to secure a majority on its own in the Lok Sabha. The national parties have been compelled to form alliances with state parties. This has led to coalition governments in the Centre since 1966.
- This has strengthened federalism and democracy in our country.
Challenges to Political Parties
1. Lack of internal democracy within parties
- Power concentrated in the hands of few.
- No organisational meetings. No keep-ing of membership register
- No internal, regular elections.
- Ordinary members do not have access to information, cannot influence decisions.
- Disagreement with the leader leads to ouster from the party’.
2. Dynastic succession
- Leaders on top have an unfair advantage to favour people close to them or family members.
- Top positions con-trolled by family members in most parties
- Bad for democracy
- The tendency is seen all over the world, even in the older democracies
3. Money and muscle power
- In Durum elections this power is very visible.
- Candidates who can raise money are nominated.
- Rich people and companies who give funds have an influence on policies.
4. Parties do not offer a meaningful choice to the voters.
- There is not much difference in ideology among parties.
Example: Labour Party and Conservative Party of Britain. - They only differ on details of implementation rather than fundamental principles.
- In India also there is not much difference among parties on economic issues
How can parties be reformed?
Efforts Made to Reform the Political Parties
- The Constitution was amended to prevent defection. Now the MPs and MLAs will lose their seat in the Parliament or a State Assembly if they defect.
- The Supreme court passed certain orders to reduce the power of money and criminals. A candidate has to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him.
- The Election Commission— Political parties are asked to file their income tax returns. They have to hold structural elections.


|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science Key Concepts - Chapter 6 Political Parties
| 1. Why do we need political parties? |  |
| 2. How many parties should we have? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the Election Commission in India? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges facing political parties in India? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between national parties and state parties in India? |  |






















